
When building modern applications using frontend frameworks such as React and React Native, managing state is always necessary and can be a major headache for developers. Developers need to decide on the right pattern to follow to manage states in their applications.

This article will cover using Legend-State as a state management system for a React application. We’ll build a simple example to look at how Legend-State works, its use cases, and how it differs from other state management tools.
To jump ahead:
The Replay is a weekly newsletter for dev and engineering leaders.
Delivered once a week, it's your curated guide to the most important conversations around frontend dev, emerging AI tools, and the state of modern software.
Legend-State is a new lighting-fast state management library that provides a way to optimize apps for the best performance, scalability, and developer experience. Legend-State is built and maintained by Jay Meistrich. Designed with modern browser features, Legend-State is used by companies such as Legend and Bravely.
Legend-State aims to resolve issues with the performance and workload of developers when trying to manage states in React applications, which are not optimized by default. Legend-State improves app performance by only re-rendering components when necessary, and it allows you to control which states on which the re-render is triggered. Legend-State makes React easier to understand and with it, developers can write less code than the naive, unoptimized React implementation.
There are many state management libraries, each with a unique set of features. Here’s how Legend-State differs from them.
Legend-State’s reactivity makes React apps faster. It minimizes the number of renders and makes sure that each update in a component results in the smallest number of renderings. Making components small can maximize React’s efficiency by requiring state changes to only re-render the bare minimum of components. Each component in the component tree re-renders whenever state updates are passed down the tree via props.
Legend-State’s fine-grained reactivity uses two components to isolate children so that they re-render from changes in their observables without needing to re-render the parent:
Computed: In this component, the children’s component changes don’t affect or re-render the parent component, but the parents’ changes re-render the childrenMemo: Similar to Computed, Memo doesn’t re-render the child component from parent changes. It only re-renders when its observables changeLegend-State is super easy to use and makes use of no boilerplate code. It has no special hooks, higher-order components, functions or contexts, etc. You just need to access the states and your components will automatically update themselves.
Legend-State is super fast, and with only 3Kb in file size, it improves the performance of a website or app. Legend-State is designed to be as efficient as possible and it only re-renders components when there are changes.
Legend-State is unopinionated, allowing teams to declare a state globally or within components. Legend-State creates state objects within React components, then passes them down to children either via props or Context:
import { useObservable } from "@legendapp/state/react"
// via props
const ViaProps = ({ count }) => {
return <div>Count: {count}</div>
}
const App = () => {
const count = useObservable(0)
return <ViaProps count={count} />
}
// via context
const ViaContext = () => {
const count = useContext(StateContext);
return (
<div>
Count: {count}
</div>
)
}
const App = () => {
const count = useObservable(0)
return (
<StateContext.Provider value={count}>
<ViaContext count={count} />
</StateContext.Provider>
)
}
Legend-State has built-in persistence plugins that save and load from local or remote storage. The plugins include local providers for Local Storage on the web and react-native-mmkv in React Native. These plugins have undergone comprehensive testing to ensure their accuracy. Firebase and Firestore remote persistence plugins for both web and React Native are being developed by Legend-State.
Additionally, Legend-State supports TypeScript and can be used in React Native applications to manage state.
Let’s build a simple voting app to understand how Legend-State works. First, let’s create a project with the following code:
npm create-react-app legend-state-app
This will initialize a new React project. Now add cd into legend-state-app and install Legend-State:
npm install @legendapp/state
After running the command above, our Legend-State management library will be installed in our project folder.
Card componentWe are going to create a Card.js file inside src/components to display each player’s information. This will show us the player’s name, nationality, country, and a button to increase and decrease votes:
import React from "react";
import { Computed } from '@legendapp/state/react';
const Card = (props) => {
const { player, increasevoteCount, decreaseVoteCount } = props
return (
<section className="container">
<h1 className="text">{player.name}</h1>
<h3 className="normal-text">{player.country}</h3>
<p className="normal-text">{player.club}</p>
<button className="button" onClick={() => increasevoteCount(player.id)}>Vote</button>
<button className="button normal" onClick={() => decreaseVoteCount(player.id)}>Unvote</button>
</section>
)
});
export default Card;
The values of the player, and the increasevoteCountand decreaseVoteCount functions will come from the parent component: App.js as props. When you click on the Vote button, it calls increasevoteCount and passes the ID of the player with it, which it also does when you click on the decreaseVoteCount.
Now, let’s use observables to define our state, which will contain all the states and their functions used in our application. Observables are objects that hold any variable (primitives, arrays, deeply nested objects, functions) that can be updated in the event of a state change.
There are different ways React uses observables:
enableLegendStateReact() function to automatically extract the state as a separate, memorized component with its tracking contextobserver HOC to make the component automatically monitor the accessed observables for changesuseSelector hook to compute a value automatically monitors any accessed observables and only re-renders the results if the computed value changesWe will render observables directly using the enableLegendStateReact() for this project. Update our App.js file with the following code:
import React from 'react';
import { enableLegendStateReact, Memo } from "@legendapp/state/react"
import { observable } from '@legendapp/state';
enableLegendStateReact();
const state = observable({
players: [
{id: 1, name: 'Messi', club: 'Paris', country: 'ARG',},
{id: 2, name: 'Ronaldo', club: 'Manchester', country: 'POR'}
],
voteForM: 0,
voteForC: 0
})
We created a state using the observable function from the Legend-State library.
Inside the observable function, we created a store that holds an array of player data and a store that keeps tabs on vote-related states, with its initial value set to 0.
To get access to the raw value of the observable, we’ll use the get() function:
function App() {
const playersData = state.players.get();
return (
<section className='App'>
<h2>Vote the Best Football player in the world</h2>
<Memo>
{() => <h1>Messi: {state.voteForM} - {state.voteForC}: Ronaldo</h1>}
</Memo>
<div className='card-container'>
{
playersData.map((player) => (
<div key={player.id} className="card">
<Card
player={player}
increasevoteCount={player.id === 1 ? voteForMessi : voteForRonaldo}
decreaseVoteCount={player.id === 1 ? unVoteForMessi : unVoteForRonaldo}
/>
</div>
))
}
</div>
</section>
)
export default App;
In the code above, we have a variable playersData which contains the value of the state property of the player. We use the playerData variable to map the player’s array and each player’s data is passed to the Card components.
We also see that the functions increasevoteCount and decreaseVoteCount are passed on to the Card component and used to increase and decrease each player’s votes. So when we click on the vote or unvote button in the Card component, it passes the players’ id value to App.js.
To increase and decrease the vote, we have to define functions to handle the operation:
// increase player vote const voteForMessi = () => state.voteForM.set(state.voteForM.get() + 1) const voteForRonaldo = () => state.voteForC.set(state.voteForC.get() + 1) // decrease player vote const unVoteForMessi = () => state.voteForM.set(state.voteForM.get() - 1) const unVoteForRonaldo = () => state.voteForC.set(state.voteForC.get() - 1)
The function gets each player’s current value and either increase or decreases the voting field. Legend-State observables use the set() function to modify the state. There are also other functions:
assign(): This function is also used to modify the observables. It is similar to the set() function, but it cannot be called on a primitive:
const state = observable({ vote: 0})
state.vote.set(1)
// ✅ Calling set on a primitive works.
state.assign({ vote: 2 })
// ✅ Calling assign on an object works.
state.vote.assign({ vote: 3 })
// ❌ Error. Cannot call assign on a primitive.
delete(): This function is used to delete a key from an objectpeek(): This function is similar to the get() function, but it doesn’t automatically track the value. It is useful when you don’t want the component or observing context to update when the value changesAt this point, our application doesn’t look very nice. So, let’s add a few styles to change the look of the application. Update index.css to the following code:
*{
padding: 0;
margin: 0;
box-sizing: border-box;
}
.container{
display: block;
padding: 10px;
width: 100%;
max-width: 50rem;
color: rgb(17 24 39 );
border-radius: 0.5rem;
box-shadow: 0 4px 6px -1px rgb(0 0 0 / 0.1), 0 2px 4px -2px rgb(0 0 0 / 0.1);
}
.text{
font-size: 1.5rem;
line-height: 2rem;
font-weight: 700;
letter-spacing: -0.025em;
color: rgb(17 24 39);
}
.normal-text{
font-weight: 500;
color: rgb(55 65 81 );
}
.button{
display: block;
width: 100%;
align-items: center;
padding: 0.75rem 0;
font-weight: 700;
font-size: 1rem;
line-height: 1.25rem;
border-radius: 0.5rem;
border: none;
margin: 6px 0;
color: rgb(255 255 255);
background-color: rgb(29 78 216);
}
.button.normal{
background-color: rgb(255 255 255);
color: rgb(29 78 216);
border: 1px solid rgb(29 78 216);
}
.button.normal:hover{
color: rgb(255 255 255);
background-color: rgb(29 78 216);
}
.button:hover{
background-color: rgb(21, 57, 156);
}
.App {
text-align: center;
padding: 10px;
line-height: 2rem;
}
.card{
margin: 6px 0;
}
@media (min-width: 768px) {
.card-container{
width: 100%;
display: flex;
align-items: center;
justify-content: center;
margin: 20px;
gap: 20px;
}
.card{
margin: 6px 0;
width: 30%;
}
}
Once we run npm start to start the application, this is what we get:
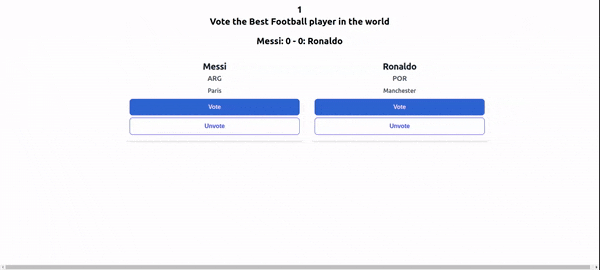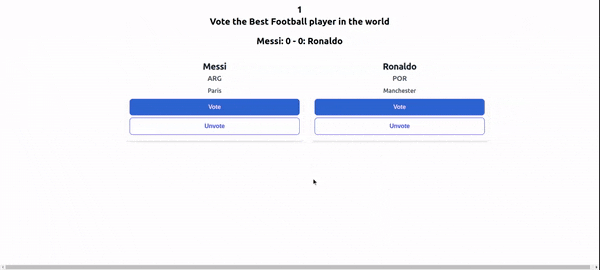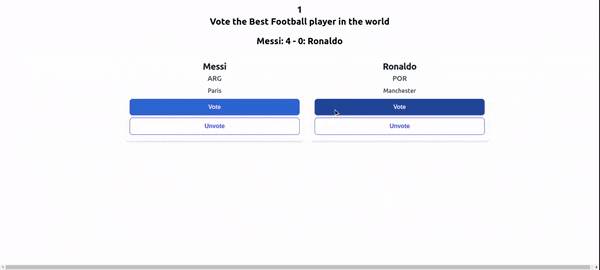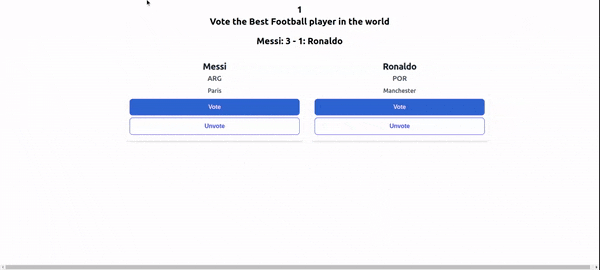
Legend-State provides a plugin that is used to persist states, which prevents data loss. Legend-State uses persistObservable to persist data from an application by storing it in local storage or remote storage. This way, the state does not reset whether we reload our page or close it.
To store our data in local storage, we will import the plugin and configure it globally:
// App.js
import { configureObservablePersistence, persistObservable } from '@legendapp/state/persist';
import { ObservablePersistLocalStorage } from '@legendapp/state/local-storage';
configureObservablePersistence({
// Use Local Storage on web
persistLocal: ObservablePersistLocalStorage
});
Now, let’s call persistObservable for each observable we want to persist:
persistObservable(state.voteForC, {
local: 'voteC',
})
persistObservable(state.voteForM, {
local: 'voteM',
})
Above, we persisted the value of the state.voteForC and state.voteForM. The local storage key is assigned a unique name. With this in place, we don’t lose any new data when voting and refreshing the page.
Legend-State also provides hooks that are used within a React component, just like the normal useState hook and useEffect hook. But this time, it only renders the observable when necessary. We’ll use some of this hook to make an API request:
import {useObservable, useComputed, useObserve, Show } from '@legendapp/state/react'
const user = useObservable(() =>
fetch("https://randomuser.me/api/").then(response => response.json())
)
Here, we used the useObservable hook to hold and make an API request using the fetch function, which gets information about a random user. The useObservable hook is also helpful for holding multiple values locally in a state or when the state is particular to the lifespan of the component:
const details = useComputed(() => {
const u = user.results.get()
return u ? `${u[0].name.first} ${u[0].gender} ${u[0].location.country}` : "";
});
useObserve(() => console.log(details.get()))
We used useComputed to return the name, gender, and country of the user. The useComputed hook is used to compute values based on many observables and will be updated if one of them changes because it keeps track of the observables accessed while computing automatically.
useObserve is similar to useEffect. It takes action only when observables change:
return (
<div>
<Show if={userName} else={<div>Loading...</div>}>
<div>
<h1>{userName[0].name.first} {userName[0].name.last}</h1>
<p>{userName[0].location.country}</p>
<h2>{userName[0].email}<h2>
</div>
</Show>
</div>
);
Here, we use the Show component from Legend-State to conditionally render our data. The Show component is used to conditionally render child components based on the if/else props, and when the condition changes, the parent component is not rendered.
In this article, we learned about Legend-State, a state management library for React and React Native applications focused on providing better performance to our applications and a better experience for developers. We created a voting app using Legend-State to manage the state and detailed how Legend-State differs from other state managers. Have fun using Legend-State for your next React or React Native application!
Install LogRocket via npm or script tag. LogRocket.init() must be called client-side, not
server-side
$ npm i --save logrocket
// Code:
import LogRocket from 'logrocket';
LogRocket.init('app/id');
// Add to your HTML:
<script src="https://cdn.lr-ingest.com/LogRocket.min.js"></script>
<script>window.LogRocket && window.LogRocket.init('app/id');</script>

Paige, Jack, Paul, and Noel dig into the biggest shifts reshaping web development right now, from OpenClaw’s foundation move to AI-powered browsers and the growing mental load of agent-driven workflows.

Discover five practical ways to scale knowledge sharing across engineering teams and reduce onboarding time, bottlenecks, and lost context.

Check out alternatives to the Headless UI library to find unstyled components to optimize your website’s performance without compromising your design.
A practical guide to building a fully local RAG system using small language models for secure, privacy-first enterprise AI without relying on cloud services.
Hey there, want to help make our blog better?
Join LogRocket’s Content Advisory Board. You’ll help inform the type of content we create and get access to exclusive meetups, social accreditation, and swag.
Sign up now