
The old buttons in Flutter are sufficient to serve most of your mobile development needs, but they can be difficult to use, especially when your app calls for custom theming.

A “new ‘universe’ of Material buttons” was made available with the release of Flutter v1.22 in October 2020. If you haven’t had time to check them out yet, I highly recommend doing so because using the new Flutter buttons can save you a lot of time when building mobile apps.
In this tutorial, we’ll introduce you to the new Material button components available in Flutter, go over some examples of how to use them, and demonstrate how the new Flutter buttons improve the developer experience.
We’ll cover the following with detailed explanations and examples:
The Replay is a weekly newsletter for dev and engineering leaders.
Delivered once a week, it's your curated guide to the most important conversations around frontend dev, emerging AI tools, and the state of modern software.
Rather than evolve the existing button classes, the Flutter created all-new button widgets and themes to replace them. The names of the new Flutter buttons are meant to sync Flutter with the Material Design spec. This means the buttons are up to date with new guidelines and also have new styles.
Put simply, the new buttons available in Flutter are are easier to understand and use. They make it simple to define common themes at the app and widget levels. For example, you can change the text color of all the TextButtons used in the app without affecting the text color of Elevatedbutton or OutlinedButton. You can also set the text color of OutlinedButton in multiple states, such as hover and focused.
Here are the new Material buttons introduced with Flutter v1.22:
TextButtonYou can simply use TextButton at a place such as AppBar to close the screen, inside the dialog for closing it, etc. You’ll want to avoid placing this button inside any scrollable list for obvious UI/UX reasons.
ElevatedButtonElevatedButton is best suited in places where the app requires direct action from the user, such as confirming an order or booking a ticket. Since it’s already elevated, you should avoid putting it over any other elevated widgets, such as cards.
OutlinedButtonIn many ways, OutlinedButton is a mixture of TextButton and ElevatedButton. It’s a TextButton if you remove the border and gives the impression of ElevatedButton if you hover or press over it. This button is a medium-emphasis button meaning it can be used at the place where the action is important but not crucial.
Here is the minimal code to implement the new Material buttons in your Flutter app:
Column(
mainAxisAlignment: MainAxisAlignment.center,
children: [
TextButton(
onPressed: () {},
child: Text('TextButton'),
),
SizedBox(
height: 20,
),
ElevatedButton(
onPressed: () {},
child: Text('ElevatedButton'),
),
SizedBox(
height: 20,
),
OutlinedButton(
onPressed: () {},
child: Text('OutlinedButton'),
)
],
),
Each new Material button in Flutter has its own theme rather than specifying a common theme that applies to other buttons as well. This gives you more flexibility than the old Flutter buttons — namely, FlatButton, RaisedButton, and OutlineButton.
The table below shows the old widgets and themes associated with the previous iteration of Flutter buttons alongside the new widgets and themes that are designed to replace them.
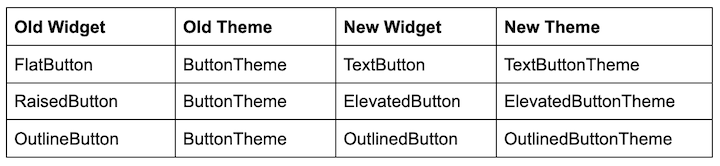
One subtle but important change to note: OutlineButton is now OutlinedButton (there is d added to the name). If you’re not careful, you may miss this change and end up writing all your code with the old button (full disclosure: this happened to me when developing the examples for this tutorial).
Speaking of which, let’s dive into some practical examples to see the new Flutter buttons in action.
To show how the new Material buttons work compared to the old Flutter buttons, we’ll create a practical demonstration of each.
The following code represents the old FlatButton vs. the new TextButton released with Flutter v1.22:
Column(
mainAxisAlignment: MainAxisAlignment.center,
children: [
FlatButton(
onPressed: () {},
child: Text('FlatButton (Old)'),
),
SizedBox(
height: 40,
),
TextButton(onPressed: () {}, child: Text('TextButton (New)'))
],
)
This generates the following output:

The first noticeable difference is that the new TextButton uses the theme colors at the app level without any extra effort. For this app, the primarySwatch is set to Colors.teal and TextButton automatically set it as the text color while FlatButton fails to do so.
primarySwatch: Colors.teal,
If you look carefully, you’ll see that on the click of a TextButton, the ripple effect is much smoother than that of FlatButton.
In the following example, we’ll attempt to change the color of the text inside the button:

Column(
mainAxisAlignment: MainAxisAlignment.center,
children: [
FlatButton(
onPressed: () {},
textColor: Colors.pink,
child: Text(
'FlatButton (Old)',
style: TextStyle(fontSize: 30),
),
),
SizedBox(
height: 40,
),
TextButton(
onPressed: () {},
style: TextButton.styleFrom(
primary: Colors.pink,
),
child: Text(
'TextButton (New)',
style: TextStyle(fontSize: 30),
),
)
],
)
Both buttons produce the same output, but the way color is assigned is different. For FlatButton, the color is given to the textColor parameter. TextButton has a style property that accepts the ButtonStyle class, which can hold a button’s defaults. TextButton.styleFrom is a convenient method to return ButtonStyle with the ability to override the defaults. primary is used to actually set the color of the text.
Having a style property for the button provides an experience similar to that of writing style for the Text widget.
At this point, you might be thinking why do we even need this tricky style property if we can do the same things with simple parameters in FlatButton itself? Imagine a case where you are required to do a lot of customization for a button to suit new custom branding. That’s where it comes in handy.
Let’s say you want to change the text color of a button, but only when it’s pressed. Here’s how you would do that:
TextButton(
onPressed: () {},
style: ButtonStyle(
foregroundColor: MaterialStateProperty.resolveWith<Color>(
(Set<MaterialState> states) {
if (states.contains(MaterialState.pressed))
return Colors.pink;
return null; // Defer to the widget's default.
}),
),
child: Text(
'TextButton (New)',
style: TextStyle(fontSize: 30),
),
)

The color is given to the foregroundColor parameter, which accepts the MaterialStateProperty. MaterialStateProperty used to define what colors to show based on the different button states, such as pressed, hover, focused, and disabled. This creates a whole new world of possible customizations.
The problem with the old Flutter buttons is that if you try to change the text color for all FlatButtons at the app level, it would change the text color of RaisedButton and OutlineButton as well, like this:
MaterialApp(
title: 'Flutter Demo',
theme: ThemeData(
primarySwatch: Colors.teal,
brightness: Brightness.dark,
buttonTheme: ButtonThemeData(textTheme: ButtonTextTheme.accent),
),
home: OldButtons(),
debugShowCheckedModeBanner: false,
);

With the new Flutter update, we now have more control over the button defaults at the app level. Using the same example, here’s how to change the text color of TextButton without affecting other buttons in Flutter v1.22:
MaterialApp(
title: 'Flutter Demo',
theme: ThemeData(
primarySwatch: Colors.teal,
brightness: Brightness.dark,
textButtonTheme: TextButtonThemeData(
style: TextButton.styleFrom(primary: Colors.red)),
),
home: NewButtons(),
debugShowCheckedModeBanner: false,
);
As you can see, we just want a different color for TextButton and we have a dedicated property, textButtonTheme, to do just that.
The new buttons in Flutter v.122 can save you a ton of time so you can focus on developing your app rather than spend time finding fixes for what should be simple solutions. In its latest update, Flutter proactively addressed many of the common challenges associated with the old Flutter buttons. Kudos to the Flutter team and community!
The old Flutter buttons still work for simpler use cases, but who knows for how long? It’s always a good practice to get your hands dirty on new features as they’re released, especially if it’s designed to eventually replace older features.
Install LogRocket via npm or script tag. LogRocket.init() must be called client-side, not
server-side
$ npm i --save logrocket
// Code:
import LogRocket from 'logrocket';
LogRocket.init('app/id');
// Add to your HTML:
<script src="https://cdn.lr-ingest.com/LogRocket.min.js"></script>
<script>window.LogRocket && window.LogRocket.init('app/id');</script>

Solve coordination problems in Islands architecture using event-driven patterns instead of localStorage polling.

Signal Forms in Angular 21 replace FormGroup pain and ControlValueAccessor complexity with a cleaner, reactive model built on signals.

Discover what’s new in The Replay, LogRocket’s newsletter for dev and engineering leaders, in the February 25th issue.

Explore how the Universal Commerce Protocol (UCP) allows AI agents to connect with merchants, handle checkout sessions, and securely process payments in real-world e-commerce flows.
Hey there, want to help make our blog better?
Join LogRocket’s Content Advisory Board. You’ll help inform the type of content we create and get access to exclusive meetups, social accreditation, and swag.
Sign up now
One Reply to "New Material buttons in Flutter"
what about the design of the disabled button?