
It’s no secret that audio visualizers are a fantastic way to spice up your music listening experience. In this article, we’ll go through how to create an audio visualizer from the ground up using only vanilla JavaScript and the inbuilt browser Canvas and Web Audio APIs.

By the end of this post, you’ll have a solid understanding of how to create your own audio visualizers and be able to experiment with different ways of visualizing audio data.
Jump ahead:
The Replay is a weekly newsletter for dev and engineering leaders.
Delivered once a week, it's your curated guide to the most important conversations around frontend dev, emerging AI tools, and the state of modern software.
Let’s start with a basic explanation of how digital audio works.
Computers don’t understand sound the way we do in the physical world. In order to turn sound into data that they can store, computers do something called sampling. Sampling is done by measuring the sound waves hitting a microphone as data points. Once the computer has these data points, also called samples, it can store them in files.
When we want to play back audio, the computer reverses the process: it recreates the sound from those recorded data points. We’ll use these data points to draw our dynamic bar charts.
That’s enough theory for now — let’s get into some code!
Even though we’ll be using vanilla JavaScript, we still need to set up a server to follow along. The reason we need a server is to bypass the CORS problem.
CORS prevents accessing resources from outside of its domain. So, to analyze the audio data, we need to have our audio files hosted on the same server as our webpage.
For this tutorial, I’m using Vite, a simple and straightforward dev server to set up, but feel free to use any other server of your choice.
To build the visualizer, we’ll be using two inbuilt browser APIs: Canvas and Web Audio API.
Canvas is an HTML5 element that allows us to draw graphics on a webpage. In this case, we’ll be using it to draw our dynamic bar charts.
Canvas is also split into two different APIs: 2D and WebGL. We’ll use the 2D version for this tutorial since WebGL deals more with 3D graphics.
Web Audio API allows us to process and play audio files directly in the browser. We’ll use it to load and play our audio files and extract the raw data we need to generate our visualizations.
With all this necessary theory out of the way, let’s get into some code!
First, we need to set up our HTML document. We’ll create a simple HTML document that contains canvas and audio elements.
Let’s name our file index.html; it will serve as an entry point for our project. When you create a vanilla Vite project, it will already have an index.html file set up for you:
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<link rel="stylesheet" href="stylesheet.css" />
<title>Audio Visualizer</title>
</head>
<body>
<div id="container">
<canvas id="canvas"></canvas>
<audio id="audio"></audio>
</div>
<script src="script.js"></script>
</body>
</html>
The important parts are within the body of the document. We have a div with an id of container. This is where we’ll be holding our canvas and audio elements.
The canvas element is where we’ll draw our dynamic bar charts. The audio element is what we’ll use to play back the audio file. We’re adding a reference to the script.js file. This is the file that will contain all of our code for analyzing the audio and generating the visuals.
We also have simple CSS styling added, which adds a black background for better contrast and positions our canvas element at the center of the screen:
* {
margin: 0;
padding: 0;
box-sizing: border-box;
}
#container {
position: absolute;
top: 0;
left: 0;
background: #000;
width: 100%;
height: 100%;
}
#canvas {
position: absolute;
top: 0;
left: 0;
width: 100%;
height: 100%;
}
Now let’s start adding the code for making all these elements actually do something.
First, let’s set up references to our canvas and audio elements and create some other variables we’ll need:
let audio1 = new Audio();
audio1.src = "tune.mp3";
const container = document.getElementById("container");
const canvas = document.getElementById("canvas");
canvas.width = window.innerWidth;
canvas.height = window.innerHeight;
const ctx = canvas.getContext("2d");
We’re creating a new Audio object with the src property set to the location of the audio file that we want to play. We’re setting the width and height of our canvas element to equal the browser window size. This way, our visualization will always fill up the entire screen.
Next, we need to set up our audio source, analyzer, and audio context objects. But first, let’s cover what each of these objects represents.
An audio source is an AudioNode object that represents the source of the audio. In our case, it will be the audio element we added.
The analyzer node helps us understand what is happening with the sound. It makes it possible for us to see and use the data from the sound so that we can create our visualizer. The analyzer contains various properties like frequencyBinCount, which we will use later to figure out how many data points we need to collect.
The audio context is responsible for managing all the Web Audio API nodes. We’ll use it to create our audio source and analyzer nodes.
Now let’s set up our audio source, analyzer, and context:
const audioCtx = new (window.AudioContext || window.webkitAudioContext)(); let audioSource = null; let analyser = null; audio1.play(); audioSource = audioCtx.createMediaElementSource(audio1); analyser = audioCtx.createAnalyser(); audioSource.connect(analyser); analyser.connect(audioCtx.destination);
We created a new instance of the AudioContext object. We also declared two other variables, audioSource and analyser, which we’ll use to create our audio source and analyzer nodes.
Next, we created our audioSource and analyser object nodes using our audio context.
Lastly, we connected our audioSource and analyser nodes to each other and to the destination of the audio context (the speakers). This setup forms a chain of nodes that the audio will flow through.
Now that we have our audio context and nodes set up, we can start writing the code for our visualizer.
First, let’s figure out how many bars we want to show and how wide each bar should be:
analyser.fftSize = 128; const bufferLength = analyser.frequencyBinCount; const dataArray = new Uint8Array(bufferLength); const barWidth = canvas.width / bufferLength;
We’re setting the fftSize property of our analyzer to 128. This will determine how many data points we collect from the sound. The higher the number, the more data points we get and the more bars we’ll display.
We’re creating a new bufferLength variable and setting it equal to the frequencyBinCount property of the analyzer. This property tells us how many data points we have based on the fftSize that we set earlier. frequenceBinCount is always half of the fftSize.
We’re creating a new dataArray variable and setting it equal to a Uint8Array of the bufferLength size. This array will hold all of the data points that we collect from the sound.
Lastly, we’re creating a new barWidth variable. The variable determines how wide each bar in our visualizer should be. We set it equal to the width of the canvas divided by the bufferLength.
Now let’s write the function that will perform the actual animation:
let x = 0;
function animate() {
x = 0;
ctx.clearRect(0, 0, canvas.width, canvas.height);
analyser.getByteFrequencyData(dataArray);
for (let i = 0; i < bufferLength; i++) {
barHeight = dataArray[i];
ctx.fillStyle = "white";
ctx.fillRect(x, canvas.height - barHeight, barWidth, barHeight);
x += barWidth;
}
requestAnimationFrame(animate);
}
animate();
x is used to keep track of where we are on the x-axis as we draw our bars. We clear the canvas so that we can start drawing from a blank slate on each frame. Then we call the getByteFrequencyData method on our analyser node. This method accepts an array as its parameter. We pass in our dataArray to this method. This will populate our dataArray with data from the sound in place.
Then we use a for loop to go through the dataArray array.
For each item, we set the barHeight variable equal to the data point. We use the fillRect method to draw a rectangle at the x, y position with the barWidth and barHeight that we set earlier.
Then we increment the x variable by the barWidth. Doing so ensures that each bar is drawn next to the previous one.
Finally, we call the requestAnimationFrame method and pass it into our animate function. This tells the browser to call our animate function on every frame.
N.B., since we’re calling *requestAnimationFrame* inside the *animate* function itself, this will cause the *animate* function to be called over and over again in a loop
Here’s what the end result should look like:

Congrats! You have built a simple bar visualizer! In the next section, we’ll work on adding some improvements to it.
The hardest part of the tutorial is behind us. In this section, we’ll add some color to our visualizer and polish the UI a bit.
Our current visualizer is filled with white rectangles, which isn’t too exciting. Let’s add some color to it!
This is where you get to experiment on your own. There’s no one way to add randomness, so we’ll play around with the dynamic values we have in our for loop to generate some random colors:
let barHeight;
for (let i = 0; i < bufferLength; i++) {
barHeight = dataArray[i];
const red = (i * barHeight) / 10;
const green = i * 4;
const blue = barHeight / 4 - 12;
ctx.fillStyle = `rgb(${red}, ${green}, ${blue})`;
ctx.fillRect(x, canvas.height - barHeight, barWidth, barHeight);
x += barWidth;
}
Feel free to experiment with the values above or come up with your own!
Here’s what it looks like:
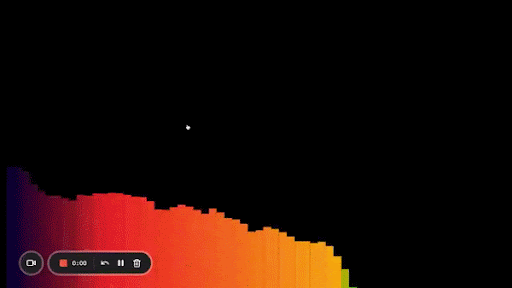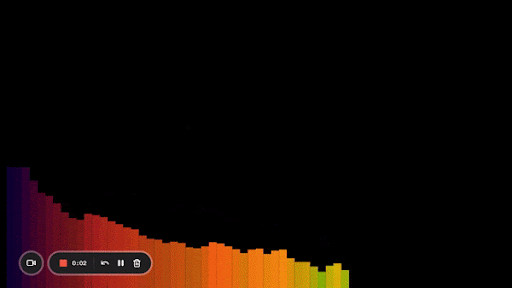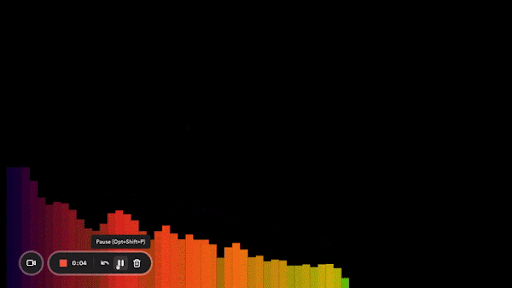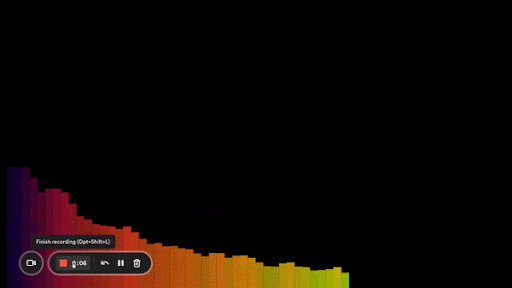
Another improvement we can make is to make our bars taller in the middle and shorter on the sides. That’s what most of the bar visualizers you see look like.
Again, at this point, we’re only making changes to animate. First, let’s separate our for loop into its own function for better readability:
let x = 0;
function animate() {
x = 0;
ctx.clearRect(0, 0, canvas.width, canvas.height);
analyser.getByteFrequencyData(dataArray);
drawVisualizer({
bufferLength,
dataArray,
barWidth
});
requestAnimationFrame(animate);
}
const drawVisualizer = ({
bufferLength,
dataArray,
barWidth
}) => {
let barHeight;
for (let i = 0; i < bufferLength; i++) {
barHeight = dataArray[i];
const red = (i * barHeight) / 10;
const green = i * 4;
const blue = barHeight / 4 - 12;
ctx.fillStyle = `rgb(${red}, ${green}, ${blue})`;
ctx.fillRect(x, canvas.height - barHeight, barWidth, barHeight);
x += barWidth;
}
};
We can make our higher bars rise from the middle by splitting our data points into two halves. We’ll animate the left side with higher frequency bars on the right, and the right side with the higher frequency bars on the left.
This will make more sense if we look at the code:
const drawVisualizer = ({
bufferLength,
dataArray,
barWidth
}) => {
let barHeight;
for (let i = 0; i < bufferLength; i++) {
barHeight = dataArray[i];
const red = (i * barHeight) / 10;
const green = i * 4;
const blue = barHeight / 4 - 12;
ctx.fillStyle = `rgb(${red}, ${green}, ${blue})`;
ctx.fillRect(
canvas.width / 2 - x, // this will start the bars at the center of the canvas and move from right to left
canvas.height - barHeight,
barWidth,
barHeight
);
x += barWidth; // increases the x value by the width of the bar
}
for (let i = 0; i < bufferLength; i++) {
barHeight = dataArray[i];
const red = (i * barHeight) / 10;
const green = i * 4;
const blue = barHeight / 4 - 12;
ctx.fillStyle = `rgb(${red}, ${green}, ${blue})`;
ctx.fillRect(x, canvas.height - barHeight, barWidth, barHeight); // this will continue moving from left to right
x += barWidth; // increases the x value by the width of the bar
}
};
Here we’re looping through our data points twice. The first time, we start at the center of the canvas and animate from right to left, and the second time, we’re going from left to right. As I mentioned, the left half has its higher frequency bars on the right, and vice versa for the right half.
Here’s what my end result looks like:
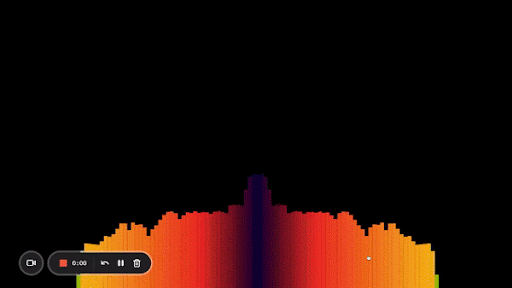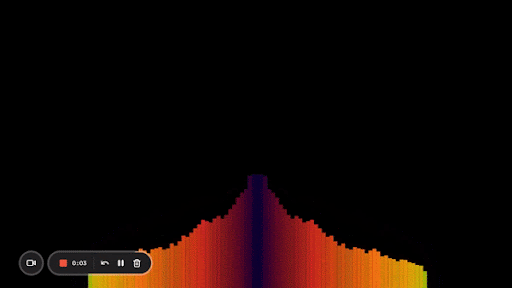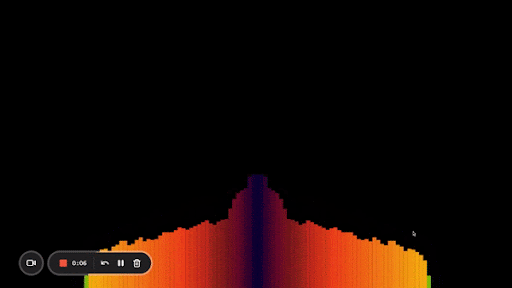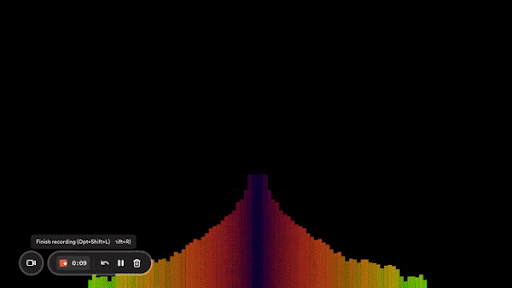
And that’s it! Now you know how to create an audio visualizer from scratch using the Web Audio API and Canvas.
The way our project is currently set up, our visualizer does not require a lot of resources to run so performance is not a real concern. However, as the complexity of your use case grows, you may start seeing some jank. If so, this could negatively affect your app’s responsiveness.
Let’s see how we can address this.
As you’re probably aware, JavaScript applications are single-threaded. So, running heavy processing operations, like painting bars on the canvas, will affect the ability of the main thread to respond to user actions. And by default, the visualizer will run on your application’s main thread.
So what can we do? Well, we can actually offload the execution of some of those heavy operations to background threads via Web Workers, thus freeing up the main thread.
Just be aware that web workers do come with some restrictions. For example, you can’t access the global window object or use some browser APIs. To view the full list of APIs available to workers, check out this list.
Fortunately, manipulating a canvas is something we can do with web workers, thanks to OffScreenCanvas. Usually, canvas manipulation or any other animations must be executed on the main thread, but OffScreenCanvas allows you to run most canvas tasks within the web worker’s context.
Let’s see what using web workers with OffScreenCanvas would look like in code:
container.addEventListener("click", function () {
let audio1 = new Audio();
audio1.src = "tune.mp3";
const audioCtx = new (window.AudioContext || window.webkitAudioContext)();
let canvas = document.getElementById("canvas").transferControlToOffscreen();
const worker = new Worker(new URL("./worker.js", import.meta.url));
canvas.width = window.innerWidth;
canvas.height = window.innerHeight;
worker.postMessage({ canvas }, [canvas]);
let audioSource = null;
let analyser = null;
audio1.play();
audioSource = audioCtx.createMediaElementSource(audio1);
analyser = audioCtx.createAnalyser();
audioSource.connect(analyser);
analyser.connect(audioCtx.destination);
analyser.fftSize = 128;
const bufferLength = analyser.frequencyBinCount;
const dataArray = new Uint8Array(bufferLength);
function animate() {
analyser.getByteFrequencyData(dataArray);
worker.postMessage({ bufferLength, dataArray }, {});
requestAnimationFrame(animate);
}
animate();
});
Most of the code stayed the same, so let’s highlight the changes:
canvas variable, we’re calling transferControlToOffscreen, which returns the OffScreenCanvas instance that we can now safely use in our web workerconst worker = new Worker(new URL("./worker.js", import.meta.url))worker.postMessage twice in our code; the first time to pass our OffScreenCanvas to the web worker and the second time within our animation function to tell the worker to redraw the barsHere’s the code in the worker.js file:
let canvas = null;
const drawVisualizer = ({ bufferLength, dataArray }) => {
let barHeight;
const barWidth = canvas.width / 2 / bufferLength;
let firstX = 0;
let secondX = bufferLength * barWidth;
const ctx = canvas.getContext("2d");
ctx.clearRect(0, 0, canvas.width, canvas.height);
for (let i = 0; i < bufferLength; i++) {
barHeight = dataArray[i];
const red = (i * barHeight) / 10;
const green = i * 4;
const blue = barHeight / 4 - 12;
ctx.fillStyle = `rgb(${red}, ${green}, ${blue})`;
ctx.fillRect(
canvas.width / 2 - firstX,
canvas.height - barHeight,
barWidth,
barHeight
);
firstX += barWidth;
ctx.fillRect(secondX, canvas.height - barHeight, barWidth, barHeight);
secondX += barWidth;
}
};
onmessage = function (e) {
console.log("Worker: Message received from main script");
const { bufferLength, dataArray, canvas: canvasMessage } = e.data;
if (canvasMessage) {
canvas = canvasMessage;
} else {
drawVisualizer({ bufferLength, dataArray });
}
};
As you can see, we moved the drawVisualizer function since it will be run by our worker now. Within the worker, we’ve declared the onmessage listener that listens to the postMessage calls from our main thread and runs drawVisualizer.
And that’s it, now your bar visualizer animation can run in the background without impeding the main thread!
In this article, we reviewed how to create our own audio visualizer from scratch.
We started by discussing the different parts of an analyzer node and what each one does. From there, we moved on to creating our data array and animating it with the help of the animate function. We made some small improvements to our visualizer by changing the color and making our bars taller in the middle. Finally, we discussed how to improve performance for more complex projects. Here’s the full code from the tutorial.
Of course, there’s so much more you can do with this, so feel free to play around some more and go wild!
If you’re looking for another project, consider building an audio plugin from scratch.
Debugging code is always a tedious task. But the more you understand your errors, the easier it is to fix them.
LogRocket allows you to understand these errors in new and unique ways. Our frontend monitoring solution tracks user engagement with your JavaScript frontends to give you the ability to see exactly what the user did that led to an error.
LogRocket records console logs, page load times, stack traces, slow network requests/responses with headers + bodies, browser metadata, and custom logs. Understanding the impact of your JavaScript code will never be easier!

Solve coordination problems in Islands architecture using event-driven patterns instead of localStorage polling.

Signal Forms in Angular 21 replace FormGroup pain and ControlValueAccessor complexity with a cleaner, reactive model built on signals.

Discover what’s new in The Replay, LogRocket’s newsletter for dev and engineering leaders, in the February 25th issue.

Explore how the Universal Commerce Protocol (UCP) allows AI agents to connect with merchants, handle checkout sessions, and securely process payments in real-world e-commerce flows.
Would you be interested in joining LogRocket's developer community?
Join LogRocket’s Content Advisory Board. You’ll help inform the type of content we create and get access to exclusive meetups, social accreditation, and swag.
Sign up now
One Reply to "Write an audio visualizer from scratch with vanilla JavaScript"
This was super helpful, but I noticed a slight error in the sample code under “Resizing the Bars” — the second loop requires some adjustments to actually render that half of the visualizer on page.
I was able to get it working by:
1. Resetting the value of x in between the two loops.
2. Setting the X argument of the call to fillRect in the second loop to canvas.width / 2 + x.
I see a different approach was taken as I examine the code further on in “Tuning the Performance”, which leverages two separate X values, but the result is the same.