Managing the budget in product projects can sometimes be like juggling flame torches while riding a unicycle on a tightrope, over sharp-toothed, jumping piranhas. There are too many changing variables and you, as the product manager, need to find the delicate balance of meeting customer and business expectations within a certain amount of available resources.

How can you do this effectively? In this article, you’ll learn what budget management is, its importance for project management, and techniques for keeping efficient budgets.
Budget management refers to the strategic planning and control of financial resources allocated to develop, produce, market, and support a product from conception to completion and beyond. When done effectively, it ensures that expenditures align with the business’s strategic goals and objectives. It also includes the creation of a comprehensive financial plan that encompasses all aspects of the project, such as research and development, production costs, marketing expenses, distribution logistics, ongoing maintenance, etc.
Managing budgets means also making adjustments as needed to optimize resource utilization, mitigate financial risks, and achieve desired outcomes within the allocated budgetary constraints. Frequent and effective communication plays a crucial role in budget management as it helps set the right expectations with stakeholders throughout the project. This includes providing regular progress reports and financial analysis to stakeholders, highlighting key performance metrics, budget variances, and potential areas for optimization and improvements.
By prioritizing budget management, you can increase the likelihood of delivering successful products that provide customer value and achieve business objectives. Managing budgets effectively is essential for product projects to control costs, optimize resource allocation, mitigate risks, make informed decisions, and communicate efficiently with stakeholders.
Here are some reasons as to why effective budget management can help product managers make their projects successful:
To ensure the successful completion of product projects within financial constraints, you have to ensure that you understand product strategy and vision very well. You also want to create a high level product roadmap that will help achieve product goals. Once you know what you need the budget for, planning and managing the budget becomes easier:

It’s important to clearly define the scope of the project with relevant stakeholders, including deliverables, timelines, and the resources required to complete the project. Break down the project into smaller tasks and estimate all the costs associated with each task. Consolidate the cost estimates and add a buffer amount to create a comprehensive project budget that outlines total expected expenditures and the return on investment.
Set up project milestones and regularly track all actual expenses at each milestone, both expected and unexpected ones, during the entire duration of the project. Compare these to the budgeted amounts and identify discrepancies or variances. Keep a detailed record of these variances and document why some of these unexpected expenses came up. This will help in planning future budgets better.
As a PM, you should be adaptable to the dynamic nature of products and their environments, responding to changing market conditions, industry trends, customer needs, internal priorities, etc. may impact product goals and also the budget. It’s important to revisit the budget, reprioritize product initiatives, adjust the project strategy, and reassess the budget to stay aligned with product goals. This could include revising cost estimates, reallocating resources, updating financial projections, and more.
Provide regular budget reports and updates to stakeholders to keep them informed about the project status and potential impact to the budget. Highlight key progress metrics, budget variances, and risk mitigation strategies that you might have employed. If you foresee any big changes to the budget, start the conversation early and paint a holistic picture of the rationale behind the changes, as well as how the project and budget can adapt to the changes.
Review and analyze the budget management process and financial analysis of the budget itself after every project is completed. Identify the areas of improvement and lessons learned, especially from unforeseen changes. Implement these, as well as use industry best practices to enhance future budget management efforts. Making improvements is a continuous process and must be done diligently.
To position projects for long-term success and contribute to the overall growth of the business, implement techniques that help with cost efficiencies and maximizing ROI.
By analyzing historical data, planning for various scenarios, and leveraging budget forecasting techniques, you can anticipate future budget needs more accurately. With continuous monitoring of the project budgets, the more information you gather over the time, the more accurate you can get with financial predictability.
Identify and mitigate potential risks that may impact the project, such as scope creep, market fluctuations, technology dependencies, overspending, etc. Develop contingency plans and have a buffer amount in the budget to address unforeseen challenges and minimize the impact on budget. The sooner you can identify and mitigate these risks, the lesser impact it will have on the budget.
Adopt an iterative approach to product development. This will enable you to break the project down into smaller, more manageable increments. Sometimes, you want to only develop a minimum viable product (MVP), focusing only on the absolute essential features required. This enables a continuous feedback loop with customers and optimization of project resources, while minimizing budget overruns.
Conduct a cost-benefit analysis on every project to evaluate the potential ROI it can generate. Prioritize those projects that have the highest value proposition. Consider factors such as revenue potential, market demand, strategic alignment, and resource availability when making investment decisions. Keep monitoring the project to assess if it stays true to its ROI potential.
Some challenges can be outside your control, but how effectively you are able to respond to these challenges will significantly impact your product project. It’s also important to communicate challenges with your team and relevant stakeholders.
No matter how well you try to plan the budget and forecast risks, there will always be some amount of uncertainty with every project. This can lead to unexpected expenses and impact the budget. Developing a detailed budget and including allowances for these unforeseen expenses can help address critical challenges, avoiding negative impact on the budget.
When requirements are arbitrary and projects are not scoped properly, scope creep can occur as the project progresses, leading to unplanned expenditures. Additional features and requirements that are added to the project ad hoc without corresponding increases in budget or resources, leads to budget overruns.
Thoroughly scoping and documenting requirements, as well as implementing robust scope and change management processes can ensure that the project scope is properly evaluated, approved, and accommodated within the budgetary constraints.
Limited resources, including financial, human, and material resources, can constrain project budgets and impact the ability to deliver quality products on time and within budget. Optimize resource utilization by carefully allocating resources based on project priorities, leveraging cross-functional teams, outsourcing non-core activities, and implementing efficient resource management processes and practices.
In the planned project budget, inaccurate cost estimates can result in budgetary discrepancies and unexpected expenses, leading to budget overruns and delays in project delivery. You can establish regular monitoring and reporting mechanisms to track actual expenses against budgeted amounts, identify variances, and take corrective action as needed to keep the project on track with the budget.
Effective budget management requires you to be diligent and organized throughout the product development process. Make sure you give yourself the time and resources needed to craft a project budget that takes into considerations like uncertainty and scope creep. The more organized you are, the more likely you’ll catch an issue before it becomes a major problem.
You can lean on strategies like iterative development and ROI analysis to give yourself a leg up. Budget management can be the difference between a successful and unsuccessful product, so use the learnings outlined in this article to position yourself and your product team to succeed!
Featured image source: IconScout
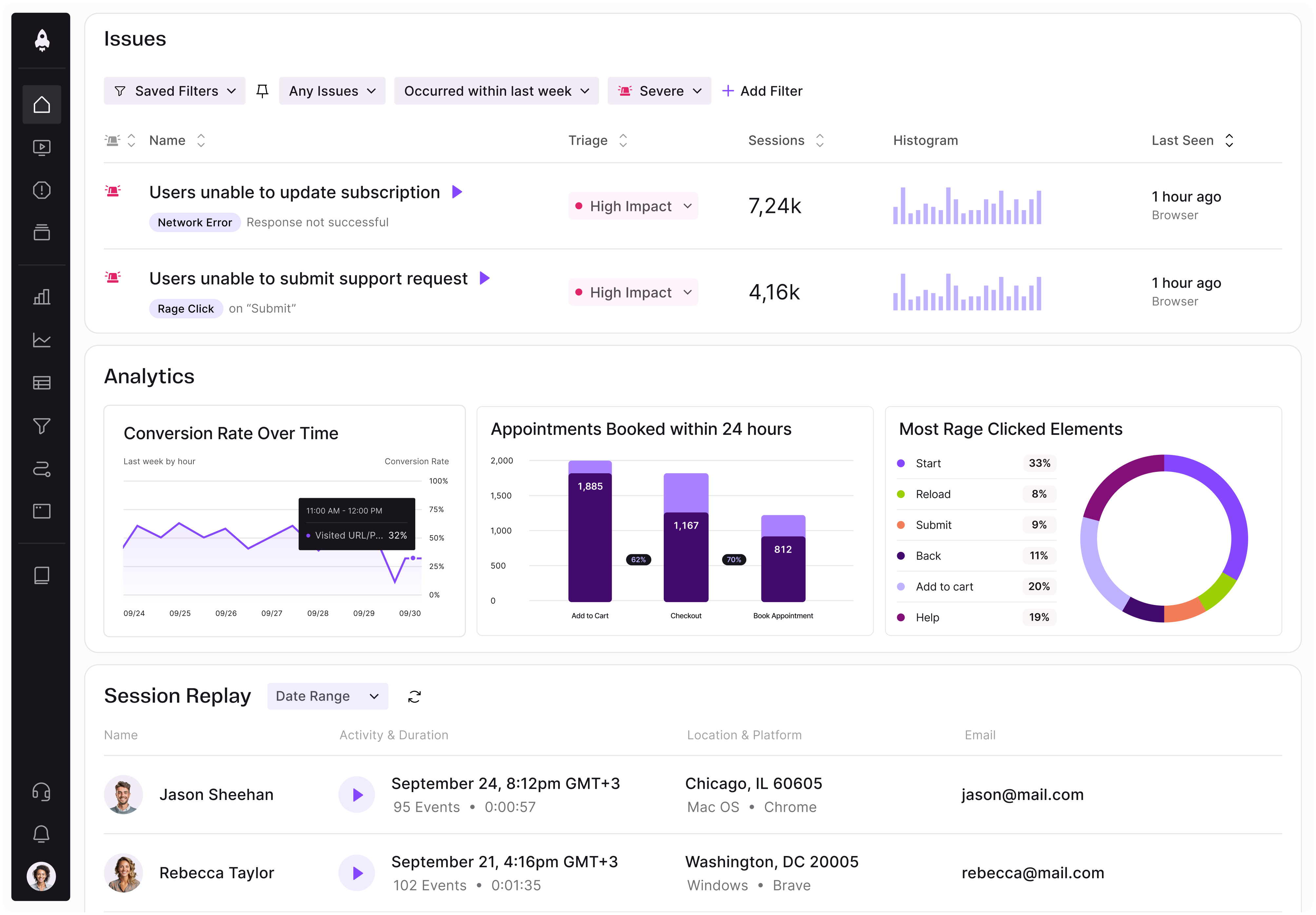
LogRocket identifies friction points in the user experience so you can make informed decisions about product and design changes that must happen to hit your goals.
With LogRocket, you can understand the scope of the issues affecting your product and prioritize the changes that need to be made. LogRocket simplifies workflows by allowing Engineering, Product, UX, and Design teams to work from the same data as you, eliminating any confusion about what needs to be done.
Get your teams on the same page — try LogRocket today.

Rahul Chaudhari covers Amazon’s “customer backwards” approach and how he used it to unlock $500M of value via a homepage redesign.
A practical guide for PMs on using session replay safely. Learn what data to capture, how to mask PII, and balance UX insight with trust.

Maryam Ashoori, VP of Product and Engineering at IBM’s Watsonx platform, talks about the messy reality of enterprise AI deployment.

A product manager’s guide to deciding when automation is enough, when AI adds value, and how to make the tradeoffs intentionally.