Ever had one of those days? You oversleep, hit traffic, arrive at work to a slew of meetings, and realize you forgot your lunch. It’s frustrating and inefficient — just like many business processes can be.

If this scenario sounds familiar, it might be time to consider Lean Six Sigma practices.
In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore what Lean Six Sigma is, its guiding principles, and the value it can bring to your organization. We’ll also show you how you can get certified and look at examples of companies that have successfully implemented LSS principles.
Lean Six Sigma is a powerful methodology that aids in optimizing processes, reducing waste, and enhancing efficiency by providing a comprehensive approach to process improvement. It helps streamline operations, minimize defects, and deliver superior customer value.
LSS comprises two main components: Lean manufacturing and Six Sigma.
Originating in Japan in the 1950s and 1960s primarily through the Toyota Production System (TPS), Lean manufacturing focuses on identifying and eliminating waste, continuous improvement, respect for people, and creating value for customers.
Six Sigma was developed by Motorola in the 1980s as a contrast to Lean manufacturing. The term “Six Sigma” refers to a statistical concept that measures process variation. Motorola aimed to improve product quality by reducing defects and variability using a data-driven approach with statistical tools.
When combined, these two methodologies form Lean Six Sigma, which gained popularity in the late 1990s. Since then, it has been widely adopted across various industries worldwide, leading to significant improvements in productivity, customer satisfaction, and cost savings.
Though Lean Six Sigma’s originated in the manufacturing industry, its principles and methodologies have particular relevance to product management in the software/tech industry.
Let’s have a look at how LSS aligns with product management practices and supports efficient product development:
Lean Six Sigma emphasizes understanding customer needs and expectations. In product management, this translates into conducting thorough market research, gathering customer feedback, and driving product development decisions based on what customers need. By aligning with Lean Six Sigma principles, we ensure that our products meet customer requirements and deliver exceptional value.
Lean Six Sigma identifies and eliminates waste, or “muda.” In the realm of product management, waste can take many forms, including excessive documentation, redundant processes, friction-causing procedures, or unnecessary features. Lean Six Sigma helps product teams streamline workflows, optimize resource allocation, and focus on activities that directly contribute to delivering value to our customers.
Lean Six Sigma offers a systematic approach to process improvement. For product managers, this means identifying bottlenecks, removing non-value-added activities, and implementing process improvements to enhance efficiency, reduce lead times, and accelerate time-to-market. Lean Six Sigma methodologies such as value stream mapping and Kaizen can be instrumental here.
The statistical analysis tools of Lean Six Sigma are invaluable for making data-driven decisions. Product managers often use tools like hypothesis testing, control charts, and regression analysis to analyze product performance, identify quality issues, and make informed decisions based on objective data. These tools enable us to drive continuous improvement, reduce defects, and enhance product quality.
Lean Six Sigma promotes a culture of continuous improvement. It encourages organizations to strive for excellence and embrace change. By fostering a mindset of continuous improvement within product management teams, we create an environment where innovation and collaboration thrive.
In the world of Lean Six Sigma, practitioners are often categorized by the color of their “belts,” much like in martial arts. These belts represent different levels of expertise and responsibility within the Lean Six Sigma methodology.
It’s important to note that moving up from one belt level to another requires not only additional training but also practical application through project work. This ensures that you don’t just understand the theory behind Lean Six Sigma, but can also apply it effectively to drive improvements.
Let’s break down what each belt signifies:
A White Belt holder has a basic understanding of Lean Six Sigma principles. They can participate in project teams and assist with local problem-solving within their immediate work area.
Yellow Belt holders have a more detailed understanding of Lean Six Sigma. They can participate as project team members and may lead small projects within their own functional area.
Green Belts have undergone formal training in Lean Six Sigma methodologies and tools. They are capable of leading projects within their own function or department.
Green Belts typically spend part of their time on process improvement teams, but their primary job function would not be process improvement.
Black Belts are experts in Lean Six Sigma who lead cross-functional projects. They have extensive training and experience in applying Lean Six Sigma methodologies across various situations.
Black Belts usually perform process improvement as their primary job function.
Master Black Belts are at the top tier of Lean Six Sigma expertise. They train and mentor Black Belts and Green Belts while also leading strategic projects that affect the entire organization.
The steps to obtain a Lean Six Sigma certification are as follows:
First, determine the level of certification you want to achieve — for example, Green Belt or Black Belt. Your decision should be based on your objectives and how involved you want to be in process improvement initiatives.
Next, enroll in a reputable Lean Six Sigma certification training program. Look for a program that offers comprehensive coursework, interactive learning experiences, and real-world case studies. This will deepen your understanding and practical application of Lean Six Sigma principles.
After you’ve learned the principles, it’s time to apply them. You can do this by participating in improvement projects within your organization or engaging in simulated projects provided by the certification program. This hands-on experience is vital for cementing your understanding of Lean Six Sigma methodologies and honing your problem-solving skills.
Set aside dedicated time to review and reinforce what you’ve learned during the training program. Practice with sample exam questions and seek additional resources to strengthen your comprehension and readiness for the certification exam.
Finally, schedule and complete the Lean Six Sigma certification exam. This exam evaluates your understanding of Lean Six Sigma concepts, methodologies, and their application in real-world scenarios.
Once you’ve successfully passed the exam, you can proudly call yourself a certified Lean Six Sigma product manager!
Let’s look at a couple of notable examples of how adopting Lean Six Sigma principles can benefit SaaS companies by improving operational efficiency, enhancing customer experience, driving growth, and increasing competitive advantage:
During the COVID-19 pandemic, Zoom, a leading provider of video-first unified communications, experienced a dramatic increase in demand. In fact, it reported a 30-fold rise in daily meeting participants within just four months. The number of customers with more than 10 employees also rose by 354 percent compared to the previous year.
In its enterprise market segment, which serves customers through distributors and partners, new orders saw a fivefold increase. Consequently, Zoom faced challenges in processing and tracking channel orders due to reliance on manual processes involving email and spreadsheets.
To address these challenges, Zoom implemented an order tracking and management solution. However, this still required staff to handle each order six or more times — including liaising with sales teams for quotes and approvals and coordinating with the provisioning team for new accounts.
This led Zoom to design an automated system that triggers workflows whenever a new order is entered — which, impressively, took only three weeks to build. This streamlined interactions between order tracking and management solutions.
Zoom’s actions aligned with several Lean Six Sigma principles:
Myndshft offers software that helps healthcare providers determine whether prior authorization is required from patients’ insurance companies for specific services or treatments. Recognizing the importance of successful onboarding experiences for customer retention, Myndshft conducts extensive one-on-one meetings with customers during their initial two weeks of adoption.
Despite providing high-level customer support, Myndshft sought a solution to resolve customer issues more quickly while maintaining patient confidentiality. It adopted LogRocket as an analytics solution to enhance their customer onboarding experiences by delivering smoother service more quickly.
Myndshft’s actions align with several Lean Six Sigma principles:
Lean Six Sigma is a powerful methodology that aims to improve processes, reduce waste, and increase efficiency. It merges the principles of Lean Manufacturing and Six Sigma to eliminate unnecessary activities, enhance product quality, and deliver outstanding value to customers.
The principles of Lean Six Sigma align with several key aspects of the PM role such as focusing on customer needs, reducing wasteful practices, optimizing processes, making data-driven decisions, and fostering a culture of continuous improvement.
Pursuing Lean Six Sigma certifications can be highly beneficial for product managers. These certifications equip you with the necessary skills to drive positive change within your organization, lead process improvement projects, optimize operations, and deliver exceptional results.
The path to certification involves setting clear goals for what you want to achieve with the certification, engaging in comprehensive training programs, applying the learned principles through practical projects in your work environment or through simulations provided by the certification program. This is followed by thorough exam preparation and, finally, successfully completing the certification exam. Once you’ve achieved this milestone, you’ll be well-equipped to apply Lean Six Sigma methodologies in your role as a product manager.
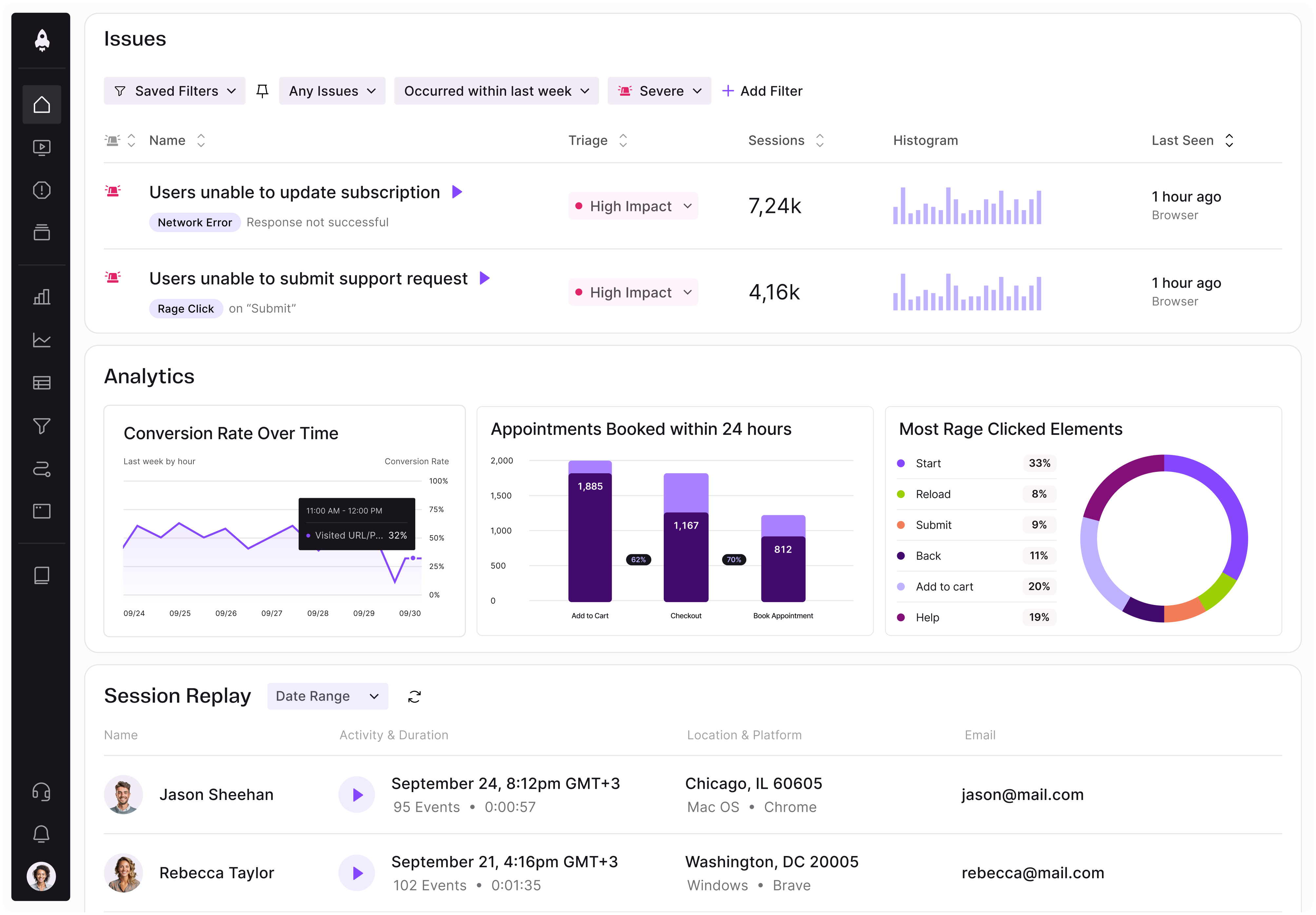
LogRocket identifies friction points in the user experience so you can make informed decisions about product and design changes that must happen to hit your goals.
With LogRocket, you can understand the scope of the issues affecting your product and prioritize the changes that need to be made. LogRocket simplifies workflows by allowing Engineering, Product, UX, and Design teams to work from the same data as you, eliminating any confusion about what needs to be done.
Get your teams on the same page — try LogRocket today.

Rahul Chaudhari covers Amazon’s “customer backwards” approach and how he used it to unlock $500M of value via a homepage redesign.
A practical guide for PMs on using session replay safely. Learn what data to capture, how to mask PII, and balance UX insight with trust.

Maryam Ashoori, VP of Product and Engineering at IBM’s Watsonx platform, talks about the messy reality of enterprise AI deployment.

A product manager’s guide to deciding when automation is enough, when AI adds value, and how to make the tradeoffs intentionally.