
React is a component-based JavaScript library that continues to grow in popularity. In a 2021 worldwide study, over 40 percent of surveyed developers reported using React. The widespread usage of React shouldn’t come as a surprise. React is flexible, easy to learn, and offers the ability to write custom components. These custom components, or individual UI blocks, are reusable and may be easily shared among other React apps.
One aspect of React that is less straightforward, however, is the integration of custom components into a static website. In this tutorial, we’ll demonstrate how to use widgets to integrate a React component with static websites built entirely from HTML.
Open up your favorite text editor, and let’s get started!
The Replay is a weekly newsletter for dev and engineering leaders.
Delivered once a week, it's your curated guide to the most important conversations around frontend dev, emerging AI tools, and the state of modern software.
A widget is a piece of UI that handles data logic and data presentation internally and independently of other elements on the webpage. Widgets are used to add dynamic content (such as a popup, image carousel, or dynamic list) to a standalone, static application.
Widgets are framework agnostic. This tutorial focuses on the integration of a React component, but the same method may be used with a component created in a framework of your choosing.
A weather widget is an example of a common widget that many people interact with daily. It displays current weather conditions in nearby locations using the user’s geolocation. This widget handles several tasks, such as obtaining permission to access user location and fetching weather data.
An application or website that embeds a weather widget does not need to be concerned with how the data is fetched or how it is displayed to the user. These tasks are handled by the widget.
Let’s create a widget that will read data from the Crypto Compare API and display the list of top cryptocurrencies by market cap.
First, we’ll need to set up a React project.
To create and run a React application, Node.js and npm must both be installed in the system.
Open the terminal, and run the following command:
npx create-react-app ReactWidgetDemo cd ReactWidgetDemo
Inside the src folder, create two new folders: components and hooks. We’ll create a custom hook to fetch data from the Crypto Compare API.
Inside the hooks folder, create a new file: useCryptoData.js.
import { useEffect, useState } from "react";
const useCryptoData = () => {
const [cryptoData, setCryptoData] = useState([]);
const [isLoading, setLoading] = useState(true);
useEffect(() => {
setLoading(true);
// fetch the data and set cryptData
setLoading(false);
}, [])
return { cryptoData, isLoading }
};
In the useCryptoData custom hook, we employ the useState React hook to create two state variables: cryptoData and isLoading.
The cryptoData state variable will store the data from the API. The isLoading state will indicate if the data fetching is in progress.
Now, we’ll use the fetch() method to retrieve data from the Crypto Compare API and then set the cryptoData state:
import { useEffect, useState } from "react";
const useCryptoData = () => {
const [cryptoData, setCryptoData] = useState([]);
const [isLoading, setLoading] = useState(true);
useEffect(() => {
setLoading(true);
fetch(
"https://min-api.cryptocompare.com/data/top/mktcapfull?limit=10&tsym=USD"
)
.then((res) => res.json())
.then((data) => {
console.log(data);
const preparedData = [];
data.Data.forEach((d) => {
const { Id, Name, FullName, ImageUrl, Url } = d.CoinInfo;
let Price, Change24hr;
if (d.DISPLAY?.USD) {
const { PRICE, CHANGEPCT24HOUR } = d.DISPLAY.USD;
Price = PRICE;
Change24hr = CHANGEPCT24HOUR;
}
preparedData.push({
Id,
Name,
FullName,
ImageUrl: `https://www.cryptocompare.com${ImageUrl}`,
Url: `https://www.cryptocompare.com${Url}`,
Price,
Change24hr
});
});
setCryptoData(preparedData);
})
.finally(() => setLoading(false));
}, []);
return { cryptoData, isLoading };
};
export default useCryptoData;
The components folder will house the main widget component file. Import the useCryptoData hook in the CryptoList component file:
import useCryptoData from "./useCryptoData";
const CryptoItem = (props) => (
<div className="item">
<img src={props.ImageUrl} className="icon" alt={props.Name} />
<div className="display-container">
<div className="name">{props.Name}</div>
<div className="fullname">{props.FullName}</div>
</div>
<div className="price-container">
<div className="price">{props.Price}</div>
<div
className={`price-change ${
parseInt(props.Change24hr) < 0 ? "danger" : "success"
}`}
>
{props.Change24hr}
</div>
</div>
</div>
);
const CryptoList = () => {
const { cryptoData, isLoading } = useCryptoData();
return (
<div>
<div className="container">
{!isLoading ? (
cryptoData.map((itemData) => (
<CryptoItem key={itemData.Id} {...itemData} />
))
) : (
<p className="loading-text">Loading Data...</p>
)}
</div>
</div>
);
};
export default CryptoList;
Next, use the CryptoList component inside the main App() component:
import CryptoList from "./components/CryptoList";
import "./styles.css";
export default function App() {
return (
<div>
<CryptoList />
</div>
);
}
Now, let’s add styling to the component to improve its appearance:
@import url("https://fonts.googleapis.com/css2?family=Open+Sans:wght@500;600&display=swap");
:root {
--dark: #1e2329;
--light: #fafafa;
--success: #03a66d;
--danger: #cf304a;
}
* {
font-family: "Open Sans", sans-serif;
}
.name,
.loading-text {
color: var(--light);
font-size: 16px;
font-weight: 600;
}
.fullname {
color: #b6b6b6;
font-size: 14px;
margin-top: 3px;
font-weight: 500;
}
.item {
display: flex;
align-items: center;
padding: 12px 0px;
border-bottom: 1px solid #949191;
}
.item:first-child {
padding-top: 0px;
}
.item:last-child {
padding-bottom: 0px;
border-bottom: 0px;
}
.container {
background-color: var(--dark);
padding: 20px;
border-radius: 12px;
box-shadow: rgba(0, 0, 0, 0.1) 0px 10px 30px;
}
.icon {
height: 24px;
width: 24px;
margin-right: 14px;
}
.price-container {
margin-left: auto;
display: flex;
flex-direction: column;
align-items: flex-end;
}
.price {
font-weight: 500;
color: var(--light);
font-size: 16px;
}
.price-change {
margin-top: 3px;
}
.price-change.danger {
color: var(--danger);
}
.price-change.success {
color: var(--success);
}
To get the React application up and running, use the following command from the project root:
npm run start
This will set up a local dev server and run the application on port 3000.
Open the browser and go to http://localhost:3000.
Go to CodeSandbox to see the demo CryptoListwidget in action.
Now it’s time to use the demo CryptoList widget in a standalone static HTML webpage. We’ll use an iframe to embed the widget.
We’ll pass the React application URL to the src attribute of the <iframe />. In this example, the URL is http://localhost:3000.
<iframe src="http://localhost:3000" style="border: none;" width="100%" ></iframe>
Here’s the iframe and widget code included with other elements in the static webpage:
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge" />
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" />
<style>
.row {
display: flex;
flex-direction: row;
}
.col {
flex: 1;
}
</style>
<title>Static website</title>
</head>
<body style="min-height: 100vh">
<div class="row">
<div class="col">
<div>Excepteur sint occaecat cupidatat non proident.</div>
<iframe
src="http://localhost:3000"
style="border: none; min-height: 98vh"
width="100%"
></iframe>
</div>
<div class="col">
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit.
</div>
</div>
</body>
</html>
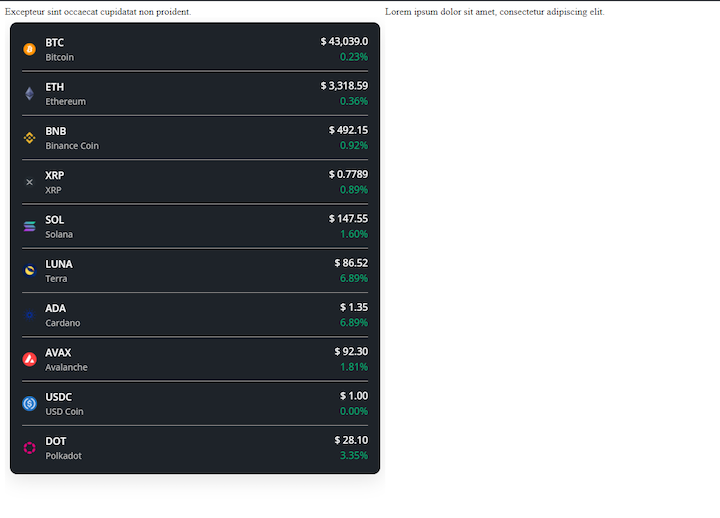
Here’s the demo CryptoList widget shown embedded in the HTML webpage:
Depending on the project it may be necessary to share widgets between React apps, rather than integrating them into a static website. To create shareable widgets for React Apps, we can create a common component library and publish it on npm. This guide contains detailed instructions on how to create an npm package for React.
Alternatively, we can import the package from a repository:
npm i https://github.com/{username}/{repo}.git
We can install the package in different React projects and import the component in our JSX files. With this approach, the widget can be maintained separately. Whenever the widget’s functionality or styling is updated, this will be reflected in the React project by simply updating the npm package.
It’s very easy to make shareable widgets in React. In this tutorial, we demonstrated how to use React to build a simple widget and then integrate it with a static HTML webpage.
As a developer, it’s important to understand the pros and cons of embedding widgets using an iframe. This may not be the preferred option for every use case. For projects that involve a large number of embedded widgets, consider migrating to Gatsby or another static-site generator for React.
To learn more about React, see its website or the React resources on MDN.
Install LogRocket via npm or script tag. LogRocket.init() must be called client-side, not
server-side
$ npm i --save logrocket
// Code:
import LogRocket from 'logrocket';
LogRocket.init('app/id');
// Add to your HTML:
<script src="https://cdn.lr-ingest.com/LogRocket.min.js"></script>
<script>window.LogRocket && window.LogRocket.init('app/id');</script>

Discover what’s new in The Replay, LogRocket’s newsletter for dev and engineering leaders, in the March 11th issue.

Buying AI tools isn’t enough. Engineering teams need AI literacy programs to unlock real productivity gains and avoid uneven adoption.

If your AI app or agent works perfectly in development but falls apart in production, you’re not alone. In a […]

Compare ESLint and Oxlint, benchmark real speed gains, and learn when migrating to Oxlint makes sense for modern JavaScript teams.
Would you be interested in joining LogRocket's developer community?
Join LogRocket’s Content Advisory Board. You’ll help inform the type of content we create and get access to exclusive meetups, social accreditation, and swag.
Sign up now
3 Replies to "Creating shareable React widgets"
Was looking for a SDK creation tutorial.. 🙁
weak article tbh. Does not address any of the concerns of writing third party js. So far below LogRocket standards.
Hi Christopher, it’s addressed in “Sharing components between React apps” section of the article. You can check out this article for more details https://blog.logrocket.com/build-component-library-react-typescript/