The web sets no limitations or restrictions on the channels through which we can present and display content or the level of interactivity and unique experiences we can integrate into our applications.

As developers, we can define how users experience the web by utilizing the many tools and technologies available, ensuring that users experience the uniqueness and beauty of the web.
One common way of spicing up the web is adding animations and transitions to applications, like a background color that changes when a user hovers over a button or blog cards sliding in from the left and right as a user scrolls down a page. These simple transitions can distinguish between a plain experience and a vibrant one.
Beyond using third-party tools like Animate.css, Animsta, GSAP, or plain old CSS, we can leverage a browser API called the View Transition API to create stunning and eye-catching animations and transitions. In this article, we will learn how the API works and explore a demo.
Jump ahead:
The View Transitions API, formally known as the Shared Element Transitions API, is an API for creating transitions and animations in single-page animations (SPA) with ease and minimal effort. It is restricted to SPAs because those are the only application it currently supports.
The API gives us control over how to define animations and transitions. We can use the default animation properties supported by browsers or create custom effects.
Also, the API automatically transitions the size and position of an element for us. It tracks and calculates the changes between the before and after states of these properties and adds appropriate transitions to them.
At the time of writing, the View Transitions API is only available in Chrome v104+ and Canary. To activate it, first, navigate to chrome://flags/. Then, enable the Experimental Web Platform features and viewTransition API for navigations.
The magic of how the View Transitions API works happens behind the scenes. The browser takes a screenshot of the current state of a page and handles the transition as the page shifts to another state. The state change could be an element moving from one position to another or page navigation, among others.
The browser updates the DOM and applies the necessary logic needed to animate between states. Then, the browser applies a cross-fade as the default transition between the previous and current states.
When the API is active, it constructs a pseudo-element tree like this:
::view-transition
└─ ::view-transition-group(root)
└─ ::view-transition-image-pair(root)
├─ ::view-transition-old(root)
└─ ::view-transition-new(root)
Let’s breakdown the pseudo-elements in the code snippet:
::view-transition: The container element for other pseudo-elements::view-transition-group: Responsible for animating the size and position between the two states::view-transition-image-pair: Holds the screenshot of the old and new states::view-transition-old(root): Holds the screenshot of the previous state::view-transition-new(root): Holds the representation of the new stateThe previous state animates from opacity: 1 to opacity: 0, while the new state goes from opacity: 0 to opacity: 1, creating the cross-fade. The animation is done with CSS animations, meaning we can customize them with CSS:
::view-transition-old(root),
::view-transition-new(root) {
animation-duration: 5s;
}
We can also set up even more complex animation customizations if needed:
//language: CSS
@keyframes slide-from-right {
from { transform: translateX(30px); }
}
@keyframes slide-to-left {
to { transform: translateX(-30px); }
}
::view-transition-old(root) {
animation: 300ms cubic-bezier(0.4, 0, 0.2, 1) both slide-to-left;
}
::view-transition-new(root) {
animation: 300ms cubic-bezier(0.4, 0, 0.2, 1) both slide-from-right;
}
We can use the default cross-fade transition or set up even more complex ones that fit our taste.
A great thing about this API is that the browser does all the heavy lifting of tracking and calculating the changes between states and handles the transitions in a highly performant manner.
Let’s create a simple demo app to see how the View Transitions API works in practice. We’ll create this demo with basic HTML, CSS, and JavaScript.
It’s a to-do app that consists of two actions of tasks: Not Done and Done. The tasks that are undone come with a clickable button to mark them as done.
The GIF below shows the UI and functionality of the app. Take note of how a transition effect takes place as the tasks move from one section to another:
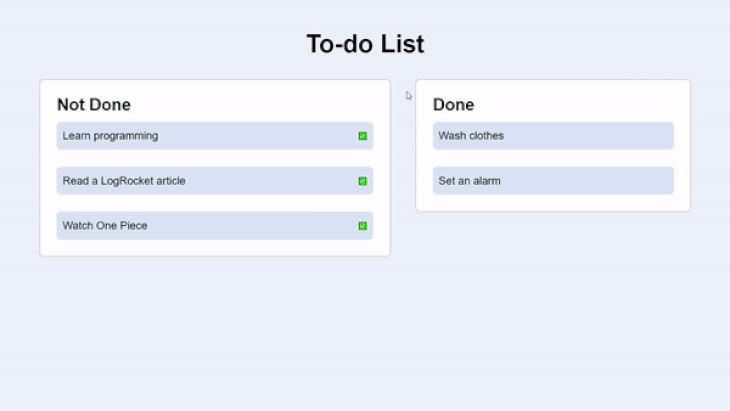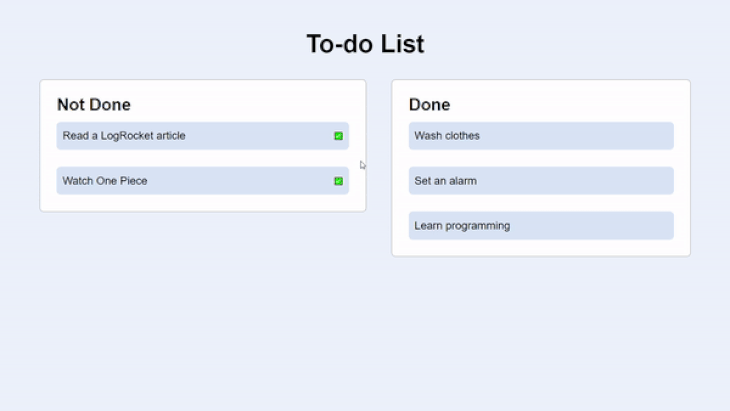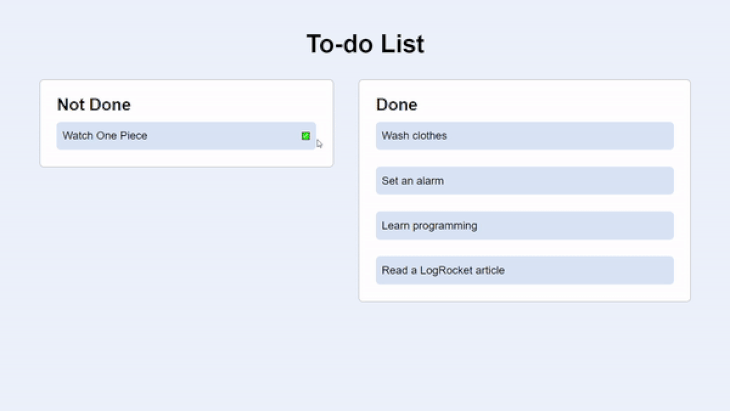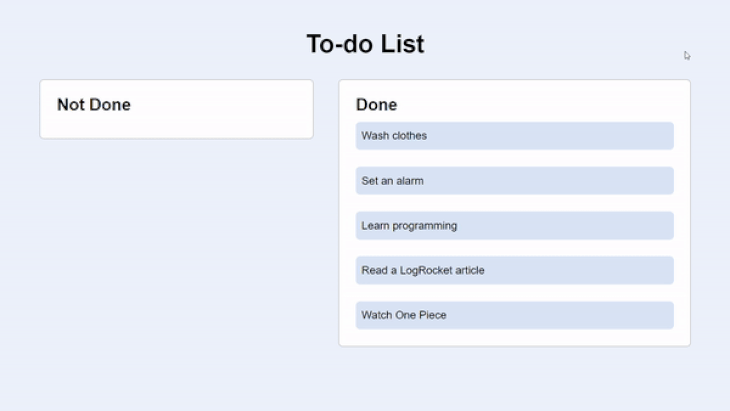
Here’s a snapshot of the HTML:
<div class="grid">
<article class="col">
<h2>Not Done</h2>
<ul id="list-not-done">
<li>
<div class="title">Learn programming</div>
<button onclick="isTaskComplete(true)">✅</button>
</li>
<li>
<div class="title">Read a LogRocket article</div>
<button onclick="isTaskComplete(true)">✅</button>
</li>
<li>
<div class="title">Watch One Piece</div>
<button onclick="isTaskComplete(true)">✅</button>
</li>
</ul>
</article>
<article class="col">
<h2>Done</h2>
<ul id="list-done">
<li>Wash clothes</li>
<li>Set an alarm</li>
</ul>
</article>
</div>
In the code above, we pass an isTaskComplete function to the click events of the buttons. We’ll learn more about what isTaskComplete does next.
Now, let’s set up the JavaScript aspect of the demo and explore what the isTaskComplete function does:
async function isTaskComplete(taskComplete) {
const task = this.window.event.target.closest("li");
// Get the id of the target list
const destination = document.getElementById(
`list-${taskComplete ? "done" : "not-done"}`
);
// We'll use this class to hide the button when a task is done
task.classList.add("task-done");
if (document.createDocumentTransition) {
const taskTransition = document.createDocumentTransition();
// Activate the animation
await taskTransition.start(() => destination.appendChild(task));
} else {
destination.appendChild(task);
}
}
Let’s break down the code above. First, the isTaskComplete function takes in a Boolean as an argument. From there, we initialized a task variable that contains the li closest to where the event occurred.
The value of the destination variable changes based on the state of the taskComplete. When taskComplete is true, the destination is list-done. However, when taskComplete is false, the destination is list-not-done.
We also added a task-done class to the task to hide the button when a task is marked as completed. In addition, we checked if the browser supports the View Transitions API with the if statement. If it doesn’t, we create a taskTransition instance using the createDocumentTransition method to trigger the transition using the start method.
If the browser doesn’t support the View Transitions API, we append the task directly without adding any transition to the change in state from one position to another.
Here’s the task-done class we added. It is responsible for hiding a task’s button:
.task-done button {
visibility: hidden;
}
This implementation sheds some light on how the View Transitions API works.
The View Transitions API opens up a new frontier of possibilities regarding the unique and pleasing experiences we can bring to the web. As great as it is, it is important to remember that, as of this writing, it is still in beta. So, the API is subject to change at any moment. However, that won’t stop us from experimenting and learning about it!
Here are some great examples, demos, and implementations of the View Transitions API that you should check out: Geoff Rich built this fruit data app with SvelteKit and wrote an article about it, Maxi Ferreira made a movie app with Astro and explained how he achieved this, and Jake Archibald created a video playlist app, and there’s a video on YouTube.
As web frontends get increasingly complex, resource-greedy features demand more and more from the browser. If you’re interested in monitoring and tracking client-side CPU usage, memory usage, and more for all of your users in production, try LogRocket.
LogRocket lets you replay user sessions, eliminating guesswork around why bugs happen by showing exactly what users experienced. It captures console logs, errors, network requests, and pixel-perfect DOM recordings — compatible with all frameworks.
LogRocket's Galileo AI watches sessions for you, instantly identifying and explaining user struggles with automated monitoring of your entire product experience.
Modernize how you debug web and mobile apps — start monitoring for free.
Would you be interested in joining LogRocket's developer community?
Join LogRocket’s Content Advisory Board. You’ll help inform the type of content we create and get access to exclusive meetups, social accreditation, and swag.
Sign up now
A breakdown of the wrapper and container CSS classes, how they’re used in real-world code, and when it makes sense to use one over the other.

This guide walks you through creating a web UI for an AI agent that browses, clicks, and extracts info from websites powered by Stagehand and Gemini.

This guide explores how to use Anthropic’s Claude 4 models, including Opus 4 and Sonnet 4, to build AI-powered applications.

Which AI frontend dev tool reigns supreme in July 2025? Check out our power rankings and use our interactive comparison tool to find out.