Financial technology (fintech) is one of the fastest-growing industries, and it’s predicted to maintain its growth in the upcoming years.

Even if you don’t work or plan to work for a fintech company itself, this technology has a tremendous impact on other industries, including healthcare, marketplaces, ecommerce, and many more. That’s why I believe all tech PMs should have at least a fundamental understanding of what’s going on in the industry.
However, to understand what’s going on in fintech, you need to understand the fintech jargon.
To help you, this article explains the most important fintech terms that you should be aware of to better navigate this field, alongside related news and trends.
Fintech product management is a growing field of product managers who specialize in fintech. What differentiates fintech product managers from other PMs is their industry knowledge.
To truly excel in fintech, one must understand its regulatory landscape and the financial processes surrounding it. Listening to users’ pain points and ideating and testing solutions is insufficient without understanding the complex financial ecosystem.
A great fintech PM must understand not only the principles of product development but also:
One thing that differentiates fintech products from SaaS is customer transparency. Regulatory bodies require fintech companies to know details about individuals who transact with them and often report this data to governments to help avoid money laundering or tax evasion.
The process of collecting data from customers is called “know your customer” or KYC for short. KYC refers to the whole data collection process, including:
Anti-money laundering laws and processes aim to prevent financial crimes related to money laundering, which involves disguising illegally obtained money as legitimate.
Fintech companies must implement strict AML tools, such as
Embedded finance refers to integrating financial services into non-financial products. A few common examples of embedded finance include
Embedded finance aims to make online financial transactions more straightforward.
Buy now, pay later (BNPL) is a financing option that allows users to purchase the product today while paying for it in installments over time, often without interest.
The benefit for the customer is the ability to preserve cash flow with more significant purchases, while it allows the company to sell more of the product to people who wouldn’t be able to afford it otherwise.
Open banking is a system where banks share customers’ financial data with third parties through a set of APIs. This allows other services and fintech products to connect and operate on this data (with customer consent), which then helps build apps and products that require banking information. This could include payment intermediaries or budget management tools, without the need for the customer to manually input the latest data and sign off for every transaction.
PSD2 is an EU regulation that enables open banking.
It required all banks to share customer data with third-party APIs (on customer request) while imposing substantial customer authentication requirements and other security rules to mitigate risks related to this data-sharing.
A NeoBank is a digital bank that operates without physical branches. It usually offers simplified banking services with lower fees and greater confidence than typical banks. Revolut is an example of a NeoBank. While it does have a banking license, it doesn’t have physical branches or classic banking services such as mortgages.
A payment process is responsible for moving funds between buyers’ and sellers’ bank accounts during the transaction. It handles:
The most well-known payment processors include Visa, Mastercard, and Worldpay.
The payment gateway serves as a bridge between the merchant and the payment processor.
It’s responsible for:
Stripe and PayPal are examples of payment processors. You put your CC info into Stripe checkout, which encrypts it and relays it to payment processors to handle the transaction.
3DS is a security feature for online payments that provides an additional layer of authentication. Examples of 3DS include:
3DS greatly improves safety for the cost of increased friction.
A point of sale is the place or system where the sale happens and financial transactions occur.
Physical points of sale examples include a credit card reader at the checkout or a McDonald’s kiosk.
Digital points of sale include Stripe Terminal, Square Online, or PayPal Zettle. As you can see, most digital payment processors also provide their POS.
DeFi refers to financial services built on decentralized blockchain technology. Decentralized finance allows users to transact in a peer-to-peer fashion without the need for banks or other financial intermediaries.
Digital smart contracts or cryptocurrency exchanges are two prominent examples of DeFi implementation.
P2P refers to interactions between two individuals without any intermediaries. Decentralized finance is peer-to-peer by principle, but there are other P2P services out there. For example, digital money lending apps in which people lend money to each other are examples of P2P FinTech products.
Blockchain is a decentralized, distributed ledger that records transactions. Blockchain requires a set of computers to maintain the same ledger that helps prevent tampering and fraudulent behavior. The main idea behind blockchain is to enable transaction verification (whether it’s money exchange, digital contract, or donation acceptance) by a large community without the need for (often expensive) intermediaries.
Cryptocurrency is a digital token that uses cryptography for security. In simple words, it’s a by-product of creating another blockchain block.
To add a new block to the blockchain, a computer must first solve a complex mathematical problem. Whenever some of the community computers solve it, a new block is added to the blockchain that lists out all the most recent transactions, and the computer that solved it is rewarded a specific amount of tokens as a reward.
These tokens have a monetary value depending on their current supply and demand.
Apart from adding and verifying transactions (such as cryptocurrency movement between one digital wallet and another), blocks in some blockchains can also include smart contracts. A smart contract is an agreement between two parties that executes automatically when specific criteria are met.
An example includes escrow services on the Ethereum blockchain. Smart contracts can hold onto buyers’ funds, automatically transferring those funds to the seller once an ownership transfer is validated on another block.
The main goal of smart contracts is to reduce the need for intermediaries.
This glossary provides a high-level overview of key terms in the fintech industry. Don’t feel bad if you don’t fully understand some of the terms. Whole books have been written explaining cryptocurrencies or the differences between payment processors and gateways.
With this high-level overview, you should at least understand high-level industry articles and discussions. If you need a deeper understanding of any specific term, there’s a ton of specific, in-depth information on all the topics I just covered.
Featured image source: IconScout
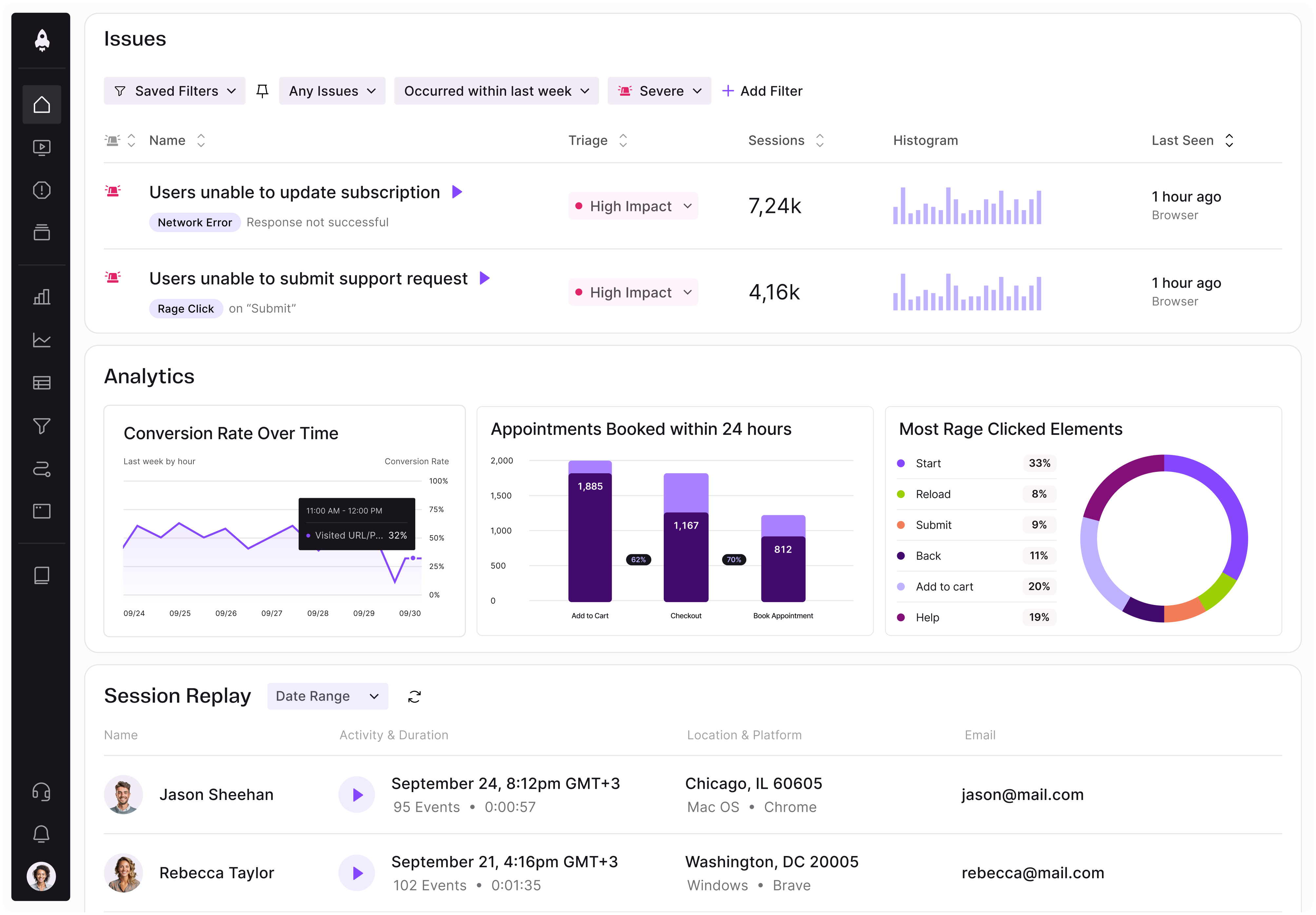
LogRocket identifies friction points in the user experience so you can make informed decisions about product and design changes that must happen to hit your goals.
With LogRocket, you can understand the scope of the issues affecting your product and prioritize the changes that need to be made. LogRocket simplifies workflows by allowing Engineering, Product, UX, and Design teams to work from the same data as you, eliminating any confusion about what needs to be done.
Get your teams on the same page — try LogRocket today.
Learn how to spot PMF erosion early, diagnose the cause, and help your product recover before decline turns into panic.
Introducing Ask Galileo: AI that answers any question about your users’ experience in seconds by unifying session replays, support tickets, and product data.

The rise of the product builder. Learn why modern PMs must prototype, test ideas, and ship faster using AI tools.

Rahul Chaudhari covers Amazon’s “customer backwards” approach and how he used it to unlock $500M of value via a homepage redesign.