
This is not just another list of trendy UI elements and UX features, nor is it a trite compilation of cool design features and components. Instead, it’s a deep look into the big changes happening in how things work online. As the way we use the internet is changing, so will the way we design experiences and interfaces across these technology-enabled solutions. We’ll talk about 10 impactful UX design trends that are changing the way we experience technology. We cover topics like using artificial intelligence to make experiences more personal, making designs more accessible for everyone, and even how jobs in design are evolving. A lot more goes into UX than flashy design systems or the latest design fads.
We’ll talk about 10 impactful UX design trends that are changing the way we experience technology. We cover topics like using artificial intelligence to make experiences more personal, making designs more accessible for everyone, and even how jobs in design are evolving. A lot more goes into UX than flashy design systems or the latest design fads.
We’ll break down what these trends mean, where they stem from, and why they matter. So, here’s an in-depth look at design trends that go beyond the basics and give you a sneak peek into the future of design.
AI drives personalized, ethical interactions, shaping intuitive UX.
“In interactive works, AI enhances the experience by creating stimulating engagements with the audience.”
AI (Artificial Intelligence) will dominate the UX landscape, propelling personalization, interactivity, voice commands, and ethical design practices. It’ll be the engine behind tailored experiences and anticipatory interactions, making solutions more intuitive and efficient.
AI’s roots trace back to machine learning and deep learning algorithms. However, ethical design, focusing on user privacy and fairness, has become a crucial aspect in AI applications, prompted by concerns about data ethics.
For more information on AI ethics, check out this article by IBM. Essentially, teams who implement AI will need to ensure that it is free of bias and respects user privacy.
While AI enables hyper-personalization, it also raises ethical concerns regarding user data and privacy. The challenge lies in balancing personalization with user consent and privacy.
There’s also the concern of what data is free for machine learning and what data is protected. This is a developing conversation that courts are battling with.
Experiment with AI-driven personalization and interactivity in your interfaces, prioritizing user consent and transparency in data usage. You can check out our blog post on leveraging AI in UX design. If you’re interested in a specific tool, we also have guides on using Midjourney to prompt visual design and ChatGPT for improving UX.
Sephora has introduced an AI-based application in collaboration with ModiFace, enabling customers to find matching shades by uploading photos, offering a seamless virtual try-on experience and product recommendations in Sephora’s inventory. This innovative use of AI technology in online shopping aims to enhance product discovery and encourage conversion by allowing users to visualize product benefits pre-purchase.

The 10Web AI website builder uses AI to swiftly create tailored websites by automatically generating unique content and images suited to individual business needs. AI personalization on dynamic websites is a great way for businesses, especially ecommerce platforms, to display more relevant content to users based on various demography and data points like browsing history, activity, location, and age. This enables a more personalized user experience not feasible on static websites.
Google Arts & Culture introduced an interactive experiment allowing users to match their selfies with art pieces from global museum collections. Leveraging this AI-driven feature, users can explore artworks linked to their selfies, engaging with over 6,000 exhibitions from 1,500 museums across 70 countries. Through the application of AI, users can discover and learn about diverse artworks and cultures worldwide, fostering an immersive digital connection between individuals and art.
In the future, UXers will be able to use AI to predict user behavior. AI algorithms can predict user behavior more accurately by analyzing extensive user data. We can leverage data from predictive analytics tools like Mixpanel or Google Analytics to anticipate user preferences, improving design decisions for a more personalized user experience.
UXers will be able to use AI for virtual prototyping and testing. Tools like InVision can use AI to create interactive prototypes for testing user interactions and functionalities by simulating real-world scenarios, allowing designers to identify and rectify potential issues before the development stage.
Accessible design ensures equal access, accommodating diverse user needs for inclusive, barrier-free digital experiences. This is more than just a fad — it’s an increasingly prevalent and essential facet of design.
“As technology becomes more and more embedded in our lives, it is paramount that everyone has access to digital products.”
Accessible design will continue to be a prominent concern as digital platforms expand beyond typical hardware interfaces like mobile and desktop. This involves creating solutions usable by people with disabilities or limitations, ensuring equal access and participation for everyone.
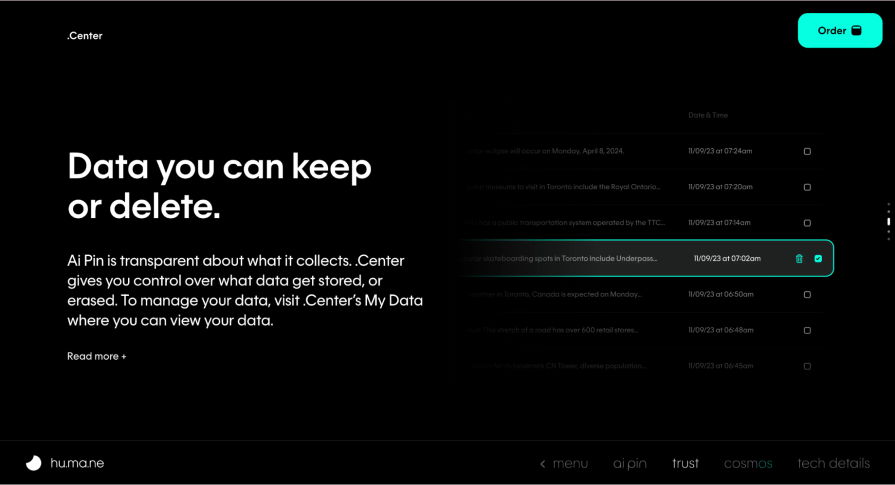
Solutions like digital lenses, AI pins, scent-free locations, and silent discos are a few examples that demonstrate the commitment to inclusivity in design and in public spaces.
The push for accessible design stems from the need to cater to diverse demographics, including those with disabilities or special needs. It signifies a shift towards designing adaptable and customizable products and experiences. These experiences accommodate different user abilities and preferences.
For businesses, accessible design broadens market reach by including all users, irrespective of their limitations. However, implementing these solutions typically poses challenges in terms of universal compatibility, design complexity, and maintaining a balance between inclusivity and overall usability. It’s up to us to balance user needs and business needs, and advocate for all users.
For UXers, incorporating accessible design practices involves identifying barriers and creating solutions that accommodate users’ varied needs. Adopting features like voice commands, familiar gestures, alternative text for images, closed captions, adjustable font sizes, and haptic feedback can be a good start. The Web Content Accessibility Guidelines can be a good place to start.
Companies are embracing accessible design to aid with visual accessibility, language translation, and content summarization for people with cognitive disabilities. Acesight VR provides navigational support through audio cues or augmented reality overlays for individuals with mobility impairments or those navigating unfamiliar environments. Other use cases include sensory adaptation solutions that adjust sensory input (sound, touch, or vibrations) to support users with sensory sensitivities or limitations.
UXers will adopt AI-driven accessibility solutions that analyze user behavior and provide tailored experiences based on individual needs. Predictive algorithms can help design interfaces that adapt to users’ preferences, making digital interactions more inclusive.
Using AI-powered tools to create virtual simulations for accessibility testing will likely become a norm. Prototyping tools infused with AI will enable designers to simulate how users with diverse abilities interact with digital interfaces, ensuring inclusivity and usability from the development phase itself.
Seamless interactions across diverse devices, ensuring unified experiences for users.
“Welcome to the era of Spatial Computing.”
Cross-platform experiences rely on seamless transitions and consistent interactions across various devices. As our use of technology evolves beyond smartphones, we need to ensure smooth and coherent user experiences across smart TVs, smartwatches, devices integrated into vehicles, IoT (Internet of Things) devices, smart glasses, and other wearable devices. This requires designers to focus on harmonizing interactions and functionalities across different platforms and screen sizes.
The push for cross-platform experiences is because users demand immersive and interconnected digital experiences beyond traditional smartphones. Users now expect interactions that seamlessly transition between these devices and conventional screens. This extends the scope of UX design from responsive web design to “responsive device design,” emphasizing adaptability and continuity in user experiences.
Delivering cross-platform experiences offers flexibility, allowing us to switch devices while maintaining a consistent user interface, familiar gestures, and functionality. However, in achieving cross-platform consistency, challenges arise such as:
Designers need to apply adaptive and scalable design principles that go beyond specific devices or platforms. User testing will be more important than ever, so test your app across several devices!
Try leveraging technologies like augmented reality (AR) for smooth transitions between devices. Experiment with new platforms where your audience might gather.
The adoption of wearable technology highlights the need for designers to optimize for multi-screen adaptability. Companies like Google and Apple are venturing into AR-enabled devices with Google Glass and Apple Vision Pro, which you navigate using eye movements, hand gestures, and voice commands. So, designing apps, products, or experiences around these would require UX designers to ensure continuity and coherence when transitioning between smart glasses and conventional screens.

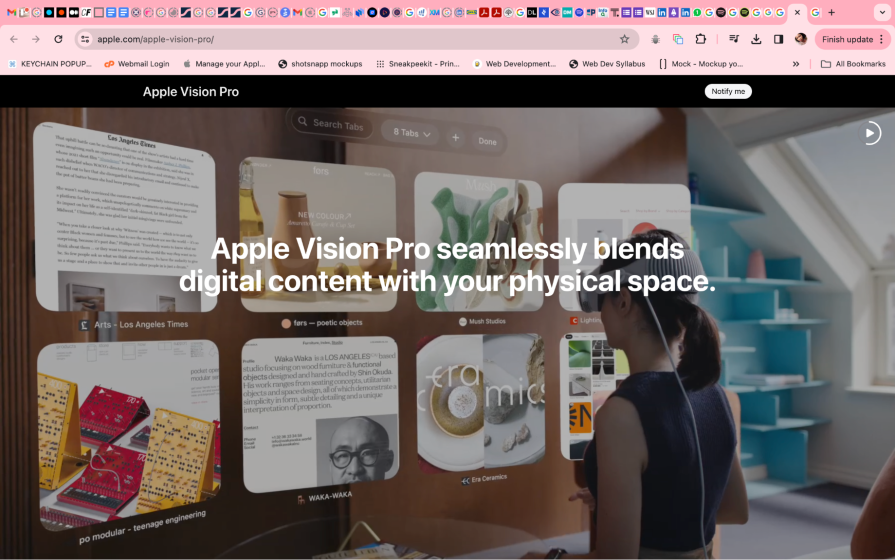
The future of UX design will center around unified experiences that seamlessly transition across an array of devices. As smart glasses and other wearable tech become more popularly used, the demand for UX designers skilled in cross-platform design will soar.
UX design evolves beyond screens, creating immersive, journey-focused experiences.
“The demand for UX and Product Designers is expected to grow, not just in quantity, but also in quality. . . This translates into a search for professionals who not only have technical skills but also the ability to think strategically and innovatively.”
The UX design role is transforming…again! There’s shifting focus from exclusively creating digital interfaces to shaping complete experiences. This extends the scope of UX design work beyond conventional interfaces to encompass the entire user journey, emphasizing the creation of immersive and inclusive experiences across various touchpoints.
This shift in UX design will cater to diverse user needs and preferences by crafting adaptable, comprehensive, and customizable experiences in the digital future.
For UX professionals, this will offer opportunities to create more inclusive designs that reach a wider market, exceeding all metrics. However, it also presents challenges around integrating various technologies like AI, AR/VR, or IoT seamlessly into the user experience while hoping to maintain. Evaluating user experiences across multiple touchpoints will also require new or more creative methodologies, tools, and approaches for testing and feedback collection.
We will need to broaden our perspectives and scope of work, considering interactions across diverse touchpoints, physical spaces, IoT devices, wearables, and more. This entails understanding user journeys beyond screen interactions to encompass various real-world scenarios. It will also require improving our business-savviness and gaining a better understanding of the industries and markets within which we work.
Engaging, responsive interactive animations elevate UX.
“Anything that moves is catching eyes these days. Think animation and variable fonts.”
Interactive animations and microinteractions are taking UX design to another level for users. No-code tools like Rive empower designers to create dynamic, engaging, responsive, and interactive experiences without requiring extensive coding knowledge. These interactive elements enrich user experiences, adding depth and intuitiveness to interfaces.
With no-code tools like Rive, designers can now produce complex and interactive animations efficiently, reducing dependency on specialized developers. This design tool is best known for being used in Duolingo, the language app that gamifies the learning experience. Microinteractions are being extended beyond gaming to your everyday products and solutions.

The primary advantage of interactive animations is to delight and engage users, bringing life to designs. They also provide users with the necessary visual feedback on their actions, guiding them through the interface and helping them understand their actions.
Interaction greatly improves usability and adds a great touch of branding and personality. It’ll be great to see how the implementation of these elements will improve to relieve the impact of heavy usage on the performance of the interface, preventing slow load times or laggy interactions, especially on low-powered devices.
As we continue to adopt animated interactions, we need to ensure they enhance the user experience without compromising usability or performance.
Embrace no-code animation platforms like Rive to experiment with interactive animations in your designs, creating engaging and responsive user interaction in your projects. It might be easier than you think!
Tools like Rive and Framer enable UX designers to create intricate interactive animations seamlessly and can be implemented for interactive controls, navigation, feedback, and warnings across vehicle UI, gaming, education, and much more.
AR and VR enrich UX with immersive, interactive experiences and conversational interfaces.
“Augmented reality-based experiential marketing has been really taking off and a lot of businesses see the value in embracing this unique approach because of its ability to communicate with the audience in a way that feels truly engaging.
—Nupur Shah, AVP and Digital Lead, West and South, via Exchange4Media
AR and VR technologies enable interactive and immersive experiences by overlaying digital elements onto the real world (AR) or creating entirely virtual environments (VR). These technologies allow users to engage in interactive and engaging experiences that blend the physical and digital realms.
AR and VR have evolved from their gaming and entertainment origins to influence design in various industries, including retail, education, healthcare, and marketing. It’s not unlikely that you know someone with a VR headset. They enable new levels of interactivity and immersion, changing the way users interact with products and services.
We’ve seen AR and VR technologies provide deeply immersive experiences, enhancing engagement and leaving a lasting impact on users. However, creating AR/VR experiences requires specialized skills and resources, making development costly.
It’s also a difficult feature to adopt in designing experiences due to the limited availability and affordability of compatible hardware. It’s better you hop on this trend now and try it out so you can consider its differences from other platforms.
UXers can explore ways to integrate conversational or two-way interactivity within AR/VR experiences. This includes creating intuitive navigation systems, interactive product visualizations, and user friendly interfaces within these immersive environments.
Major brands like Ikea, L’Oreal, and Audi are leveraging AR/VR for interactive product demonstrations, virtual showrooms, and immersive advertising campaigns. Companies are incorporating conversational interfaces within these experiences, allowing users to engage with products or services naturally, enhancing their overall user journey.
AR/VR also has applications for immersive advertisements, offering unique storytelling opportunities that will make marketing campaigns more memorable and impactful.

AR/VR technologies will continue to become more prominent in creating immersive marketing and advertising experiences, especially as e-commerce continues to rise. Conversational interfaces and two-way interactivity will be crucial for designing user-friendly and accessible technologies for a broader audience. As hardware becomes more advanced and affordable, we can expect a surge in innovative AR/VR solutions across various industries.
In 2024, typography becomes a brand cornerstone, embracing custom, diverse expressions. Unique typography will be everywhere.
“There are typeface designs for any product, mood, or scenario imaginable — and then some. But even with a seemingly endless number of fonts available today, the world of typography is continually ripe for innovation.”
Typography is once again taking center stage as the primary form of brand and design expression. More designers are painstakingly crafting their own unique typefaces, treating typography as a fundamental design element, and not just a means of conveying text.
Since the Gutenberg printing press to the digital age, typography has significantly evolved as technology has progressed. Today, designers are pushing boundaries in various ways, reimagining the rules and extending the impact of typography on brand identity and user experience. Creating custom typefaces allows for greater control over visual identity, aiding in brand recognition and setting a distinct tone for communication.
In a world where a handful of fonts reign supreme, and AI claims to be able to create your own typeface, original typography is more important than ever.
Designing bespoke typefaces offers exclusivity, reinforcing brand identity and expressing creativity. Variable fonts offer dynamic adjustments to suit diverse environments, while Femme Type and Vocal Type spotlight diversity, fostering inclusivity in typographic representation.
However, typeface design requires expertise, time, and resources. And readability and compatibility issues across devices can hamper widespread adoption across platforms.
Designers should try out different fonts to experiment with adaptable typography and create custom typefaces aligned with brand ethos. Of course, it’s important to prioritize legibility, scalability, and adaptability and so Femme Type and Vocal Type can promote diversity.
Check out this in-depth report by Monotype on the future of typography. It’s for 2023, but many of the trends will persist in full force in 2024.

Typography will play an integral role in visual storytelling, with more designers crafting bespoke typefaces to reinforce brand narratives and evoke emotional connections. AI-powered typography design tools will simplify typeface creation and democratise this trend across design disciplines.
UX prioritizes sustainability and promotes eco-consciousness.
“A sustainably designed product or service is one that considers the entire lifecycle of the product during development, from manufacturing to disposal.”
—Interaction Design Foundation, “Design for a Better World with Don Norman”
Sustainability profoundly influences design, requiring eco-conscious practices in recent times. Apple’s shift from the lightning cable to USB-C for its iPhones is a recent example how design adapts to environmental considerations, prioritizing longevity and recyclability.
Digital-focused UX designers may assume that sustainability is irrelevant to software design. However, new sectors like crypto mining expose the ecological impact of purely digital products.
Sustainable design aligns creativity with environmental responsibility. This has been a growing push as users become more eco-conscious. Innovators redefine product lifecycles, seeking reusable materials and minimal waste to reduce environmental impact.
Sustainable design champions reducing carbon footprints, promoting eco-awareness, and fostering ethical consumption. However, it necessitates resource-intensive research and design, impacting production costs. You’ll need to balance researching sustainable solutions with your business’s needs.
UX professionals should be involved in designing eco-friendly materials, production methods, package design, and recycling solutions. Let your users know what you’re doing — you can tell them why their package is made of a different material, or give them instructions on how to recycle their product.

Google’s approach to sustainable design includes committing to extended update support for its Pixel device. Pixel 8 series guarantees updates for seven years, Pixel 6 and later for at least five years, encompassing security, software, and potential feature enhancements.
Likewise, Apple creates an image of product longevity and recyclability through sustainable design principles, as this ensures that users will not need to purchase a new design every year. The prospect of a more easily repairable modular MacBook Pro seems to be a step in the right direction.
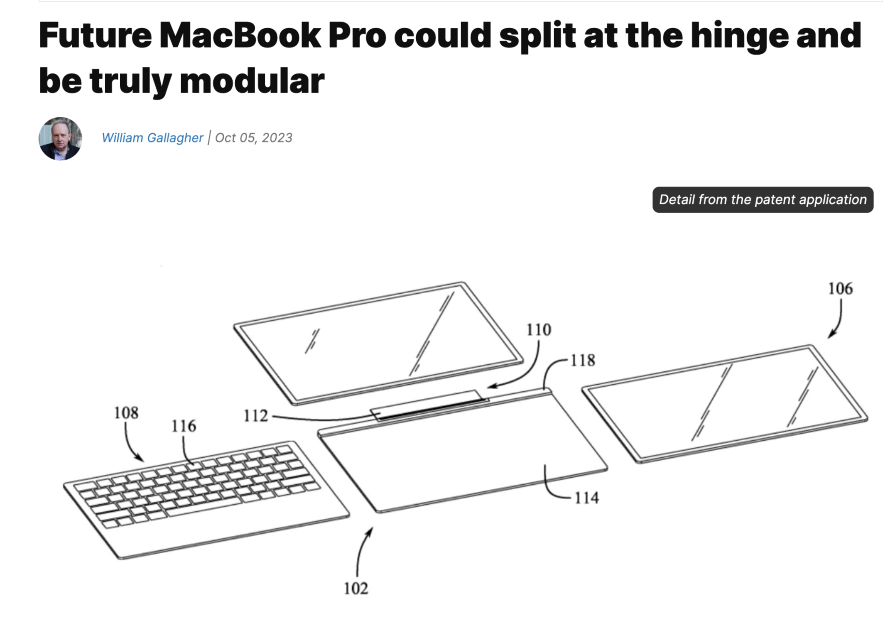
Sustainable design will thrive as a key driver in innovative product development, urging more companies to adopt eco-friendly practices. We can anticipate an increased emphasis on sustainable materials and manufacturing, influencing diverse design sectors like fashion and architecture, and shaping eco-conscious consumer behavior.
In 2024, we’ll be leveraging user data to shape design strategies and tailor experiences for individuals.
“Without data, user experience design does not exist; the end result is limited to the design team’s perceptions and experiences.”
Data-driven design involves utilizing user data to craft tailored experiences. This is about analyzing extensive user data, including demographics and behavior patterns, to drive design strategies that cater to individual user needs. It enforces a culture of research and continuous discovery within the design process.
Data-driven design stems from the abundance of user data available based on our usage and interactions with digital products. Companies like Spotify, Amazon, and Netflix have successfully utilized user data to drive business growth and enhance user experiences; think of Spotify Wrapped or Netflix’s recommendations based on your category preferences. As digital transformation continues across industries, UX professionals will need to become proficient in data-driven design.
Design decisions influenced by data let us customize experiences, increasing user engagement and satisfaction. Testing is crucial for us UX specialists.
However, concerns about user privacy, data security, and potential biases in algorithms used for personalization remain critical challenges that companies must navigate in 2024. We have to avoid invading privacy while still getting the data that can help you do your job.
This year, designers should develop their data analytics skills to gain actionable insights into user behavior and preferences. This would also require implementing analytics tools to evaluate user journeys, segment audiences, and deliver personalized content or services.
Experiment with some new data tools this year. Then, think of how you can serve data to your users to curate their experience.
Spotify excels in personalization by curating playlists based on its users’ listening habits, creating highly tailored and engaging music experiences. This InfoQ article provides a deeper look into Spotify’s approach.
Its legendary Spotify Wrapped uses data to create marketing content, and it’s being adopted by companies across industries like ecommerce and financial services.

Similarly, Amazon’s recommendation engine analyzes user data to suggest products, enhancing their users’ shopping experience by offering personalized product suggestions.
Proficiency in data analytics will become essential for all UX professionals. The impact of personalized experiences is reflected in business growth. Mastering data-driven methodologies and tools will empower UX designers to harness user data effectively, shaping the future of user-centric and hyper-personalised design strategies.
Designing voice user interfaces involves the integration of voice-based interactions, leveraging voice technology to create hands-free experiences.
“There was a time when user interfaces could only be interacted with by a touchscreen, a keyboard, or a mouse. Today, however, there’s been an explosion in voice user interfaces—allowing for hands-free interactions using just our voices.”
Voice interfaces incorporate voice commands as a primary means of interaction between users and digital systems. It enables devices to understand spoken language and respond with appropriate actions or information.
This goes beyond mere voice recognition to interpreting natural language, facilitating interactions across various platforms.
The idea of being able to control a device just by speaking to it used to be the stuff of futuristic science fiction. Voice User Interface (VUI) design traces back to artificial intelligence and natural language processing technologies. Today, developments in machine learning and speech recognition algorithms allow users to engage with technology in more human-like ways. Almost all of us have used voice interaction by now.
Designing for voice interfaces enhances accessibility and convenience, especially for multitasking or augmenting interaction for users with physical limitations. However, challenges still exist regarding accuracy in voice recognition as well as privacy concerns regarding data storage. I’m sure you’ve had a voice assistant mishear you before…and you might have worried if it listened to your conversations.
UX designers should prioritize voice-first design, ensuring minimal reliance on visual feedback. Focus on natural, personalized conversations, ensuring trust and adaptability to different user contexts.
Prioritize accuracy, context awareness, and user privacy for successful voice user interface design. Check out this Smashing Magazine article for a comprehensive guide on designing for VUIs.
Companies like Amazon with its Alexa, Google with its Assistant, and Apple with Siri have pioneered the third generation of voice interfaces, enhancing user experiences in smart homes, mobile devices, and beyond. Integration of voice-based interactions in navigation systems and customer service helplines demonstrates the vast applicability of this trend.
We will witness an increased reliance on voice interfaces as the way users interact with technology continues to change. As voice technology becomes more sophisticated, we anticipate its integration into various applications and domains, driving innovation and improving accessibility in digital interactions.
2024 is the year of personalized, accessible, immersive, and interactive holistic design experiences. The future of UX design is at an exciting inflection point, and it is evident that design is growing in importance as companies seek to innovate on experience and products, while prioritizing sustainable practices and maintaining ethics around data and AI.
There is not a more exciting time to be a UX designer than now!
LogRocket's Galileo AI watches sessions and understands user feedback for you, automating the most time-intensive parts of your job and giving you more time to focus on great design.
See how design choices, interactions, and issues affect your users — get a demo of LogRocket today.

Security requirements shouldn’t come at the cost of usability. This guide outlines 10 practical heuristics to design 2FA flows that protect users while minimizing friction, confusion, and recovery failures.

2FA failures shouldn’t mean permanent lockout. This guide breaks down recovery methods, failure handling, progressive disclosure, and UX strategies to balance security with accessibility.

Two-factor authentication should be secure, but it shouldn’t frustrate users. This guide explores standard 2FA user flow patterns for SMS, TOTP, and biometrics, along with edge cases, recovery strategies, and UX best practices.

2FA has evolved far beyond simple SMS codes. This guide explores authentication methods, UX flows, recovery strategies, and how to design secure, frictionless two-factor systems.