You might associate problem-solving with the math exercises that a seven-year-old would do at school. But problem-solving isn’t just about math — it’s a crucial skill that helps everyone make better decisions in everyday life or work.

Problem-solving involves finding effective solutions to address complex challenges, in any context they may arise.
Unfortunately, structured and systematic problem-solving methods aren’t commonly taught. Instead, when solving a problem, PMs tend to rely heavily on intuition. While for simple issues this might work well, solving a complex problem with a straightforward solution is often ineffective and can even create more problems.
In this article, you’ll learn a framework for approaching problem-solving, alongside how you can improve your problem-solving skills.
When it comes to problem-solving there are seven key steps that you should follow: define the problem, disaggregate, prioritize problem branches, create an analysis plan, conduct analysis, synthesis, and communication.
Problem-solving begins with a clear understanding of the issue at hand. Without a well-defined problem statement, confusion and misunderstandings can hinder progress. It’s crucial to ensure that the problem statement is outcome-focused, specific, measurable whenever possible, and time-bound.
Additionally, aligning the problem definition with relevant stakeholders and decision-makers is essential to ensure efforts are directed towards addressing the actual problem rather than side issues.
Complex issues often require deeper analysis. Instead of tackling the entire problem at once, the next step is to break it down into smaller, more manageable components.
Various types of logic trees (also known as issue trees or decision trees) can be used to break down the problem. At each stage where new branches are created, it’s important for them to be “MECE” – mutually exclusive and collectively exhaustive. This process of breaking down continues until manageable components are identified, allowing for individual examination.
The decomposition of the problem demands looking at the problem from various perspectives. That is why collaboration within a team often yields more valuable results, as diverse viewpoints lead to a richer pool of ideas and solutions.
The next step involves prioritization. Not all branches of the problem tree have the same impact, so it’s important to understand the significance of each and focus attention on the most impactful areas. Prioritizing helps streamline efforts and minimize the time required to solve the problem.
For prioritized components, you may need to conduct in-depth analysis. Before proceeding, a work plan is created for data gathering and analysis. If work is conducted within a team, having a plan provides guidance on what needs to be achieved, who is responsible for which tasks, and the timelines involved.
Data gathering and analysis are central to the problem-solving process. It’s a good practice to set time limits for this phase to prevent excessive time spent on perfecting details. You can employ heuristics and rule-of-thumb reasoning to improve efficiency and direct efforts towards the most impactful work.
After each individual branch component has been researched, the problem isn’t solved yet. The next step is synthesizing the data logically to address the initial question. The synthesis process and the logical relationship between the individual branch results depend on the logic tree used.
The last step is communicating the story and the solution of the problem to the stakeholders and decision-makers. Clear effective communication is necessary to build trust in the solution and facilitates understanding among all parties involved. It ensures that stakeholders grasp the intricacies of the problem and the proposed solution, leading to informed decision-making.
While problem-solving has traditionally been associated with fields like engineering and science, today it has become a fundamental skill for individuals across all professions. In fact, problem-solving consistently ranks as one of the top skills required by employers.
Problem-solving techniques can be applied in diverse contexts:
Despite the variation in domains and contexts, the fundamental approach to solving these questions remains the same. It starts with gaining a clear understanding of the problem, followed by decomposition, conducting analysis of the decomposed branches, and synthesizing it into a result that answers the initial problem.
Let’s now explore some examples where we can apply the problem solving framework.
Problem: In the production of electronic devices, you observe an increasing number of defects. How can you reduce the error rate and improve the quality?
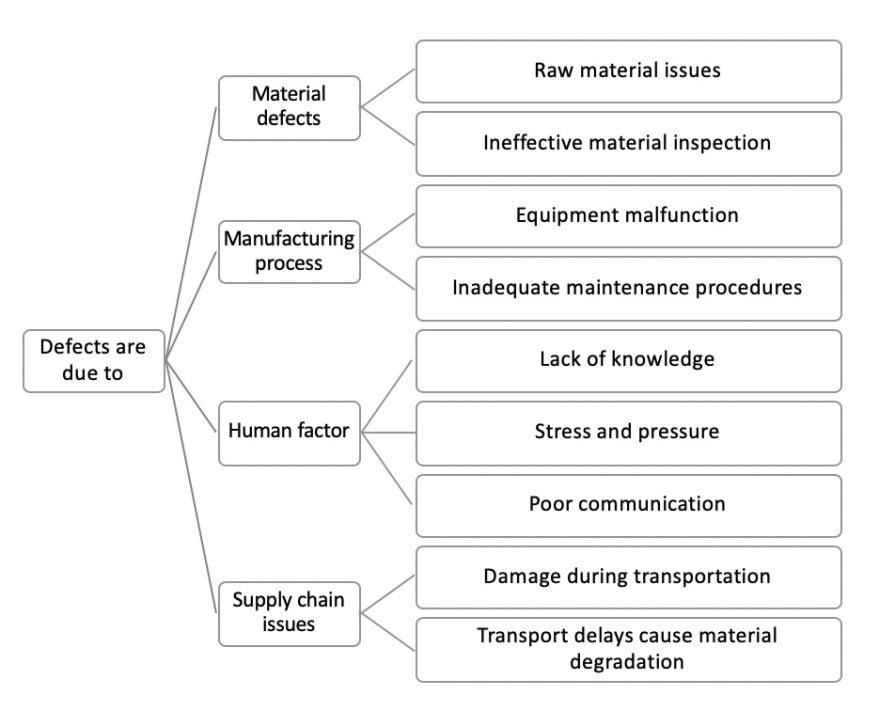
Before delving into analysis, you can deprioritize branches that you already have information for or ones you deem less important. For instance, while transportation delays may occur, the resulting material degradation is likely negligible. For other branches, additional research and data gathering may be necessary.
Once results are obtained, synthesis is crucial to address the core question: How can you decrease the defect rate?
While all factors listed may play a role, their significance varies. Your task is to prioritize effectively. Through data analysis, you may discover that altering the equipment would bring the most substantial positive outcome. However, executing a solution isn’t always straightforward. In prioritizing, you should consider both the potential impact and the level of effort needed for implementation.
By evaluating impact and effort, you can systematically prioritize areas for improvement, focusing on those with high impact and requiring minimal effort to address. This approach ensures efficient allocation of resources towards improvements that offer the greatest return on investment.
Problem: What should be my next job role?
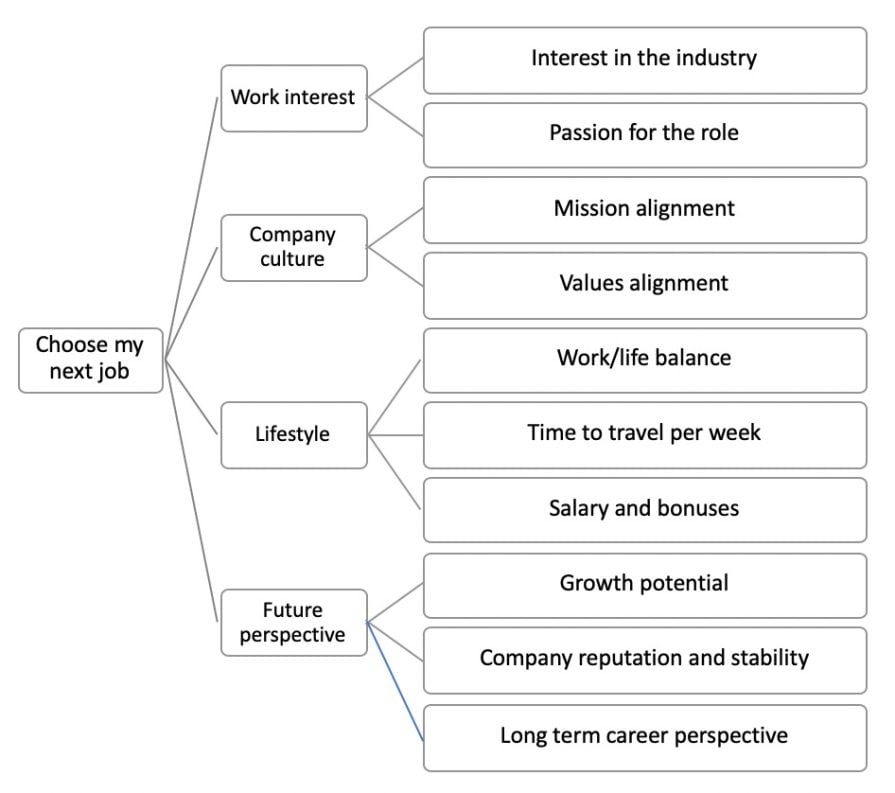
When breaking down this problem, you need to consider various factors that are important for your future happiness in the role. This includes aspects like the company culture, our interest in the work itself, and the lifestyle that you can afford with the role.
However, not all factors carry the same weight for us. To make sense of the results, we can assign a weight factor to each branch. For instance, passion for the job role may have a weight factor of 1, while interest in the industry may have a weight factor of 0.5, because that is less important for you.
By applying these weights to a specific role and summing the values, you can have an estimate of how suitable that role is for you. Moreover, you can compare two roles and make an informed decision based on these weighted indicators.
This framework provides the foundation and guidance needed to effectively solve problems. However, successfully applying this framework requires the following:
Problem-solving requires practice and a certain mindset. The more you practice, the easier it becomes. Here are some strategies to enhance your skills:
Problem-solving extends far beyond mathematics or scientific fields; it’s a critical skill for making informed decisions in every area of life and work. The seven-step framework presented here provides a systematic approach to problem-solving, relevant across various domains.
Now, consider this: What’s one question currently on your mind? Grab a piece of paper and try to apply the problem-solving framework. You might uncover fresh insights you hadn’t considered before.
Featured image source: IconScout
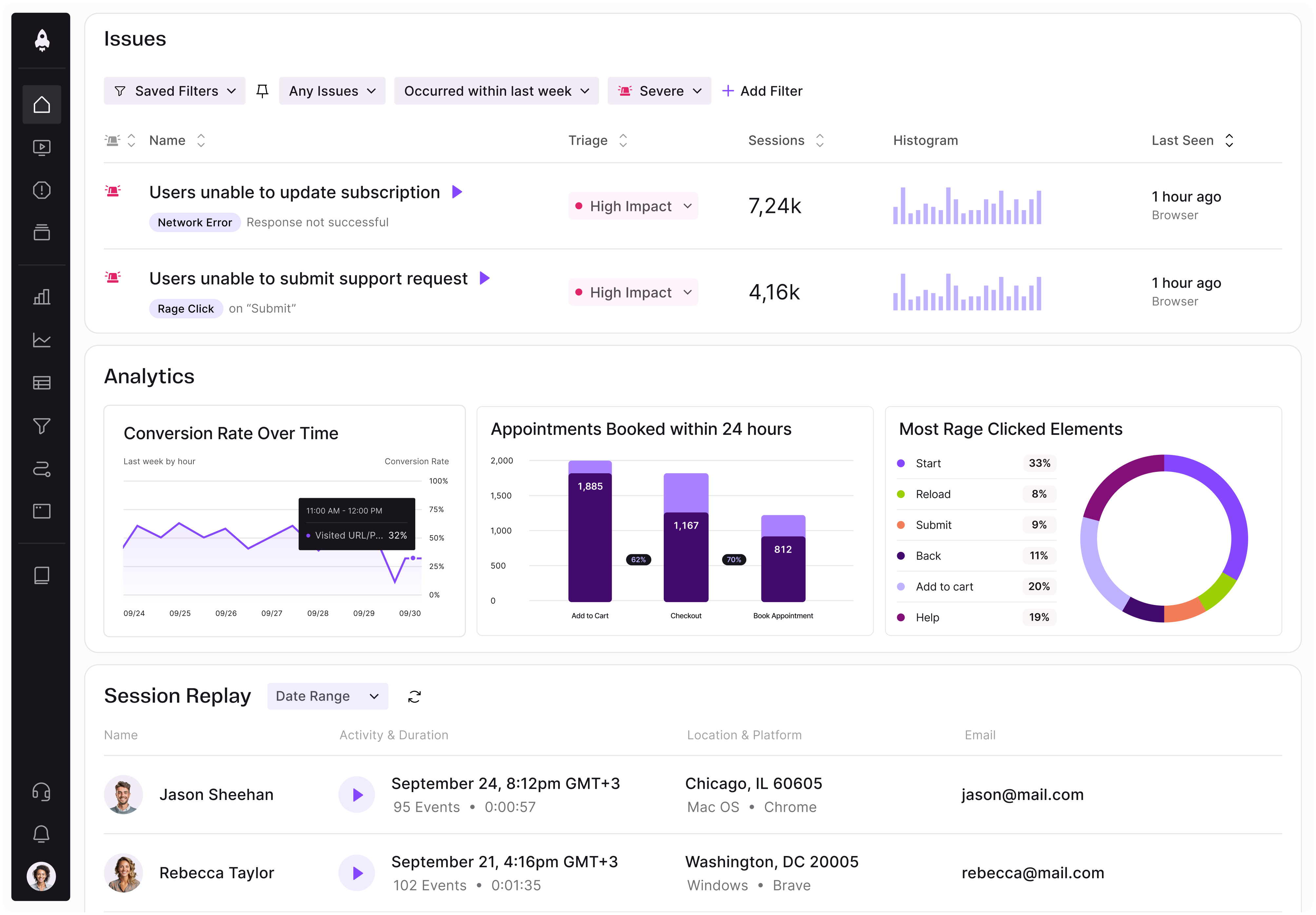
LogRocket identifies friction points in the user experience so you can make informed decisions about product and design changes that must happen to hit your goals.
With LogRocket, you can understand the scope of the issues affecting your product and prioritize the changes that need to be made. LogRocket simplifies workflows by allowing Engineering, Product, UX, and Design teams to work from the same data as you, eliminating any confusion about what needs to be done.
Get your teams on the same page — try LogRocket today.
Learn how to spot PMF erosion early, diagnose the cause, and help your product recover before decline turns into panic.
Introducing Ask Galileo: AI that answers any question about your users’ experience in seconds by unifying session replays, support tickets, and product data.

The rise of the product builder. Learn why modern PMs must prototype, test ideas, and ship faster using AI tools.

Rahul Chaudhari covers Amazon’s “customer backwards” approach and how he used it to unlock $500M of value via a homepage redesign.