In today’s rapidly evolving digital landscape, the pressure on product leaders to build superior products is on the rise. User expectations for modern digital products are continuously increasing as well. Seamless user experience, smooth application performance, and high reliability are today’s baseline. But there is a deeper layer to this.

Users seek more and more easy access to data that provides them with meaningful insights and helps them make better data-informed decisions. This is where embedded analytics comes into play.
In this article you will learn what embedded analytics are, their key benefits, and the common challenges for implementing them within your product.
Embedded analytics enables users to gain data insights directly within the application they are using. This is done by providing data dashboards or comprehensive reporting functionalities to users.
Contrary to the traditional business intelligence (BI), embedded analytics solutions are integrated into the business applications that the users are already using. Essentially, the data analytics tool is an inherent part of the user’s primary application. This improves users’ experience, as the users do not need to login in a separate BI software — they can continue to use the same application they are familiar with.
Embedded analytics solutions have also found their way into news institutions, perhaps without you even realizing it. You have probably already come across websites that seamlessly embed data analytics solutions.
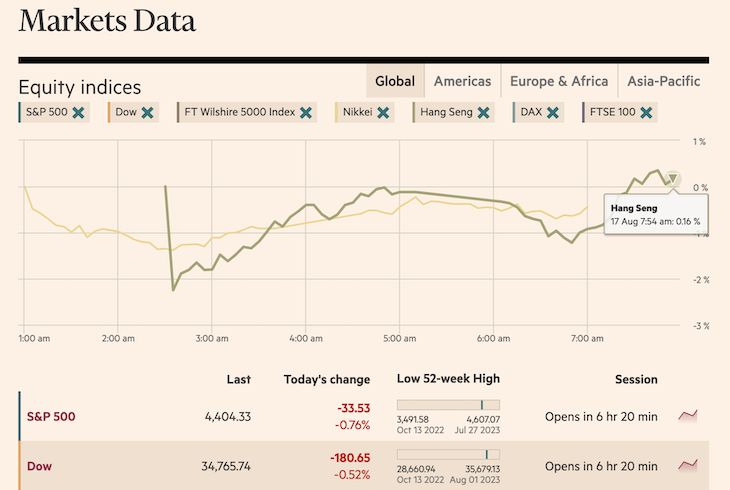
One example is The New York Times, which during the height of the COVID pandemic, employed embedded analytics to present data insights about Coronavirus cases, hospitalizations, and related data within their online articles.
Financial Times is another example. They use data visualizations to present the latest market data.
Importantly, the data analytics reports and visualizations are dynamic — the data presented is up to date, and is also interactive, allowing users for example to filter and explore the data themselves.
In essence, embedded analytics have quietly transformed the way websites or applications present and engage with complex information, enhancing the reader’s understanding and interaction with the content:
This embedded analytics trend opens up new opportunities for product managers. The direct integration of analytics into your product offers a powerful way to enhance the value proposition of your product and elevate the experience of your users.
However, it’s important to recognize that while this technology solution is undoubtedly beneficial, it alone shouldn’t be the primary driver. The users and their experience should remain at the heart of the solution.
The role of the product manager remains centered on the user. This involves understanding user needs and expectations, the data insights they need, the decisions they confront, and understanding how data-driven insights can facilitate their decision-making process.
Once these insights are researched, you can consider embedding data insights into the product interface to empower users with real-time, actionable information. This goal of choosing embedded analytics as a solution should be to bridge the gap between raw data and meaningful insights, thus empowering users to make well-informed decisions within the natural rhythm of their tasks.
The advantages of incorporating embedded analytics are multifaceted, benefiting both users and the overall business. Embedded analytics aid:
Leveraging data analytics, visualizing information, and generating insightful reports gives users valuable advantages. Embedded analytics bridges the gap between data collection and analysis, providing quick access to valuable insights. Users can promptly identify trends, patterns, and anomalies, and make timely actions and decisions informed by data.
While leveraging analytics alone is a great advantage, embedding these analytics within the core business application takes it a step further. As this analytics is “embedded,” it’s integrated directly into the primary user interface. This allows users to effortlessly access real-time information without the need to toggle between disparate tools and without interrupting their workflow.
Embedded analytics can bring a fresh look to your product, making it even more valuable and bringing a new competitive advantage. Empowering users with actionable insights becomes a compelling draw, attracting both new and retaining existing customers.
Implementing embedded analytics can be a strategic choice to not only improve the product but also become a new revenue stream. For example, the new data-analytics module can be offered as a new add-on to the product with premium features.
While the benefits of implementing embedded analytics are substantial, they do come with some considerations. These are the most common challenges encountered during implementation:
The process of embedding analytics requires technical adjustments within your application. This involves integration with external data providers and analytics components that must smoothly align with your application’s user interface. This technical implementation demands dedicated effort, potentially even affecting your product’s underlying architecture.
Another common challenge is data quality. Embedded analytics heavily rely on accurate and reliable data. If the data used is incomplete, outdated, or inconsistent, the analytics results can be misleading. This damages the user experience and undermines the credibility of the embedded analytics feature. Maintaining data quality requires ongoing effort, such as data validation and ensuring that data sources are up to date.
While embedded analytics can offer valuable insights, they might also introduce a learning curve for users who are not familiar with interpreting data visualization. Balancing the addition of new features without overwhelming users requires careful design and user testing to ensure that the analytics component enhances the product’s value without compromising its usability.
Introducing embedded analytics involves handling new streams of data. Ensuring that the analytics process is compliant with data protection regulations can be challenging. Proper data encryption, access controls, and clear communication about data usage are essential to build and maintain user trust while leveraging the benefits of embedded analytics.
Embedded analytics is not just another product feature. Instead, product managers should view it as a strategic component that has the potential to reshape the product’s strategic trajectory. It can serve as a distinct competitive advantage, open doors to new revenue streams, or attract new and retain existing customers.
Integrating embedded analytics into a product requires a well-thought-out strategy to maximize its benefits and ensure effective implementation. Here are a few key strategies for successfully integrating embedded analytics in your product:
Start the process by establishing clear objectives for embedding analytics within your product.
What are the specific goals and benefits you intend to deliver to your users? What is the strategic significance this solution will bring to your product? What are the types of data insights users require and the decisions they seek to inform? What visualization methods would be comprehensible for them? What is the desired level of interactivity within the visualizations?
Engage in user research, surveys, and feedback sessions to gain a thorough understanding of your target audience’s needs and preferences. Conducting this research is necessary before delving into the implementation.
Once you know that embedded analytics is the way to go and you have a clear goal in mind, you need to select the right analytics tool and platform that aligns with your product’s goals and user requirements.
If you have unique and highly specific requirements that off-the-shelf solutions may not fully meet and the analytics is a big asset for your product, building your own embedded analytics tool can be the way to go. But in most cases, purchasing an existing embedded analytics platform is the right solution, as it significantly reduces development time and is more cost effective.
There are different analytics platforms on the market: Tableau, Sisense, Qlik, Looker, and Yellowfin are just a few.
Before selecting the right tool, it’s important to evaluate a few considerations:
Determine the data visualizations that will best convey insights to your end-users. Explore ways to align dashboard design with your brand identity for a cohesive look and feel.
You can provide users with the ability to personalize their analytics according to their preferences. For example, configurable dashboards, filters, and visualization settings, can be used to empower users to concentrate on the data that they find most important.
Selecting the appropriate visualization techniques predominantly fall within the scope of the UX designer. It should become integrated in the ongoing feature development process, incorporating feature refinement or user testing. However, establishing a set of guiding principles as a baseline can streamline the overall process.
As your product gains access to new data, the potential benefits are accompanied by new security and privacy risks. Security should never be compromised. It’s crucial to ensure that the embedded analytics solution aligns with industry regulations and adheres to best practices in data privacy, security, and compliance.
First, choosing a reliable vendor is crucial. But the commitment to protect data extends within your organization as well. You need to set strict rules for how data is managed, track where the data comes from, who can access it. By following these rules, you make sure that any sensitive information is safely protected.
This careful approach not only keeps your embedded analytics working well but also makes users feel secure and confident.
To enhance your product effectively, start with small steps and refine over time. Instead of overwhelming users with complex data features at once, start with a simple approach and build on it gradually.
This approach allows users to become familiar with the new data tools and gives you the chance to gather feedback for ongoing improvements based on their input.
Integrating product analytics into newly introduced data visualization features is a wise move. It helps you understand how much users are adopting these features, how they are benefiting from the analytics, and where enhancements can be made.
Embedded analytics is not a novel technology, it’s becoming the new norm today. As technology continues to evolve, we are likely to witness new advancements in this area.
One direction involves improved user-friendly interfaces and even more interactive and engaging visualizations. These enhancements are aimed at making data interpretation accessible to everyone, especially non-technical users. Furthermore, with AI playing an increasingly significant role in embedded analytics, users will be empowered to interact with data in an even more intuitive and conversational manner.
Another notable area of development is integration and connectivity. Seamless connectivity is becoming the new norm. Embedded analytics platforms will be easier to integrate with other tools and platforms, fostering an ecosystem where data flows effortlessly.
Given the growing prominence of AI in today’s technological landscape, predictive analytics is also on the rise. This entails analytics that not only showcase historical data but also predict trends and provide valuable insights into the future. Users will gain the ability to anticipate future trends, identify potential issues, and receive actionable recommendations based on data analysis.
Embedded analytics is changing how we use data. It goes beyond being just a feature – it’s a new way of making data valuable for users. As technology keeps evolving, embedded analytics will continue to enhance user experiences by providing accessible and intuitive data-driven insights.
For product managers, this trend requires finding a balance between technical feasibility and the user needs. By embracing embedded analytics, product managers can make products smarter, more competitive and most importantly, can help users make better data-informed decisions.
Featured image source: IconScout
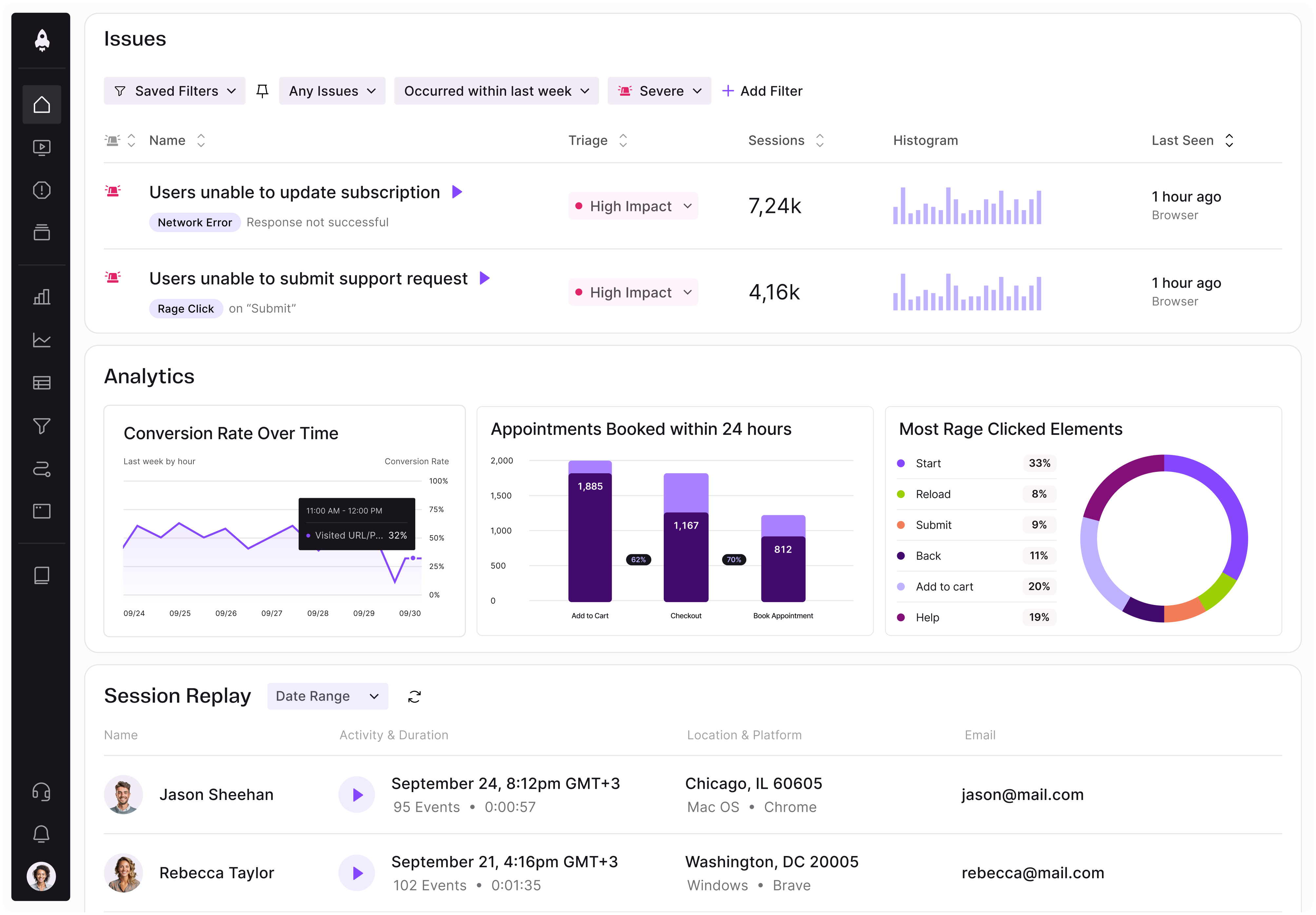
LogRocket identifies friction points in the user experience so you can make informed decisions about product and design changes that must happen to hit your goals.
With LogRocket, you can understand the scope of the issues affecting your product and prioritize the changes that need to be made. LogRocket simplifies workflows by allowing Engineering, Product, UX, and Design teams to work from the same data as you, eliminating any confusion about what needs to be done.
Get your teams on the same page — try LogRocket today.

Rahul Chaudhari covers Amazon’s “customer backwards” approach and how he used it to unlock $500M of value via a homepage redesign.
A practical guide for PMs on using session replay safely. Learn what data to capture, how to mask PII, and balance UX insight with trust.

Maryam Ashoori, VP of Product and Engineering at IBM’s Watsonx platform, talks about the messy reality of enterprise AI deployment.

A product manager’s guide to deciding when automation is enough, when AI adds value, and how to make the tradeoffs intentionally.