A well-thought-out pricing strategy not only reflects the value your product offers to customers, but also helps you achieve your revenue goals.
In this guide, we’ll provide an overview of factors that influence product pricing. We’ll also walk through a four-step process to help you establish an effective pricing strategy that aligns with your business objectives.
Pricing is the amount a company charges consumers for its products or services.
Determining the right price for products requires careful consideration. Setting the price too low can result in missed revenue, while setting it too high may limit sales volume.
Pricing can either attract or repel consumers, so it needs to be calculated strategically. It should be set at an amount that reflects the value delivered to the consumer while remaining appealing enough to draw them in.
Establishing a product pricing strategy involves multiple stakeholders and teams. Product teams work diligently to build the right features into a product and UX teams strive to provide the best possible user experience. Meanwhile, sales and marketing promote the product within the target segment and customer support assists customers when they encounter issues.
Ideally, all these teams collaborate to deliver value to the customers commensurate with the price they pay for the product.
As crucial as your pricing strategy is when launching a new product or feature, it’s equally important to review the strategy when market dynamics, customer needs, or product updates change.
To assess your product pricing strategy, the first step is to consider all the factors that influence product pricing.
Products should be priced at a point that convinces users to purchase them. To achieve this, the perception of the product and the value it offers must be worth the asking price in the market.
To determine this price point, you need to examine several factors closely, notably:
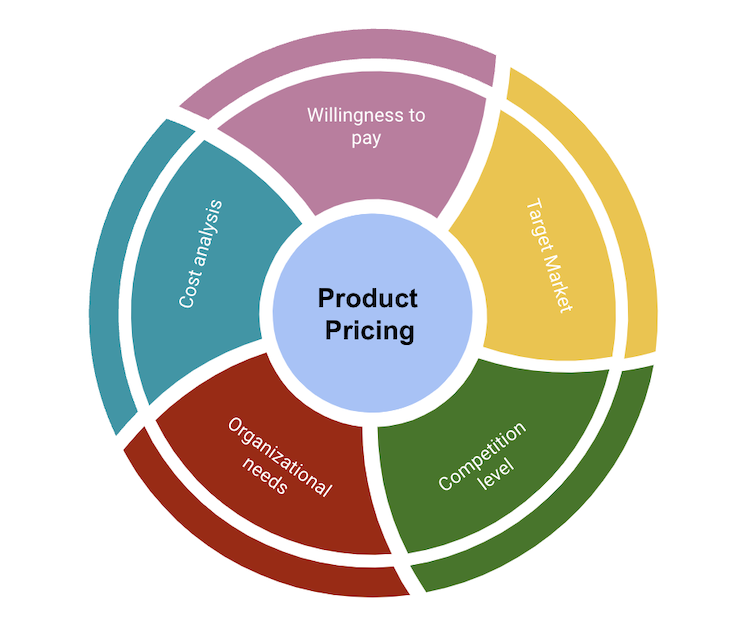
It’s crucial to thoroughly understand the target market, user personas, and the situations in which they would be willing to purchase your product. Analyze their demographics and needs to evaluate the value they seek from the product.
It’s also important to study and analyze similar products offered by competitors in the same market. Understanding how competitors price their products and their market share can help you see where your product is positioned compared to others based on the value offered.
Consider whether customers would be willing to pay for the product. Is the value offered at the product’s price point attractive enough for customers to make a purchase? Are customers likely to opt for a lower-priced product, even if it might be of lower quality?
Price sensitivity is a crucial consideration when formulating a product pricing strategy.
The costs involved in creating and distributing the product should impact your pricing strategy. Maximizing revenue is a top priority, and the pricing strategy should align with this goal.
Discounted prices can increase revenue in the short term due to higher sales volume. But for long-term profit goals, the pricing strategy should focus on attracting loyal customers over time.
Because product pricing directly influences revenue and profit margins, it’s essential to consider the company’s business objectives and ensure the pricing strategy is aligned to achieve those goals.
Pricing products is a challenging task. Higher pricing can deter customers, while lower pricing can result in reduced revenue. Striking a balance and accurately pricing a product to reflect the value it offers to customers is a tricky endeavor.
For B2B products, it becomes even more complicated because you must consider the customer’s budget when determining the price point. In the case of B2B SaaS, numerous options are available, such as tiered levels, flat fees, freemium models, and more, making it difficult and overwhelming to decide on price points.
Let’s explore a few straightforward steps to determine the right price for your product:
There are three main pricing strategies to consider when evaluating the right approach for your product:
Cost-plus pricing involves setting the price point by adding a markup on the total cost involved in creating the product. The disadvantage of this strategy is that changing costs over time can lead to reduced profit margins later on.
Competitive pricing involves setting a price similar to the price point offered by competitors. It helps attract and gain loyalty from price-sensitive customers. However, customers might perceive your product as similar to competitors’ and overlook any differentiation due to similar pricing.
Products are priced at what customers are willing to pay based on market research and competitive analysis. This pricing is based on the perception of the product in the customer’s mind. It’s an ideal strategy for subscription-based models.
Factors such as product demand, potential increase in buyers, competitor analysis, and customer needs play a crucial role in determining the right pricing strategy. Even after setting a pricing strategy and selling a product, the pricing needs to be reviewed from time to time as the product matures. This can help achieve optimized pricing aligned with business goals.
Customer lifetime value (CLV) is the average revenue generated from a customer over the entire lifetime usage of their account. It allows us to see how much revenue a customer can bring in over time.
The formula to calculate CLV is:
CLTV = (A – B) * C
(A = revenue per period, B = cost to deliver the product each period, C = time period for which the customer is retained).
For SaaS businesses, a good rule of thumb is to aim to have a CLV greater than the cost to acquire a customer. Initially, due to lower traction, the cost-to-revenue ratio is higher, but as sales increase, the ratio gets smaller.
There are numerous pricing models to choose from, each of which can be useful depending on the situation.
The table below lists some of the most popular pricing models, how each model works, and when to consider using them:
| Model name | How to do it | When to use it |
| Premium pricing | Set higher prices than competitors |
|
| Penetration pricing | Offer a new product or service at a low initial price to gain customers’ attention | When a new product is expected to have a high demand and can be copied easily by other competitors |
| Dynamic/surge/time-based pricing | Adjust the pricing on the fly as per changing demand in the market | When a product or service is highly flexible, this model can help improve pricing decisions by resetting the price targets in real-time based on market demand |
| Marketing and promotional pricing | Offer discounted products temporarily to increase sales volume | When you need to improve:
|
| Tiered pricing | Each tier has a set of features catered to the needs of the customer and each tier is offered at a set price | When there are is wide range of customers with different needs |
| Per-user pricing | Product is priced based on the number of users using the product | When customers have needs based on the number of users using the product, but they all need to use the same set of features |
| Freemium pricing | Offer very basic features for free but charge for additional features on a monthly or annual basis | When you need to to attract customers; because the basic set of features is free, freemium models can lead users to purchase the paid features to unlock additional functionality |
Pricing is a crucial aspect of a product because it can either attract customers or push them away. Before launching a product in the market, you should A/B test it to gauge buyer behavior.
Customer interviews and quantitative price testing can help you understand the optimal price point for the product. Focused interviews and surveys within the target market segment can help you gather insights on how customers perceive the product and make purchasing decisions.
You should also analyze competitors’ product pricing and the features offered at that price point. Consider how your product is different from competitors’ and whether customers would be willing to pay extra if your product is priced higher.
Monitor any changing market conditions, such as decreasing demand or changing customer needs, so that the product’s pricing can be adjusted if necessary.
Whether you’re running a SaaS business or selling another type of product or service, it’s important to consider all factors that might influence the optimal price. The right price point indicates the value the product will deliver to customers and the effort that goes into putting the product together before it reaches the customer.
When there are changes in market demand, customer needs, or product strategy, it’s critical to review pricing to ensure it aligns with the business’ goals and vision. Adjusting pricing based on the situation will help steer your product positioning in the right direction.
Featured image source: IconScout
LogRocket identifies friction points in the user experience so you can make informed decisions about product and design changes that must happen to hit your goals.
With LogRocket, you can understand the scope of the issues affecting your product and prioritize the changes that need to be made. LogRocket simplifies workflows by allowing Engineering, Product, UX, and Design teams to work from the same data as you, eliminating any confusion about what needs to be done.
Get your teams on the same page — try LogRocket today.

Rahul Chaudhari covers Amazon’s “customer backwards” approach and how he used it to unlock $500M of value via a homepage redesign.
A practical guide for PMs on using session replay safely. Learn what data to capture, how to mask PII, and balance UX insight with trust.

Maryam Ashoori, VP of Product and Engineering at IBM’s Watsonx platform, talks about the messy reality of enterprise AI deployment.

A product manager’s guide to deciding when automation is enough, when AI adds value, and how to make the tradeoffs intentionally.