In today’s business market, you’re threatened by possible disruptions that can affect your daily operations including your ability to deliver products and offer services. These disruptions may include pandemics, cyber-attacks, or natural disasters.

However, there are certain structures that you can put in place to make sure you remain continuously operating if such disruptions ever occur. In order to do this, you need business continuity management (BCM). In this article, you’ll learn the concept of BCM and the insights it offers with respect to product management.
BCM is a structure that is set by an organization ahead of time to ensure that its daily operations continue to run in case any unforeseen incidents occur such as cyber-attack, pandemics, supply chain disruptions, or natural disasters. BCM involves a team of personnel in charge of developing strategies, plans, and actions to identify, assess, and curb possible risks to business operations. The key objective of BCM is to ensure that the organization continues to run critical activities, deliver products and services, and maintain performance during and after a disruption.
BCM is very significant in product management as it ensures the ongoing functionality of an organization’s operations, during any unforeseen incidents. BCM helps to curb risks associated with technological failure, supply chain disruptions, and other unexpected incidents.
For example, in March 2023, the Camden County Police Department was hit with a ransomware attack that disrupted its daily operations and ongoing investigation. Files were encrypted, with the attackers demanding hundreds of thousands of dollars to decrypt the files. Because there was an efficient BCM in place, the Camden County Police Department was able to recover 80 – 85 percent of its files in less than a month.
You can overcome an unforeseen crisis without affecting your capacity to deliver products and services by adopting BCM. For example, the Suez Canal blockage in 2021 caused a major disruption in global trade and supply distributions. While other shipping organizations without an adequate BCP were queued to pass through the canal, Danish shipping company Maersk was able to come up with different shipping routes and suppliers. Shipments were rerouted and production plans were changed to reduce the effect of the disruption which could have caused delays.
BCM consists of several key components to ensure you can continue your vital operations during disruptions. These components altogether contribute to the ability of the organization to bounce back:
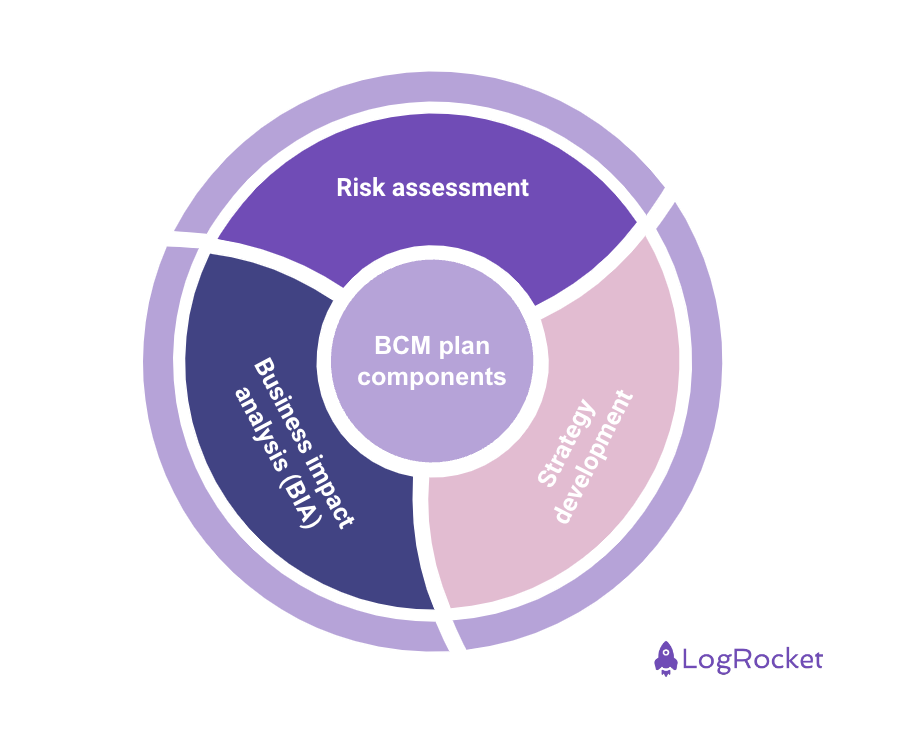
Risk assessment is effectively finding, analyzing, and evaluating numerous potential risks and vulnerabilities that could affect operations. It’s an essential component of BCM since it acts as the first step in identifying and addressing possible threats to an organization’s continuity. A thorough risk assessment may help organizations understand the possibility of various crisis situations such as supply chain disruption, cyber attacks, pandemics, and natural disasters.
Organizations can carry out risk assessment with the following steps:
There are different risk assessment tools or frameworks that can be used in BCM processes. These tools can be used collectively or individually depending on your needs. Some of these tools are the bowtie model, risk matrix, failure tree analysis, what-if analysis, and failure modes and effects analysis (FMEA).
As a strategic component of the BCM framework, business impact analysis assists in conducting a thorough evaluation of operations to figure out the possible impact of disruptions. It involves assessing the operational, financial, and reputational implications of any incident. BIA establishes recovery time objectives (RTO) and recovery point objectives (RPO) for every key business activity to assist organizations in continuing regular operations and minimizing the impact of a disruption.
The strategy development phase is when the insights gathered from risk assessments and BIA are converted into practical plans for maintaining and quickly restoring key business operations during a disruption. The major goal is to create a recovery roadmap that ensures an organized and efficient approach to business continuity by directing how the organization responds to various incidents. This includes communication protocols, IT system recovery, resource allocation, and alternative work sites.
To help you get started with implementing BCM within your organization, keep the following steps in mind.
Acquiring endorsement and active support from senior management is essential for implementing BCM in product management. This commitment and support aid in allocating resources including funding, technology, and personnel required for the development and management of the BCM programs.
A thorough risk assessment helps to identify possible disruptions and vulnerabilities that might affect product development and delivery. Simultaneously, BIA enables a clear examination of various product management activities including the financial, operational, and reputational outcomes of unexpected incidents. Understanding these risks and their implications allows the product management team to focus resources and efforts on the most crucial areas.
Organizations can outline policies and procedures on how the product management team should operate during an unexpected incident including the roles and specific steps to be taken. BCM policies and procedures for product management should include rules covering areas such as technology recovery, communication protocol, and supply chain.
Awareness helps to ensure that the product management team understands the importance of BCM and its role in guaranteeing continuity during a disruption in product operations. With awareness activities, the product management team can recognize potential threats, understand their roles in implementing the BCM plan, and work together to protect product operations.
The efficiency of the BCM plan can be evaluated by simulating various disruptive events to guarantee that it can be carried out smoothly during real-life emergencies. These exercises enable product management teams to identify weaknesses, validate response mechanisms, and optimize continuity strategies.
While creating your BCM plan is an important first step, your work doesn’t stop there. You still need to actively maintain and update your plans to ensure that they continue to work in the future.
Regular engagements with department heads, staff, and external partners ensures that the plan accurately represents actual organizational procedures and potential hazards. For the BCM plan to be effective, the team must collaborate with the stakeholders of the organization during the review process to exchange ideas or perspectives.
You should always assess and implement technological improvements regularly to keep IT systems, data recovery procedures, and communication tools up-to-date and effective during disruptions. This strategy aligns the BCM plan with the most recent technological resources, increasing the organization’s resilience in case of sudden disruptions.
Reassessing possible risks regularly ensures that the plan is still in line with current and developing threats, allowing organizations to address new difficulties ahead of time. If you incorporate continuous risk assessments you better adjust your BCM strategies to the changing business environment, improving overall readiness and resilience.
Analyzing the outcomes of previous incidents provides significant insights into the plan’s performance and highlights areas for improvement. You can refine your BCM plans by incorporating lessons learned from these evaluations, which will improve response capabilities and resolve any weaknesses or gaps discovered during actual incidents.
Business continuity management has an important role in every organization. To maintain its operations during disruptions, you must establish, implement, and constantly improve your business continuity management practices. You can effectively secure your operations from disruptions by understanding essential components such as risk assessment, business impact analysis (BIA), and strategy development.
Featured image source: IconScout
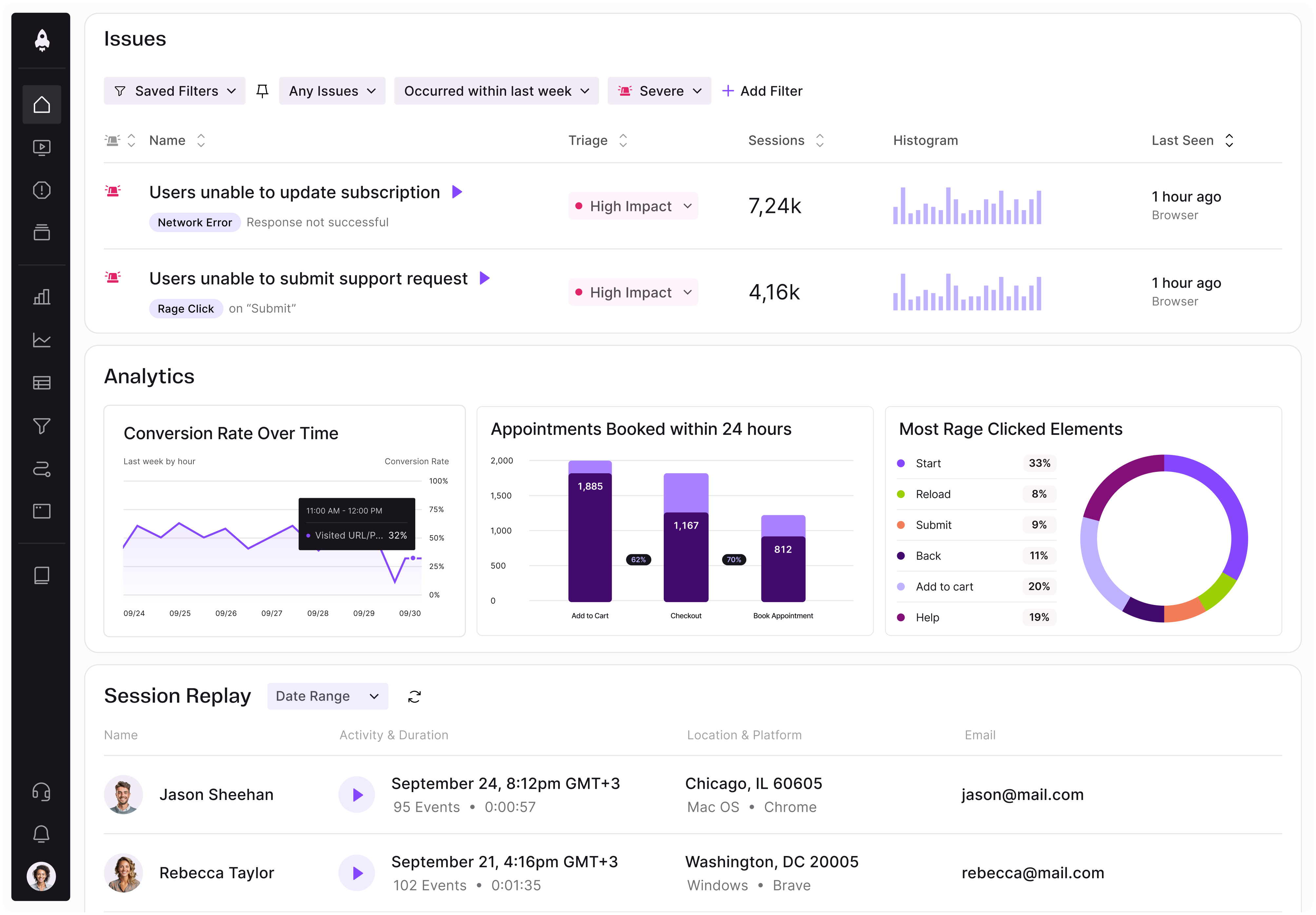
LogRocket identifies friction points in the user experience so you can make informed decisions about product and design changes that must happen to hit your goals.
With LogRocket, you can understand the scope of the issues affecting your product and prioritize the changes that need to be made. LogRocket simplifies workflows by allowing Engineering, Product, UX, and Design teams to work from the same data as you, eliminating any confusion about what needs to be done.
Get your teams on the same page — try LogRocket today.

Rahul Chaudhari covers Amazon’s “customer backwards” approach and how he used it to unlock $500M of value via a homepage redesign.
A practical guide for PMs on using session replay safely. Learn what data to capture, how to mask PII, and balance UX insight with trust.

Maryam Ashoori, VP of Product and Engineering at IBM’s Watsonx platform, talks about the messy reality of enterprise AI deployment.

A product manager’s guide to deciding when automation is enough, when AI adds value, and how to make the tradeoffs intentionally.