Experience design is becoming an essential component of modern product, system, and service offerings in an effort to provide users with memorable and positive interactions with products, systems and services. A well-planned experience can increase customer satisfaction, loyalty, and ultimately, business success.
In this article, we delve deep into experience design. We will investigate its key elements and strategies for crafting memorable experiences for users. Additionally, we’ll discuss the role of user research in understanding user needs and the techniques available to enhance overall user experiences.
Experience design (commonly referred to as XD or user experience design) is the practice of crafting products, systems, or services with users in mind and designed around their needs, desires and behaviors — with an aim toward providing them with meaningful experiences while adding value and delighting users. This often requires understanding user needs, desires and behaviors before designing a solution to fulfill those requirements while meeting or exceeding user expectations.
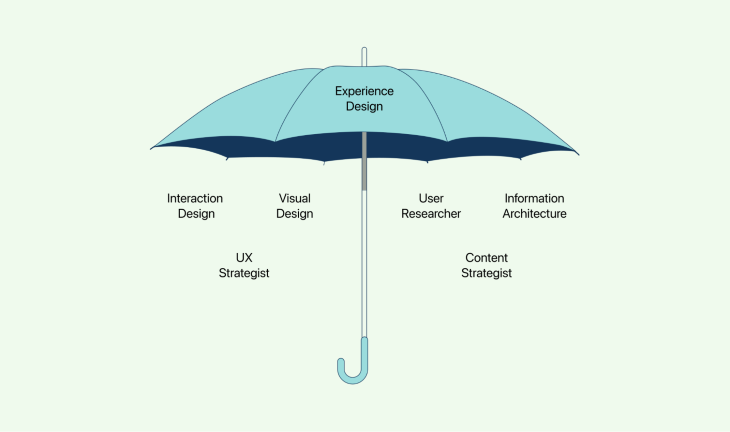
Experience design involves many facets, such as interaction design, visual design, user research, information architecture and more. Its ultimate aim is to produce products or services that not only meet users’ functional requirements but also offer them an enjoyable and memorable experience. User experience is one element of experience design.
Experience design is a multidisciplinary field that encompasses numerous key components and professions. These components play an integral part in creating the user experience. Let’s take a closer look at these components:
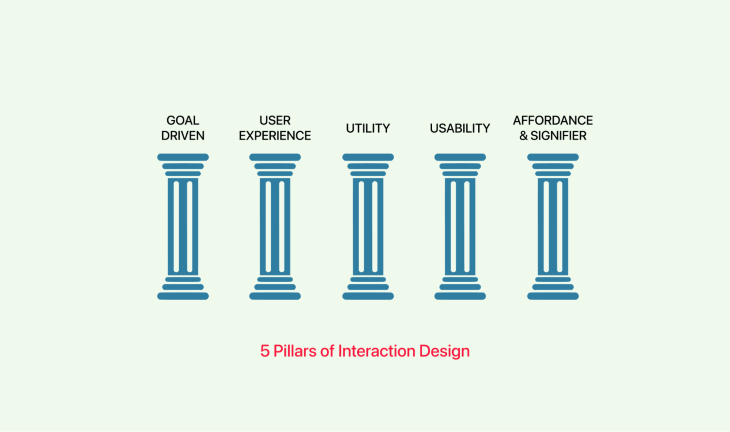
Interaction design is a field that examines how users engage and interact with digital products, systems, or interfaces. It involves creating intuitive yet seamless experiences that help users meet their goals efficiently and effectively.
By carefully crafting such experiences, interaction designers strive to bring humans and technology closer together while forging meaningful bonds between humans and technology that enhance user experiences.
At the core of interaction design is usability: designers take into account user needs, preferences, and behaviors when crafting interfaces that are intuitive and simple for their users. They strive to reduce friction and cognitive load to ensure seamless interactions within digital environments — from button placement to information flows. Every element must be designed to facilitate smooth interactions that create meaningful experiences for users.
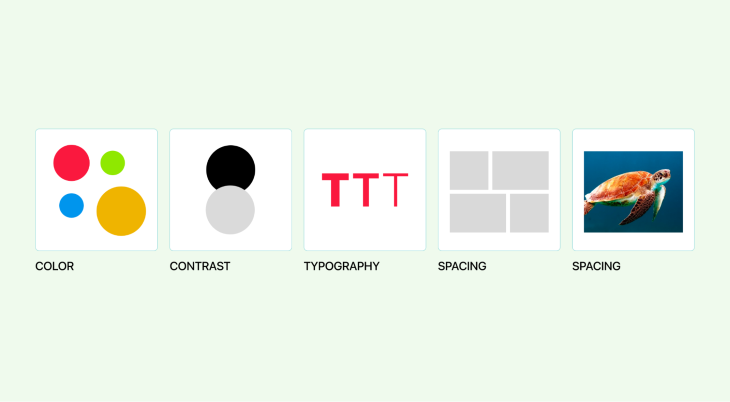
Visual design is an essential element in crafting memorable user experiences. This field involves employing colors, contrast, typography, imagery, spacing, and layout strategically in order to communicate information effectively, stir emotions, and establish brand identities. By harnessing visual elements effectively, designers can engage their target audiences while leading them in engaging the correct message at all times.
Apple’s logo provides an impressive example of visual design. Featuring a minimalist apple silhouette, its simple yet striking aesthetic immediately conveys their values of elegance, simplicity, and innovation — creating brand recognition while building trust among users.
User research is a crucial element of design, providing invaluable insights about user behaviors, preferences, and pain points. By conducting extensive user research, designers can gain a clear picture of their target audience to make more informed decisions and craft user-centric experiences.
Before creating a mobile banking app, conducting user research can reveal users’ needs and challenges. By observing interactions and conducting interviews, designers can uncover pain points such as complex navigation or security concerns. This research gives designers valuable information they can use in the design process, ultimately creating an app that exceeds user expectations.
Information architecture is the practice of organizing information within digital spaces to facilitate intuitive navigation and retrieval of content. This involves creating hierarchies with clear categorizations as well as labeling systems that guide users through complex websites or applications.
Think about a news website where information architecture plays a central role. By organizing news articles into categories like “World,” “Business,” and “Entertainment,” users are easily able to locate and access relevant articles. Furthermore, subcategories within each section such as “Politics” or “Technology” allow even greater granular navigation options for efficient content discovery.
Experience design requires extensive user research and understanding user needs as its foundational pillars. By immersing themselves in user culture, designers can gain invaluable insights that inform the design process and result in experiences that truly engage people.
User research encompasses various techniques:
These methods help gather information about user behaviors, motivations, and pain points. By gathering this data through interviews and usability testing or data analysis methods, user research enables designers to answer crucial questions: who your users are, their goals and interactions with products/services, etc. By seeking answers for such inquiries, researchers gain an in-depth knowledge of their target audiences, enabling them to design experiences tailored specifically towards meeting real user needs.
Understanding user needs is at the core of user-centered design. By empathizing with users, designers can craft experiences that fulfill functional requirements as well as emotional or psychological ones.
Consider, for instance, designing a mobile banking app. Through user research, designers can uncover user pain points such as difficulty managing finances or understanding complex banking terms.
Armed with this knowledge, designers can then use it to streamline user interface design, enhance navigational features and provide clear explanations, empowering users with ease and confidence when managing finances with their app.
Prioritizing user research like this minimizes risk from designing on assumptions or personal biases while assuring that the end product meets user expectations and goals. This ultimately leads to increased user satisfaction, higher engagement levels, and stronger brand loyalty.
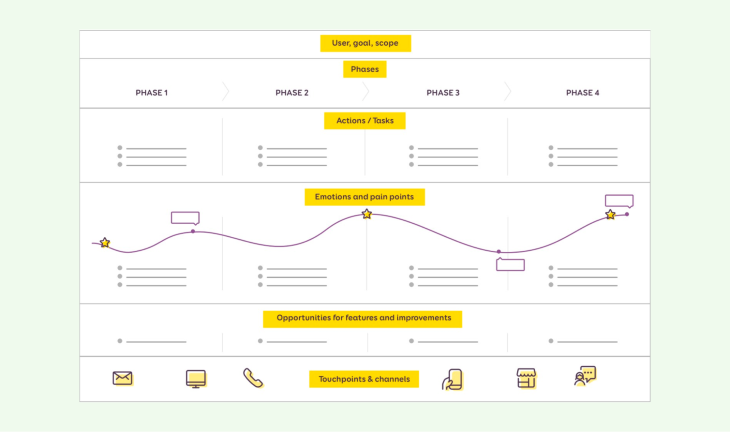
User journey mapping is a powerful way for experience designers to visualize the entirety of a user’s experience across various touchpoints and interactions with a product, system, or service. By visualizing users’ journeys visually, designers can identify potential pain points, areas for improvement, and opportunities for creating memorable encounters.
Here are a few strategies for crafting memorable user journey mapping experiences:
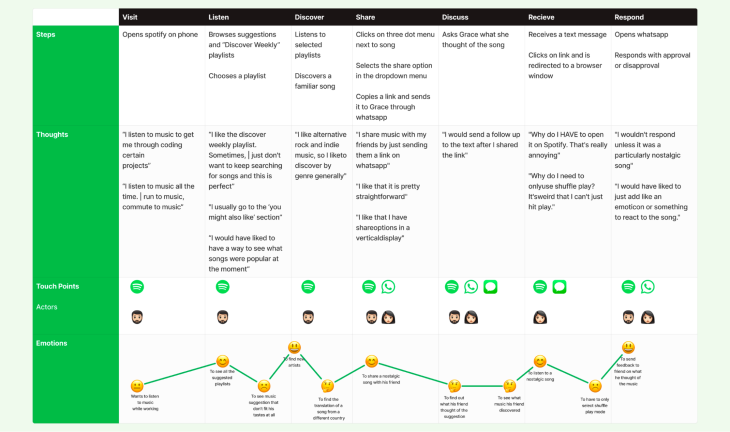
The above example shows us the user journey mapping of Spotify’s music sharing experience. The journey starts when the user opens the app and ends when the user saves the music or song track to their playlist or when the user likes the song.
A user journey paired with detailed surveys and research is an effective way to identify user pain points.
Storytelling has long been an integral part of human communication. Within experience design, employing storytelling techniques can enhance user engagement through memorable, emotional interactions.
Storytelling in experience design involves crafting a narrative to guide users along their journey, stirring emotions and tapping into desires and aspirations. Presenting information and functionality as narrative structures allows designers to engage users and give them an engaging experience.
One way storytelling techniques can be implemented is through user onboarding. Instead of overwhelming users with instructions and features, designers can craft an onboarding experience that gradually introduces users to the product or service, gradually weaving a story around each user journey while emphasizing benefits they may realize and creating engaging user journeys from start to finish. By crafting such narrative-driven journeys, designers can encourage curiosity, encourage exploration, and increase user engagement from day one.
Another approach is incorporating storytelling elements into visual design. Through captivating images, emotive colors, and thoughtful typography choices, designers can create an atmosphere that connects emotionally with users.
For instance, an ecommerce website offering outdoor adventure gear could use narratives and images that transport users to breathtaking landscapes that fuel wanderlust while forging deeper ties with its brand.
Storytelling can also be employed to elevate microinteractions within an interface. Through animated transitions, delightful feedback, and contextual messages, designers can create an experience full of progression, surprise, and delight for their users. Such storytelling microinteractions bring personality into user interactions, transforming them from functional into enjoyable user journeys.
Emotional design is an innovative method in experience design that uses emotional psychology to craft products, systems, or services that evoke positive emotional responses in users and leave an indelible mark on them.
To successfully employ emotional design, designers gain insight into users’ emotional needs through exhaustive user research (see a trend here?). By understanding users’ preferences and desires, designers can tailor the experience so it resonates emotionally with users, forging stronger bonds.
Designing for delight is an integral aspect of emotional design. By crafting experiences that elicit positive emotions such as joy and surprise from users, designers can cultivate lasting moments of delight that foster brand loyalty and remain with users long after their initial encounter with a product or service. Delightful experiences leave a lasting impression.
Designers create emotional design through easter eggs, hidden interactions, and personalized touches.
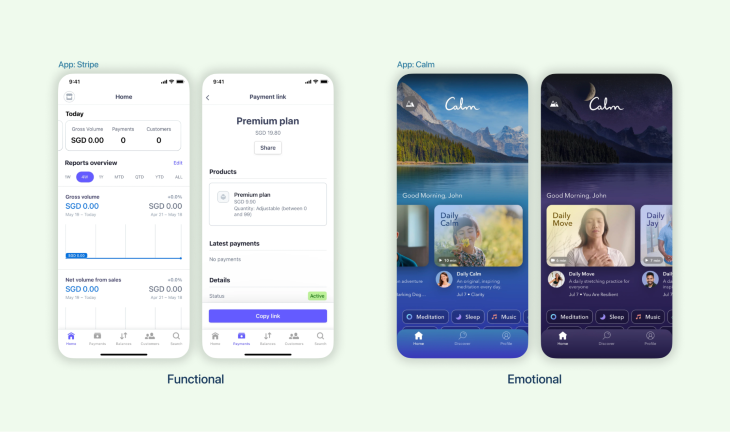
In the example above, users may feel emotionally linked to the Calm app since it delivers an experience to which they can relate in real life. Stripe, on the other hand, is an entirely functional application whose main objective is to get things done.
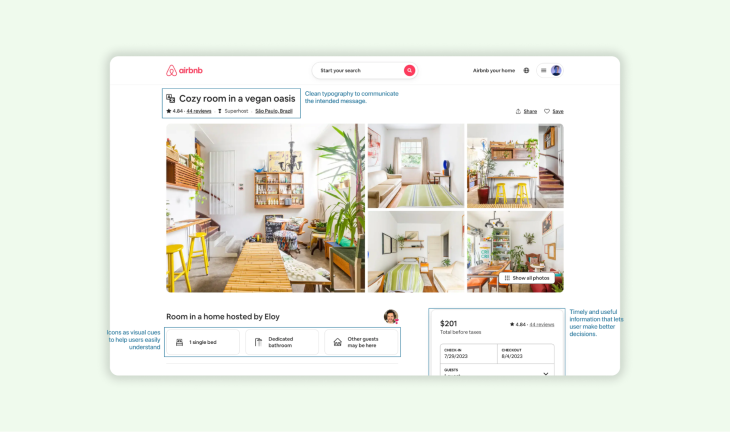
Visual and interactive elements play a pivotal role in experience design. By carefully designing these elements, experience designers can craft engaging user experiences.
One way to enhance user experience is through clear and intuitive visual cues. Designing icons, buttons and other interface elements that are easy for users to understand helps them easily navigate and interact with products – as these cues provide visual guidance reducing cognitive load and making the experience more intuitive.
Designing visually engaging and pleasing designs is another effective strategy for increasing consumer engagement with your product or service. Color, typography, and layout choices have an enormous effect on how users perceive and engage with it; by including visually attractive elements into designs, designers can evoke positive emotions in users and foster an enjoyable atmosphere which instills feelings of delight and enjoyment for users.
Designing for accessibility is of utmost importance. Ensuring all visual and interactive elements are accessible to all users — including those with disabilities — is crucial for inclusivity. Adherence to accessibility guidelines and best practices enables a wider range of users to fully engage with and appreciate the experience.
Interactive elements are key to creating engaging experiences. Animations, transitions and gestures bring interfaces to life by making interactions feel dynamic and responsive; adding depth and interactivity while immersing users into the experience and increasing engagement with it.
Experience design has evolved as a critical subject for firms wanting to stand out in an increasingly competitive marketplace. Companies can develop lasting relationships and create memorable experiences that resonate with customers long after their encounter ends by focusing on the human side, understanding user needs, and building immersive experiences.
Header image source: IconScout
LogRocket's Galileo AI watches sessions and understands user feedback for you, automating the most time-intensive parts of your job and giving you more time to focus on great design.
See how design choices, interactions, and issues affect your users — get a demo of LogRocket today.

Security requirements shouldn’t come at the cost of usability. This guide outlines 10 practical heuristics to design 2FA flows that protect users while minimizing friction, confusion, and recovery failures.

2FA failures shouldn’t mean permanent lockout. This guide breaks down recovery methods, failure handling, progressive disclosure, and UX strategies to balance security with accessibility.

Two-factor authentication should be secure, but it shouldn’t frustrate users. This guide explores standard 2FA user flow patterns for SMS, TOTP, and biometrics, along with edge cases, recovery strategies, and UX best practices.

2FA has evolved far beyond simple SMS codes. This guide explores authentication methods, UX flows, recovery strategies, and how to design secure, frictionless two-factor systems.