
QR code generation algorithms can turn textual data such as URLs, emails, phone numbers, and Wi-Fi connection details, into dynamically generated visual QR code matrices that anyone can scan with their mobile phones.
Web app developers often include QR codes in their webpages to let users navigate to URLs from a mobile device or to interconnect mobile and desktop apps instantly. For example, many modern messaging apps display a QR code on the desktop version to log in instantly by scanning with the already-logged-in mobile app.
There are many open source libraries for generating classic QR codes in the backend or frontend of your app. Due to the standard QR code system’s error correction technique, we can include logos and add custom styles to generate futuristic QR codes that still work on any standard QR code scanner.
The open source qr-code library offers an animate-able, SVG-based, <qr-code> web component that you can use to render stylish QR codes with pure HTML or any other popular frontend framework. In this tutorial, we’ll explore qr-code library features by writing some HTML snippets, and we’ll learn how to integrate this library with frontend frameworks.
The Replay is a weekly newsletter for dev and engineering leaders.
Delivered once a week, it's your curated guide to the most important conversations around frontend dev, emerging AI tools, and the state of modern software.
<qr-code> ?<qr-code> is a self-contained frontend-library-agnostic web component that we can use to create stylish, animated, SVG-based QR codes using HTML or any frontend library. <qr-code> exposes various attributes to customize the QR code style according to your web app theme and provides a simple JavaScript API to use animations.
This QR code library internally uses the open source qrcode-generator library for QR code matrix generation and the Stencil web component toolchain for generating an optimized, frontend-library-agnostic web component. This QR code generation library generates an SVG-based QR code graphic based on the output matrix of the qrcode-generator library.
<qr-code><qr-code> comes with the following notable features and competes with other open source JavaScript QR code generation libraries.
A traditional QR code is a 2D matrix image that has black squares to represent a single bit of the encoded QR data stream. A stylish QR may use circles or connected polygons instead of traditional dots. Moreover, a modern QR code typically has a logo in the middle of the matrix.
This library lets you use circles as QR code segments, place logos or any SVG element on the QR code pattern, colorize as you wish, and animate with five inbuilt animation presets.
<qr-code> is a minimal web component with better defaults, but it offers various attributes to customize QR code design according to your design preferences. You can customize positional pattern block colors, data bit element colors and styles, and animations.
This library also lets you build custom animations using a simple inbuilt animation API.
<qr-code> is not developed only for a specific frontend library — it’s a standard web component that natively works on any popular web browser. You can use this library to create animated, styled QR codes even on your plain HTML static website.
Every popular frontend library typically supports using web components within library-specific app components so that you can use <qr-code> in React, Angular, and Svelte-like popular frontend frameworks/libraries easily.
This QR code creation library is developed with Stencil using TypeScript, so you don’t need to install TypeScript definitions separately from another npm module — TypeScript definitions come with the library source itself!
<qr-code> in webpagesYou’re now familiar with this QR library’s features that can help you create stylish, animated QR codes in your web apps. Let’s see this QR code component in an HTML page to learn how to use it and customize it according to your design requirements.
qr-codeYou can install this library into your web development projects from the @bitjson/qr-code npm module using any Node package manager. I’ll import it into an HTML document via the unpkg global CDN to demonstrate its features in this tutorial.
Create a new HTML document and include the qr-code library’s latest release as follows:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" />
<title>QR codes tutorial</title>
<script src="https://unpkg.com/@bitjson/qr-code/dist/qr-code.js"></script>
<style>
body {
display: flex;
justify-content: center;
align-items: center;
height: 100vh;
margin: 0;
}
qr-code { width: 300px }
</style>
</head>
<body>
</body>
</html>
Once we include the script, it registers a new custom element, <qr-code>, so we can use the above document to learn all supported QR code component features. We’ll discuss how to integrate <qr-code> with frontend libraries in an upcoming section.
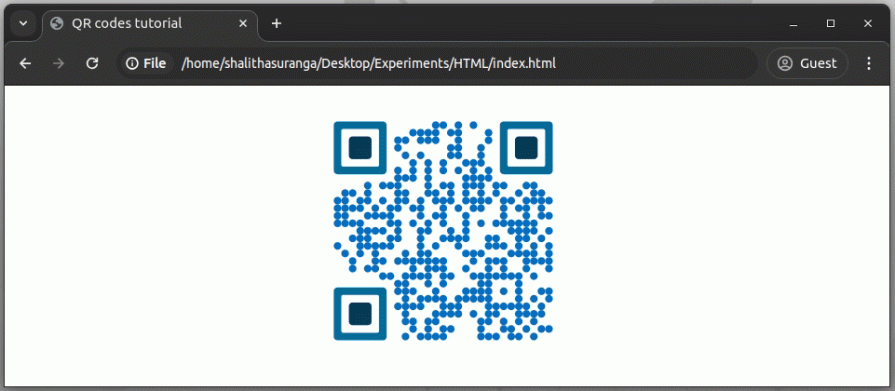
Let’s create a basic QR code by using default styles. This library lets you create a simple QR code by passing QR code contents using the content attribute. Place the following HTML content between the body tag of the above HTML document:
<qr-code contents="https://example.com"> </qr-code>
The above HTML snippet renders QR code bits below using black circles and black squares for positional rings:
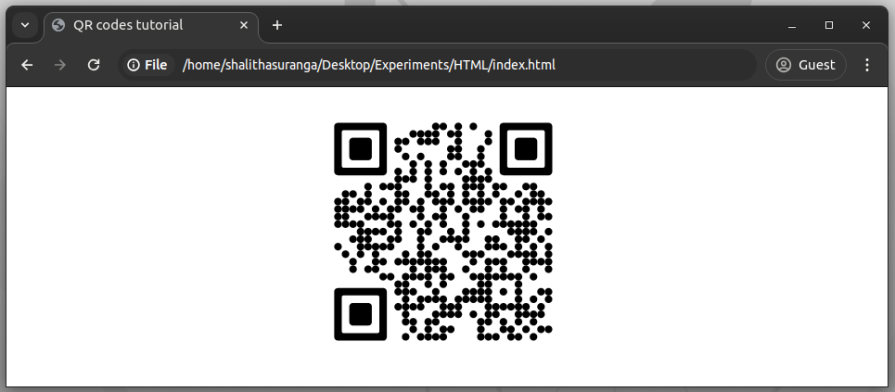
Note that we need to set the QR code component size by using the width CSS attribute for the parent <qr-code> element. We used 300px width for the QR code from the global style tag of the HTML document.
Every standard QR code typically has two types of atomic element types: position detection patterns and data bits. By default, this library fills every QR code element with black color, but it exposes three component attributes to customize colors as well.
The following code snippet renders a QR code element that has three different colors:
<qr-code contents="https://example.com" module-color="#006fc4" position-ring-color="#026d9c" position-center-color="#023d57"> </qr-code>
The above HTML snippet uses custom colors for positional patterns and data bits as follows:
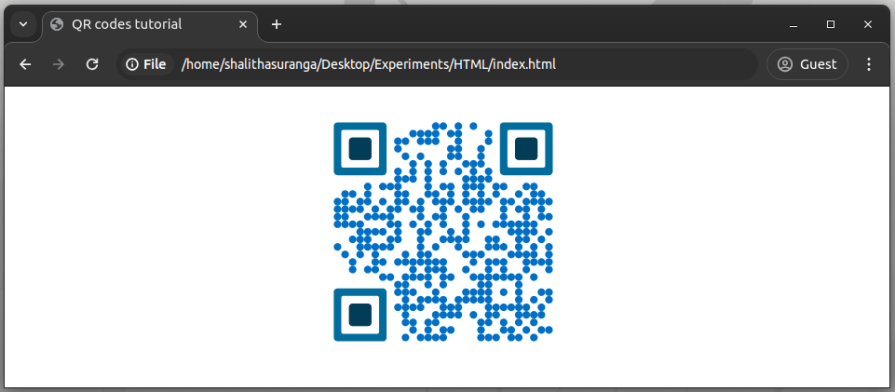
You can also change the background color of the QR code by using the background-color CSS property for the <qr-code> element.
By default, this library renders the QR code bit elements using SVG circle shapes, but it lets you switch to squares with a Boolean attribute, as shown in the following sample:
<qr-code contents="https://example.com" squares="true"> </qr-code>
The above HTML snippet renders the following classic QR code:
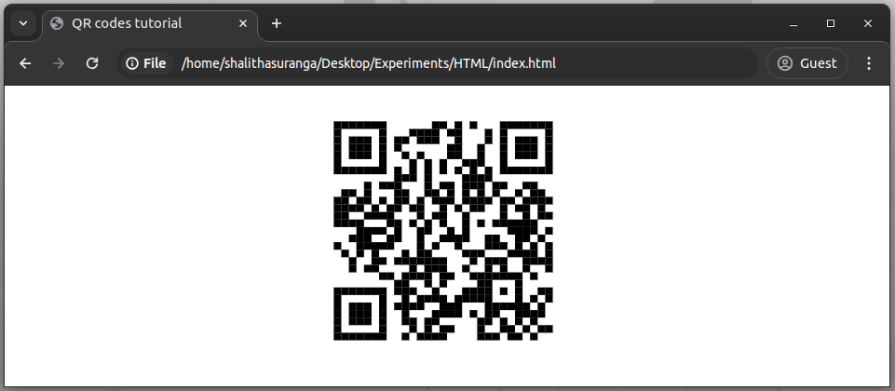
Color customization attributes won’t work with classic square patterns.
Using colors won’t affect QR code accuracy, but make sure to use colors that highlight the QR code pattern elements from the background, otherwise the QR code scanner will fail to detect your QR code as a valid one.
Modern QR codes also consist of branding elements like business logos. Remember the last time you used WhatsApp Web — it displays the app logo in the middle of the QR code. Based on the error correction level, we can put different logo sizes into the middle of the QR code. This library lets you place any graphical element in the middle of the QR code using the highest error correction level (H – 30 percent of data can be recovered).
Look at the following example:
<qr-code contents="https://example.com" module-color="#a42c48" position-ring-color="#ffb32b" position-center-color="#8a293d"> <img slot="icon" src="https://raw.githubusercontent.com/codezri/static-media/main/reshot-icon-haha.svg"> </qr-code>
The above code snippet places an SVG emoji as a logo (from Reshot) in the middle of the generated QR code, as shown in the following preview:
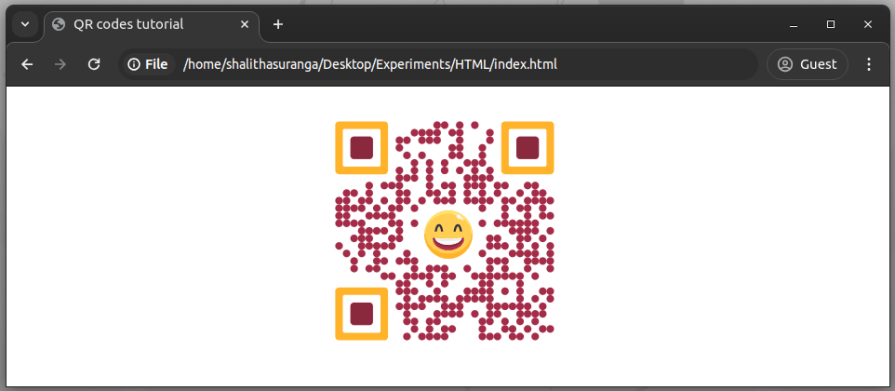
Here, we used the <img> tag to load an external SVG resource as a logo, but you can add any SVG graphic directly to the QR code element. All you need to do is to add slot="icon" to your vector logo element, and the library will handle the rest.
Look at another example that draws a custom shape using SVG tags without using the <img> tag:
<qr-code
contents="https://example.com"
module-color="#a42c48"
position-ring-color="#ffb32b"
position-center-color="#8a293d">
<svg slot="icon" viewBox="0 0 50 50">
<circle r="18" cx="20" cy="25" fill="#ffb32b"/>
<circle r="18" cx="32" cy="25" fill="#8a293d"/>
</svg>
</qr-code>
Here’s the result:
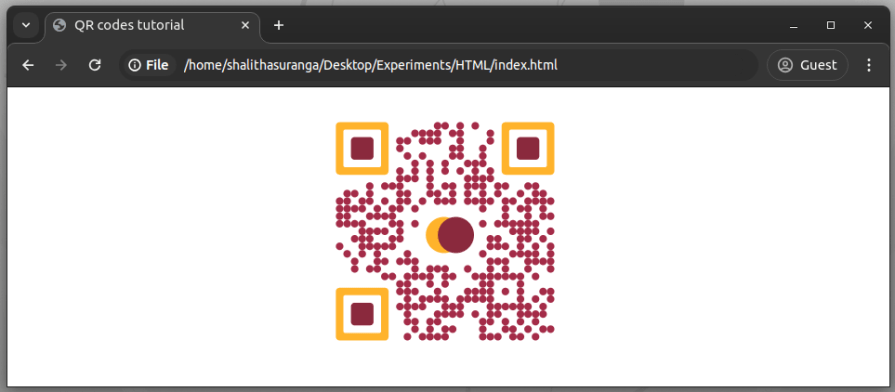
This QR code component exposes the mask-x-to-y-ratio attribute (default value is one) to scale the logo element size.
The library offers a simple API to animate QR codes by internally using the just-animate npm module. This web component automatically binds the animateQRCode() function into the parent QR code DOM element, so you can use it to add intro animations when the SVG is rendered:
<qr-code
id="qr"
contents="https://example.com"
module-color="#a42c48"
position-ring-color="#ffb32b"
position-center-color="#8a293d">
<img slot="icon" src="https://raw.githubusercontent.com/codezri/static-media/main/reshot-icon-haha.svg">
</qr-code>
<script>
document.getElementById('qr').addEventListener('codeRendered', () => {
document.getElementById('qr').animateQRCode('MaterializeIn');
});
</script>
The above code snippet renders the QR code by using the MaterializeIn animation preset as follows:
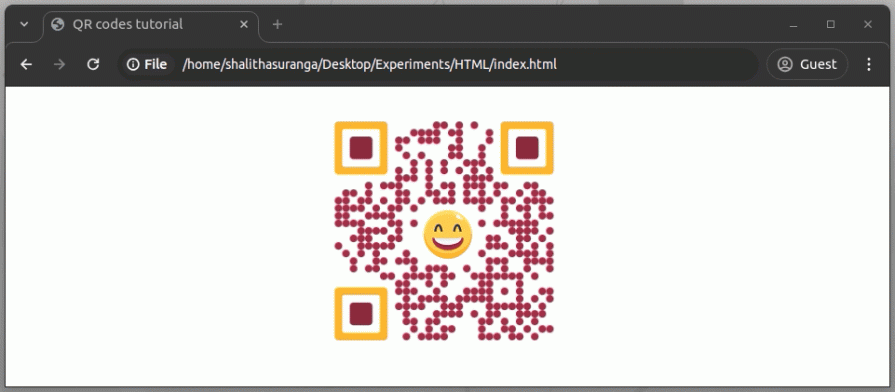
qr-code offers an animation API that is not limited to creating intro animations, so you can call the animateQRCode() function anytime, i.e., when the user visits the link from a mobile device.
You can use five inbuilt animation presets:
FadeInTopDownFadeInCenterOutMaterializeInRadialRippleRadialRippleInVisit the official website of the library to see previews of these inbuilt animation presets.
You can also create a custom animation by using the library’s animation API:
.animateQRCode((targets, x, y, count, entity) => ({
targets,
duration: 800 + (x * y) + y * 2,
easing: 'cubic-bezier(.51,1.62,.59,1)' ,
web: {
opacity: [0, 0.7, 0.2, 1],
transform: entity == 'module' ? ['skew(50deg)', 'skew(0deg)'] : []
},
}))
The above code snippet plays a custom animation, as shown in the following preview:
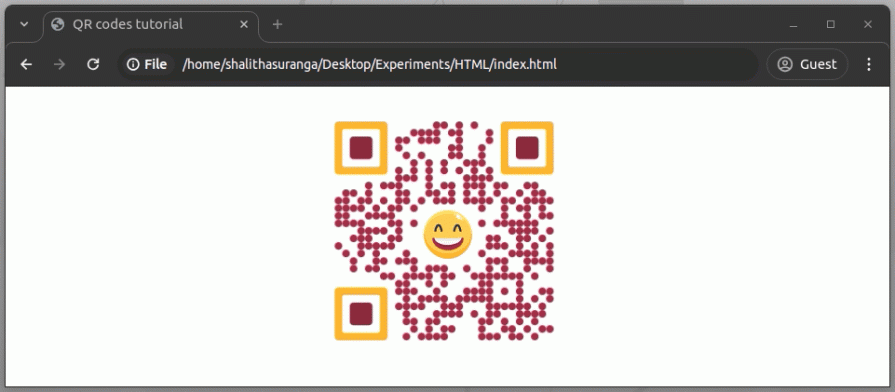
The animateQRCode() function accepts a callback that gets triggered for each atomic element of the QR code with the following variables. You can use these variables to animate QR code elements individually:
| Parameter # | Suggested variable name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | targets |
DOM references to the current atomic QR code element |
| 1 | x |
The x-axis coordinate of the element |
| 2 | y |
The y-axis coordinate of the element |
| 3 | count |
Count of the all QR code elements |
| 4 | entity |
Element type: module (data bit), position-ring, position-center, and icon |
You can build any complex animation using just-animate animation objects and Web Animations API transformation functions.
In most scenarios, developers use a QR code to send a scanable link to a mobile device. But, if your app generates a QR code for offline use, you may have to implement options to download and print generated QR codes. For example, a modern resource management web app may offer a QR code to download or print that users can paste on physical equipment instead of traditional barcodes.
We can use the following function to implement the QR code download action:
function downloadQR() {
const svg = document.getElementById('qr')
.shadowRoot.querySelector('svg').outerHTML;
const blob = new Blob([svg.toString()]);
const anc = document.createElement('a');
anc.download = 'qr-code.svg';
anc.href = window.URL.createObjectURL(blob);
anc.click();
anc.remove();
}
The above function extracts the SVG source from the web component. Then, it triggers the click event of a virtually generated hyperlink that points to the SVG Blob URL. Once you call the above function, the browser automatically downloads the generated QR code.
For printing your generated QR codes, you’ll have to use a workaround as web browsers don’t offer a standard way to print a targeted DOM element. Choose one option according to your development preference and requirements:
printdLet’s try one approach. We can use the following media query with the HTML document we used in this tutorial for demonstrations:
@media print {
#qr { width: 100% }
}
The above CSS snippet enlarges the QR code element for printouts as follows:
For simple websites, you can hide elements that you don’t want in the printout, as shown in the following sample CSS snippet:
@media print {
header, footer {
display: none;
}
#qr { width: 100% }
}
<qr-code> with frontend frameworksEvery popular frontend framework supports using web components within standard framework components, so you can directly use <qr-code> within any modern frontend framework or library. I’ll demonstrate so by using this library to create a stylish QR code in React.
Create a new React project with Create React App (CRA) using the following command:
npx create-react-app qr-codes cd qr-codes
Install the QR code library as follows:
npm install @bitjson/qr-code # --- or --- yarn add @bitjson/qr-code
Add the following CSS code to the index.css file to style the main app layout:
body {
display: flex;
justify-content: center;
align-items: center;
height: 100vh;
margin: 0;
}
Import the QR code library from the App.js file as follows:
import * as qr from '@bitjson/qr-code';
Create a reusable, React component using the <qr-code> web component using the following code snippet:
const QRCode = (props) => {
const ref = useRef(null);
useEffect(() => {
qr.defineCustomElements(window);
if(ref.current) {
ref.current.addEventListener('codeRendered', () => {
ref.current.animateQRCode('MaterializeIn');
});
}
}, []);
return (<qr-code ref={ref} {...props}></qr-code>);
}
Finally, use the newly created QRCode React component from the App component to render an animated, stylish QR code as follows:
function App() {
return (
<QRCode
contents="https://example.com"
module-color="#006fc4"
position-ring-color="#026d9c"
position-center-color="#023d57"
/>
);
}
After making the above changes, start your app. Then, you’ll see the following QR code with an intro animation:

Similarly, you can integrate <qr-code> with any popular frontend framework/library. You only need to make sure to trigger the defineCustomElements() Stencil toolchain function when the library component gets mounted.
<qr-code> a great option?There are many QR code libraries on the internet, but they don’t offer all the features that the qr-code library has. Moreover, most QR code generators use HTML canvas or construct an image by limiting vector-based easy scaling support.
The following comparison table details the differences between qr-code vs. qrcode, react-qr-code, and qrcode-with-logos libraries. You can see how qr-code is a good option for generating animated, stylish QR codes for any web app:
| Comparison factor | qr-code |
qrcode |
react-qr-code |
qrcode-with-logos |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Inbuilt animation API and presets | Yes | No | No | No |
| Color customizations | Yes | Basic (only data bit pattern colors) | Basic (only data bit pattern colors) | Basic (only data bit colors and logo border colors) |
| Stylish QR code element shapes (i.e., circles) | Yes | No | No | No |
| Adding logos | Yes | No | No | Yes |
| Rendering method | SVG | Canvas, SVG, and PNG | SVG | Canvas and PNG |
| Integration type | Standard web component | Library, so developers need to create a wrapper component | React component | Library, so developers need to create a wrapper component |
| TypeScript definitions | Yes (from the source) | Yes (external) | Yes (from the source) | Yes (from the source) |
| Error correction level customization | No (hardcoded as H) |
Yes | Yes | Yes |
In this tutorial, we learned how to use the qr-code library to create stylish, animated, SVG-based QR codes using plain HTML code and JavaScript. Also, we used the library in a new React app showing that we can create QR codes on any popular frontend framework/library.
Most QR code libraries generate QR codes on HTML canvas, so we can’t easily implement animations and make them responsive as vector graphics. Meanwhile, some QR code generation modules offer a solution only for a specific frontend framework/library, i.e., react-qr-code only for React.
Moreover, most QR code libraries don’t offer inbuilt animations and modern styles — they typically generate classic QRs with black squares without animations.
The qr-code library offers a frontend-library-agnostic minimal web component that helps you create stylish, animated, SVG-based QR codes. qr-code offers enough features to implement modern animated QR codes based on your design specifications, and that means we can say goodbye to classic, black square-based QR codes!

Discover five practical ways to scale knowledge sharing across engineering teams and reduce onboarding time, bottlenecks, and lost context.

Discover what’s new in The Replay, LogRocket’s newsletter for dev and engineering leaders, in the March 4th issue.

Paige, Jack, Paul, and Noel dig into the biggest shifts reshaping web development right now, from OpenClaw’s foundation move to AI-powered browsers and the growing mental load of agent-driven workflows.

Check out alternatives to the Headless UI library to find unstyled components to optimize your website’s performance without compromising your design.
Would you be interested in joining LogRocket's developer community?
Join LogRocket’s Content Advisory Board. You’ll help inform the type of content we create and get access to exclusive meetups, social accreditation, and swag.
Sign up now