
In this article, we’ll explore the upcoming React Native version and the changes to the React Native architecture.

Let’s jump right into it.
The Replay is a weekly newsletter for dev and engineering leaders.
Delivered once a week, it's your curated guide to the most important conversations around frontend dev, emerging AI tools, and the state of modern software.
A key architectural change coming to React Native is the new, native TurboModule system and the Fabric Renderer.
In the next sections, we’ll examine how these key architectural changes impact working with React Native applications by upgrading the Android Gradle plugin to be compatible with the latest nightly release version of React Native. We’ll specifically cover:
For our Android application, the following prerequisites must be met:
The taste of the pudding is in the eating, so with that little quip, let’s get our hands dirty by bootstrapping a new React Native application.
npx react-native init reactNativeNew
Once that is done, it’s time to focus on getting our application ready to receive the nightly release of the latest version of React Native.
cd android && ./gradlew wrapper -gradle-version 7.3 -distribution-type=all
The AGP version updates the top-level build.gradle file.
Install the new Gradle plugin:
cd .. yarn add react-native-gradle-plugin code android/settings.gradle
Edit the settings.gradle file to include the following lines at the end of the file:
includeBuild('../node_modules/react-native-gradle-plugin')
if (settings.hasProperty("newArchEnabled") && settings.newArchEnabled == "true") {
include(":ReactAndroid")
project(":ReactAndroid").projectDir = file('../node_modules/react-native/ReactAndroid')
}
Adding the Gradle plugin to our build script:
code android/build.gradle
Now, add the following code block:
buildscript {
dependencies {
classpath("com.android.tools.build:gradle:7.0.4")
classpath("com.facebook.react:react-native-gradle-plugin")
classpath("de.undercouch:gradle-download-task:4.1.2")
// NOTE: Do not place your application dependencies here; they belong
// in the individual module build.gradle files
}
}
Edit the module-level Gradle file like so:
code android/app/build.Gradle
And now, add the following code block at the top level:
apply plugin: "com.android.application"
import com.android.build.OutputFile
// Add those lines
apply plugin: "com.facebook.react"
// Add those lines as well
react {
reactRoot = rootProject.file("../node_modules/react-native/")
codegenDir = rootProject.file("../node_modules/react-native-codegen/")
}
In the dependencies section of the /android/app/build.gradle file, add the below code:
dependencies {
implementation fileTree(dir: "libs", include: ["*.jar"])
//noinspection GradleDynamicVersion
// replace this
implementation "com.facebook.react:react-native:+" // From node_modules
// with this
implementation project(":ReactAndroid") // From node_modules
In order to access the most up-to-date changes to React Native, it is expected that the target application makes use of a specific nightly release. Before upgrading the app to a specific nightly release, it is recommended to first upgrade the application to the latest open source release.
yarn add react-native
Once the application is upgraded to the latest open source release successfully, we can target the nightly release. The below command helps with that.
yarn add [email protected]
Install the latest version of react-native-codegen, which is a tool for automating the compatibility between JavaScript and native code at build time, instead of at runtime.
yarn add react-native-codegen
With our Android application up to date with the latest version of React Native, it’s time to explore the new renderer system: Fabric.
Fabric is React Native’s new rendering system. The Fabric renderer seeks to improve the interoperability of React Native with host platforms, which are responsible for embedding React Native in Android, iOS, macOS, Windows, etc.
In the current architecture, when a React Native application is run, the JavaScript code is bundled together into a package called JS Bundle, and the native code is kept separate. The JavaScript thread runs the JS Bundle, and the native/UI thread runs the native modules and handles UI rendering. The communication between the JS and native threads is enabled by a bridge, which sends data to the native threads after serializing as JSON. This bridge can only handle asynchronous communication.
With Fabric, logic is rendered in C++, which improves the interoperability between the host platforms. The Fabric renderer is implemented in C++, and the C++ core is shared among platforms, providing greater consistency and making React Native easier to adopt on new platforms.
Furthermore, the new architecture decouples the JavaScript interface from the engine, enabling the use of other JavaScript engines such as Hermes, V8, or Chakra.
A host view is a tree representation of views in the host platform (e.g., Android, iOS).
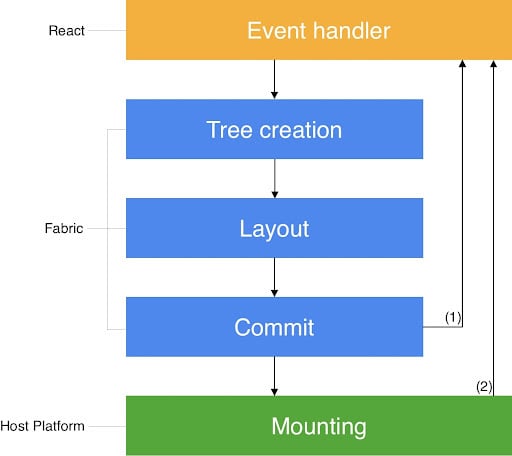
Source: reactnative.dev/
The improved interoperability between React Native and host views is enabled by the C++ core, which is shared among different host platforms and enables React Native to render React surfaces synchronously.
It wasn’t always this way — in the legacy React Native architecture, the layout was asynchronous, which led to a layout “jump” issue when embedding a React Native rendered view in a host view.
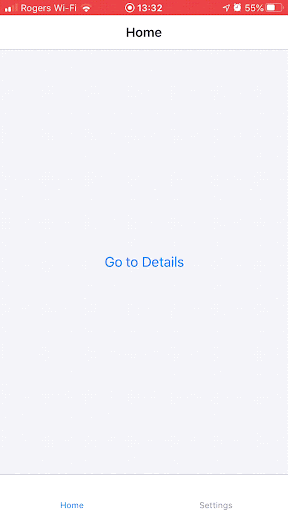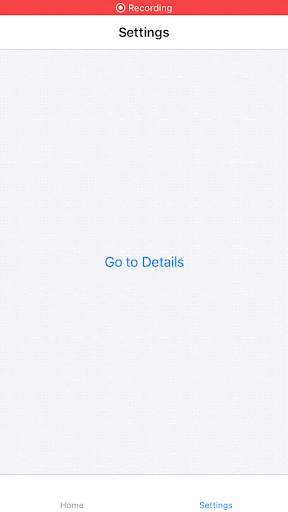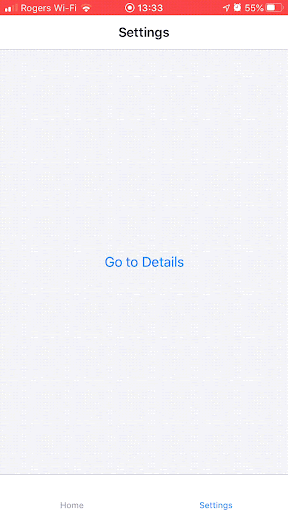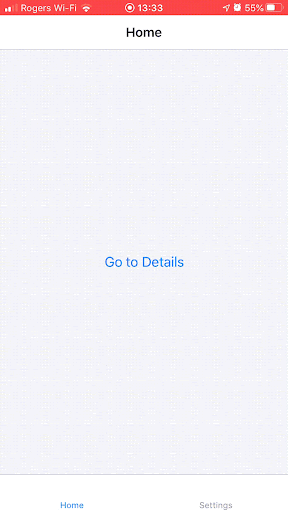
Source: React Navigation GitHub issue #6996
Data fetching in applications is now much more intuitive, thanks to the integration with React Suspense. Other new features available in React are now enabled in the Fabric renderer, such as the new Concurrent Features available in React 18. This includes the startTransition feature, which keeps the UI of our applications responsive during expensive state transitions.
Server-side rendering is also made easier with the new renderer.
The render pipeline occurs in three phases:
Let’s look into each of them more closely.
In this phase, React executes product logic to create React element trees, which consist of React elements. A React Element is a plain JavaScript object that describes what should appear on the application screen.
The React element tree is used to render the React shadow tree in C++. The React Shadow Tree is created by the Fabric Renderer and consists of React shadow nodes, which are objects that represent the React host components that are to be mounted, and contains props that originate from JavaScript.
const App = () => {
return (
<View>
<Text>App.js</Text>
</View>
);
};
In the Render phase, as each React element is invoked, the renderer synchronously creates a React shadow node. Take note that this synchronous creation of a React shadow node only occurs for React host oomponents, and not for React composite components. When translated into a React Shadow Block, the above code would see the <View> translated into a ViewShadowNode object.
A great thing about the new renderer is that any parent-child relationship between React element nodes will correspond to the relationships among React shadow nodes. The above process shows how the React shadow tree is assembled; once the React shadow tree is complete, the renderer triggers a commit of the React element tree.
Below is a visual representation of the render phase:
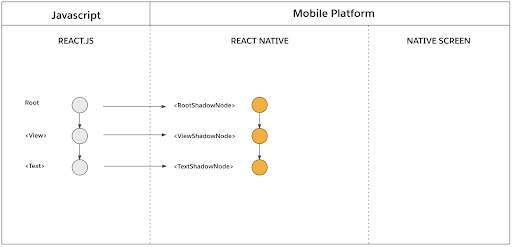
Source: reactnative.dev
The cross-platform layout engine Yoga is hugely important in handling operations that happen during the commit phase, which consists of two operations: layout calculation and tree promotion.
The layout calculation calculates the position and size of each React shadow node. This is achieved by invoking Yoga to calculate the layout of each React shadow node.
Once the calculation determines the amount of available space, the Tree Promotion operation promotes the new React shadow tree as the next tree to be mounted. This promotion represents the latest state of the React element tree.
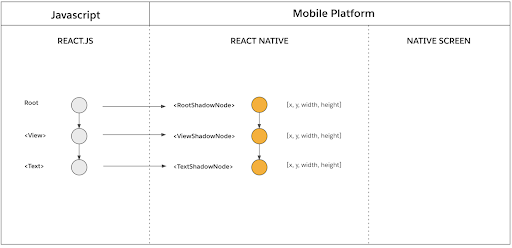
Source: reactnative.dev
This is the phase in which the React Shadow Tree (which contains the data from the layout calculation) is transformed into a host view tree with rendered pixels on the screen. The Fabric renderer creates a corresponding host view for each React shadow node and mounts it on screen.
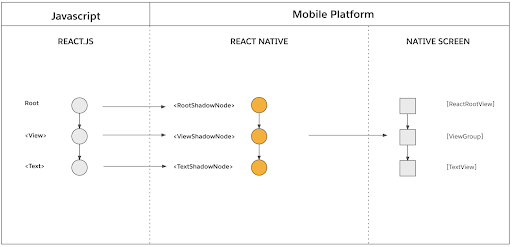
Sources: reactnative.dev
The TurboModules system is an enhancement of Native Modules. In their current architecture, a table holds the module registry, and when the JavaScript code calls a specific native module, the indices of the module and the methods are passed to Java/ObjC, which invoke the specific methods.
A proposed solution to the eager initialization of Native packages is the use of the LazyReactPackage, but this is not an effective method because the annotation processor ReactModuleSpecProcessor does not run with Gradle; hence, the LazyReactPackage doesn’t work with the open source release.
With the new implementation, JavaScript will expose a top level Native Module Proxy, called global.__turboModuleProxy, to access a native module. If we used the example of "SampleTurboModule", the application code will call the require('NativeSampleTurboModule'). In the NativeSampleTurboModule, the TurboModuleRegistry.getEnforcing() function is called, which holds a reference to the Native Modules and then calls global.__turboModuleProxy("SampleTurboModule").
This triggers the JSI function and a getModule function is invoked, which is defined for Java and ObjC, and returns a JSI object for the specific TurboModule (i.e., GeoLocation, FileStorage, DeviceInformation) that previously would have been initialized at app startup. This allows JavaScript code to load each module when it is required, instead of initializing them before the app is opened.
The React Native next version promises an improvement in startup time, and developer experience, with improved interoperability between all threads, a new web-like rendering system(Fabric). A key aspect that excites me about the new architecture, is the ability to easily build applications for Smart TVs.
LogRocket's Galileo AI watches sessions for you and and surfaces the technical and usability issues holding back your React Native apps.
LogRocket also helps you increase conversion rates and product usage by showing you exactly how users are interacting with your app. LogRocket's product analytics features surface the reasons why users don't complete a particular flow or don't adopt a new feature.
Start proactively monitoring your React Native apps — try LogRocket for free.

React Server Components and the Next.js App Router enable streaming and smaller client bundles, but only when used correctly. This article explores six common mistakes that block streaming, bloat hydration, and create stale UI in production.

Gil Fink (SparXis CEO) joins PodRocket to break down today’s most common web rendering patterns: SSR, CSR, static rednering, and islands/resumability.

@container scroll-state: Replace JS scroll listeners nowCSS @container scroll-state lets you build sticky headers, snapping carousels, and scroll indicators without JavaScript. Here’s how to replace scroll listeners with clean, declarative state queries.

Explore 10 Web APIs that replace common JavaScript libraries and reduce npm dependencies, bundle size, and performance overhead.
Would you be interested in joining LogRocket's developer community?
Join LogRocket’s Content Advisory Board. You’ll help inform the type of content we create and get access to exclusive meetups, social accreditation, and swag.
Sign up now