A data-driven culture is instrumental in guiding every stage of the product development process. By leveraging data to understand customers, validate ideas, optimize user experience, and make informed decisions, businesses can create products that resonate with their target audience, leading to higher customer satisfaction and increased business success.

Product managers use various data sources, such as customer feedback, user behavior data, market research, and performance metrics, to make informed decisions, set priorities, and drive improvements. The goal is to create products that align with customer needs, deliver value, and achieve business objectives based on concrete evidence rather than intuition or assumptions.
Broadly, two types of data are used in product management to make informed decisions:
Qualitative data provides depth and context and plays a role in understanding the “why” behind user behavior and preferences. Quantitative data offers statistical validation and scalability and provides measurable, objective metrics to track product performance and validate hypotheses.
To explore the data-driven aspects, you must understand the source of data, its nature, and use cases to apply them within the context.
Qualitative data is descriptive and subjective. It is valuable for generating new product ideas, identifying user problems, improving user experience (UX), and informing product strategy based on customer feedback. It is collected through customer interviews, focus groups, open-ended surveys, user observations, and usability testing.
Quantitative data is numerical, measurable, and objective. It is crucial for measuring product success, tracking key performance indicators (KPIs), validating hypotheses, and making data-driven decisions. It is collected through website analytics, app usage metrics, surveys with closed-ended questions, A/B testing, and sales data.
There are a handful well-known data-driven companies that serve as shining examples for product managers. The following companies have adopted data-driven strategies to enhance their decision-making processes and gain a competitive edge:
These examples illustrate that organizations that embrace data-driven decision-making tend to be more agile, customer-focused, and competitive in their respective industries.
Netflix relies on data analytics to comprehend its audience’s viewing habits and preferences. It uses a sophisticated data-driven recommendation system to suggest personalized content to its users.
The platform collects data on users’ viewing habits, interactions, and preferences to identify patterns and predict the type of content a user is likely to enjoy. This data-driven approach has significantly increased user engagement and retention on the platform.
Airbnb uses models based on data such as location, property type, seasonal demand, and local events to recommend the most advantageous pricing for hosts. Analyzing this data enables Airbnb to maximize booking rates and revenue for hosts while still providing guests with competitive prices.
Amazon is recognized as a top player in the ecommerce industry for its innovative approach to using data to make informed decisions. By collecting and analyzing vast amounts of data on customer preferences, behavior, and interactions, Amazon can offer personalized product recommendations, optimize pricing, and enhance the overall customer experience. Amazon’s success is often attributed to its effective use of data to increase customer satisfaction and loyalty.
Spotify uses data analysis to comprehend the music preferences of its users and suggests customized playlists and songs. This has enabled Spotify to enhance user retention and maintain its competitiveness in the music streaming industry.
Ride-sharing giant Uber uses data to enhance its operations and provide better experiences for both riders and drivers. The company can optimize routes, set dynamic pricing, and predict demand patterns using real-time data. Thanks to this data-driven approach, Uber has expanded rapidly and revolutionized the traditional taxi industry.
Product managers are responsible for establishing and hitting measurable and specific KPIs that align with the organization’s goals. For example, a product manager who oversees a partner app and platform for a ride-sharing company might have a goal to increase the conversion rate by a certain percentage by the end of the year.
To achieve this, the PM might conduct A/B testing, create a data-driven roadmap plan, analyze customer feedback, study user journeys, track product and business KPIs, and leverage data to align measurable outcomes with their goals.
As a PM, having the skill to analyze data and communicate it to stakeholders in a simple and comprehensible manner is essential.
The following examples demonstrate how PMs uses data to make decisions on a day-to-day basis:
Going back to our ride-sharing example, let’s say you work at a company similar to Uber that enables users to hail taxis through a mobile app. You want to improve the app’s efficiency by notifying driver-partners early so they can position themselves in high-demand areas.
To do this, you can use data analysis to identify gaps between supply and demand for taxis. You can gain insight into customer behavior and demand trends by studying several weeks of data associated with a specific city, hub, or period. This information enables you to strategically place driver partners at high-demand hubs, reducing estimated arrival time and increasing efficiency.
These app features that notify drivers of demand and improve communication are made possible through robust analytics and forecasting models. A data-driven PM can stay ahead by using data to improve app features and performance for users and partners. Understanding how the company analyzes historical data to predict future actions can be a benchmark for product strategies.
Another example of data-driven product management — again, returning to our ride-sharing example — is when you decide to run an A/B test between two driver cohorts* *to validate whether generic or personalized push notifications can lift conversions and loyalty.
Imagine you are the PM for a mobile app that provides diet planning and specific recipe recommendations for users based on their BMI and weight. Your goal is to improve user engagement and retention.
Here is a straightforward approach that PMs can apply in simple and complex decision-making processes. These steps are designed to help you ensure that your product decisions are based on actual insights and have a better chance of achieving desired business objectives:
A sample hypothesis based on our example could be:
“We assume that customize the diet plan and recipe recommendations per the customer’s food preferences, and then users will be more likely to engage and use the app for a long time.”
It can also be quantified. Then, the hypothesis can be written as:
“A personalized diet plan and recipe recommendations, per the customer’s food preferences, will increase engagement by <x%> and user retention by <y%>.”
To validate the Hypothesis, create an A/B test by dividing the user base into two groups:
A successful PM relies on data rather than assumptions and feature lists to achieve valuable outcomes and ensure the product’s success. By focusing on key data aspects, the PM can take advantage of the limitless opportunities available to improve the product.
Data-driven product managers use data to guide the following day-to-day activities:
Moreover, using objective data can be a valuable tool for influencing stakeholders. PMs can increase the likelihood of gaining stakeholder approval by showcasing how a product or feature can save time and money, boost adoption, or decrease churn.
Here are a few ways in which the PM can facilitate this type of conversation using data and analytics:
This practice assists PMs in creating tailored success roadmaps for each user group’s needs.
The PM’s responsibilities include analyzing funnel data, conducting surveys, performing cohort analysis, conducting usability testing, and conducting A/B testing. To gather and analyze all this data effectively, it is important to use specific tools and techniques for each task.
In addition to the usual suspects — e.g., Microsoft Excel, Google Analytics, and Power BI — many powerful tools are available to help PMs to drive growth through data insights, including: \
LogRocket provides helpful usage analytics, such as which features are used most often and which parts of your application are not used enough. This data can help product managers identify popular features and better understand user preferences, which can guide decisions on future updates and enhancements.
LogRocket also allows for monitoring user interactions with new features, which can help assess the success of new releases and identify areas for improvement. By analyzing user sessions, product managers can gain insights into the typical user journey within the app, which can inform decisions on UI/UX improvements and optimize the user flow.
Coupler.io helps in data and analytics by simplifying the process of importing data from various sources. By integrating with popular applications such as Airtable, HubSpot, Trello, Jira, and more, Coupler.io makes it easy to extract data and schedule automatic data refreshes at regular intervals. This way, you can make decisions based on real-time data.
Additionally, you can perform data transformations, calculations, and analyses using familiar spreadsheet functions and formulas. This flexibility allows for more in-depth analytics and customized reporting.
Tableau is a powerful data visualization and business intelligence platform that enables users to create interactive and dynamic visualizations from various data sources. It simplifies complex data and helps users gain insights quickly.
Kissmetrics is another analytics platform focused on customer behavior analysis and tracking user interactions with the product. It offers tools for cohort analysis and funnel tracking.
Data is crucial in making informed product decisions. This methodology enables businesses to recognize customer requirements, comprehend their actions and concerns, and enhance the overall experience. Ultimately, this results in heightened user contentment, increased involvement, and improved retention rates.
Featured image source: IconScout
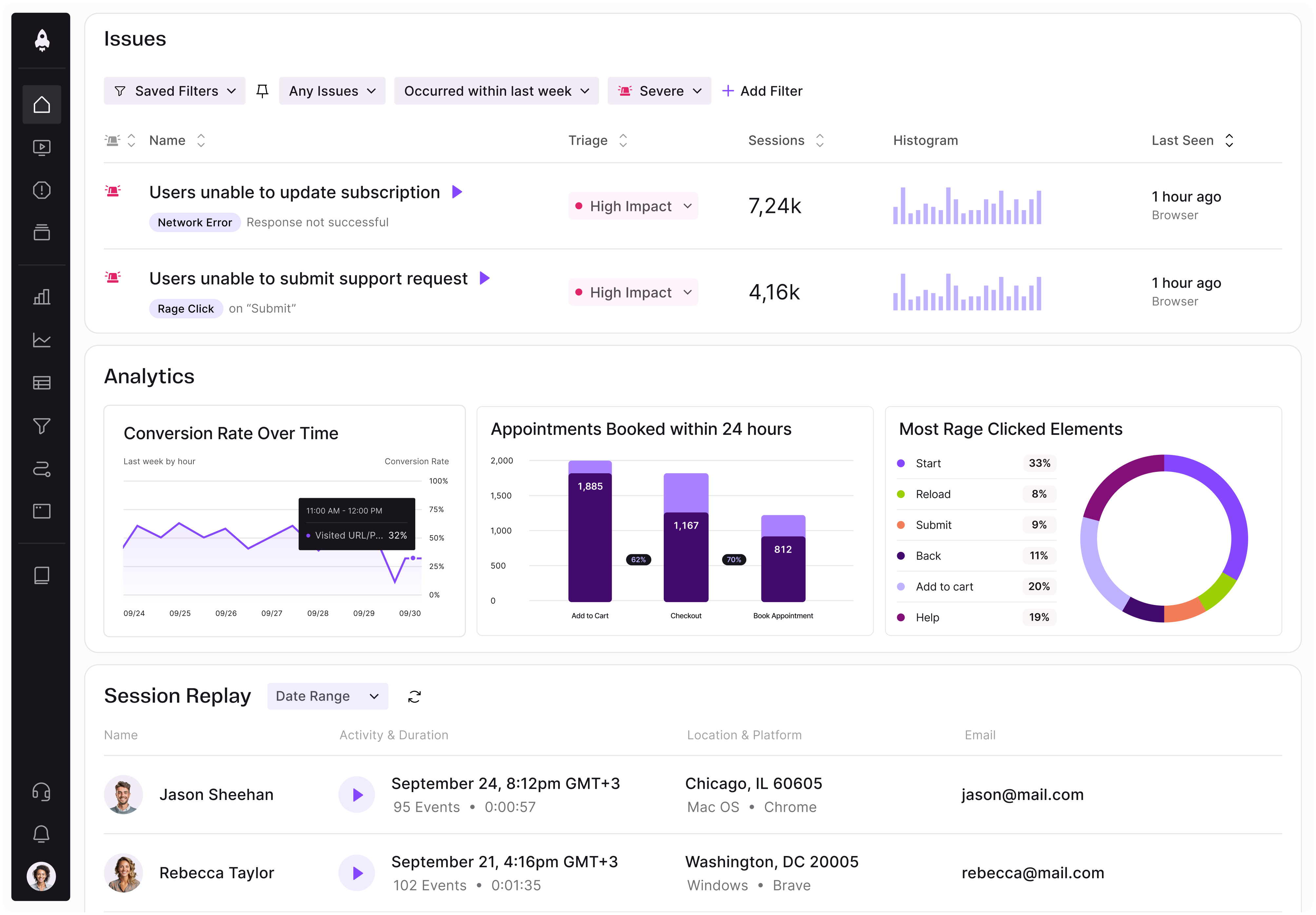
LogRocket identifies friction points in the user experience so you can make informed decisions about product and design changes that must happen to hit your goals.
With LogRocket, you can understand the scope of the issues affecting your product and prioritize the changes that need to be made. LogRocket simplifies workflows by allowing Engineering, Product, UX, and Design teams to work from the same data as you, eliminating any confusion about what needs to be done.
Get your teams on the same page — try LogRocket today.
Learn how to spot PMF erosion early, diagnose the cause, and help your product recover before decline turns into panic.
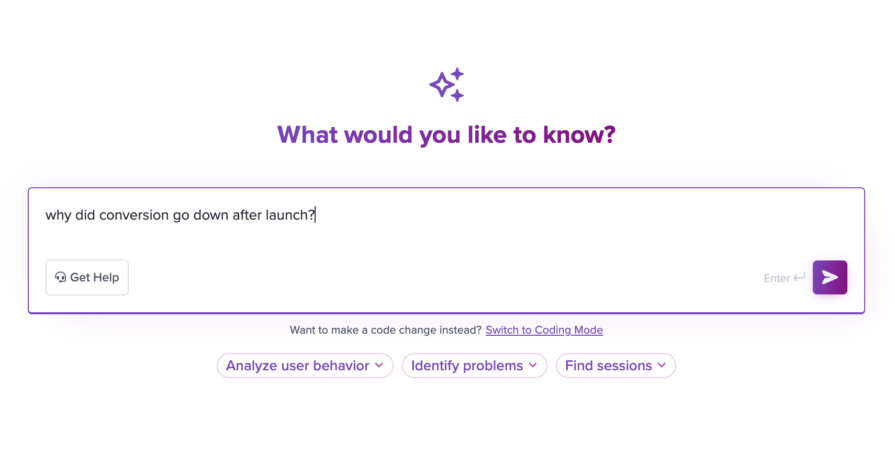
Introducing Ask Galileo: AI that answers any question about your users’ experience in seconds by unifying session replays, support tickets, and product data.

The rise of the product builder. Learn why modern PMs must prototype, test ideas, and ship faster using AI tools.

Rahul Chaudhari covers Amazon’s “customer backwards” approach and how he used it to unlock $500M of value via a homepage redesign.