
Writing end-to-end tests for applications helps to ensure applications behave as expected. It also comes in handy when we add new features to existing applications because it ensures the newly introduced features integrate well with our already existing features.

If that isn’t the case, our test suite will fail, which prompts us to make the appropriate changes across our application to ensure the test is successful.
To make this article easy to follow, I’ve created this boilerplate project that exposes several resolvers which are essentially a CRUD operations for User and Todo types.
After setting up the project there are a few queries and mutations we can perform.
These queries and mutations will give us an overview of how the project works.
It’s important that we’re familiar with the expectations of the resolvers that our GraphQL servers expose — that’s fundamental for effective and proper testing.
The boilerplate project includes documentation to help us understand the basics of the project.
To get started with testing we need a separate database. This helps us maintain the integrity of our original database.
We’ll have a different set of environmental variables for running tests as indicated in
~/config/test.env
These variables are loaded in as we run our test suites from our package.json in our script tag:
"scripts": {
"test": "env-cmd -f ./config/test.env",
.....
},
To start writing tests, we need to install Jest a library that helps with writing tests:
npm install --save-dev jest // ~/Documents/ultimate-todo mkdir tests cd tests
We’ll update our package.json to run our tests:
"scripts": {
"test": "env-cmd -f ./config/test.env jest --runInBand",
.....
},
Until now, we’ve been making requests to our GraphQL server from a GraphQL client playground hosted by default at http://localhost:4000/. However, we need to make a request to our server from our code.
To do that, we need to install apollo-boost.
We’re also going to install Babel register because Jest needs to be able to use our server, which has code written in es6. Babel register helps Jest to understand our code.
The Replay is a weekly newsletter for dev and engineering leaders.
Delivered once a week, it's your curated guide to the most important conversations around frontend dev, emerging AI tools, and the state of modern software.
npm install apollo-boost graphql cross-fetch @babel/register -D
I also prefer to set up Jest config to start, and then tear down the server after running all the test suites.
// ~/Documents/ultimate-todo/tests
mkdir config
cd config
//create both files
touch globalSetup.js globalTeardown.js
//globalSetup.js
require('@babel/register');
const server = require('../../src/app').default;
module.exports = async () => {
global.httpServer = server;
await global.httpServer.listen();
};
//globalTeardown.js
module.exports = async () => {
await global.httpServer.stop();
};
Jest is going to use the file gbolbalSetup.js when the tests start and gbolbalTeardown.js when the tests ends.
All we have to do now is set this up in our package.json so that Jest can pick them up when running our test suites.
.....
"jest": {
"globalSetup": "./tests/config/globalSetup.js",
"globalTeardown": "./tests/config/globalTeardown.js"
},
....
Now that we have all the setup out of the way, let’s write some tests.
// ~/Documents/ultimate-todo/tests touch user.tests.js // file to contain tests for the user type.
We’re going to start by writing tests for the creatUser mutation.
If we explore the implementation of our mutation, we can clearly see that there are 3 possibilities.
We will be writing tests to account for all of these outcomes.
// ~/Documents/ultimate-todo/tests/utils
import ApolloClient from 'apollo-boost';
export const client = new ApolloClient({
uri: 'http://localhost:4000/',
onError: (e) => { console.log(e) },
});
//~/Documents/ultimate-todo/tests/user.test/js
import 'cross-fetch/polyfill';
import ApolloClient, { gql } from 'apollo-boost';
import { prisma } from '../src/generated/prisma-client';
import { client } from './utils/getClient';
beforeAll(async () => {
await prisma.deleteManyUsers()
})
describe('Tests the createUser Mutation', () => {
it('should not signup a user with a password less than 8 characters', async () => {
const createUser = gql`
mutation {
createUser(data: {
name: "Gbolahan Olagunju",
email: "[email protected]",
password: "dafe",
}){
token
user {
name
password
email
id
}
}
}
`;
await expect(client.mutate({
mutation: createUser
})).rejects.toThrowError("password must be more than 8 characters");
})
it('should successfully create a user with valid credentials', async () => {
const createUser = gql`
mutation {
createUser(data: {
name: "Gbolahan Olagunju",
email: "[email protected]",
password: "dafeMania"
}){
token
user {
id
}
}
}
`;
const res = await client.mutate({
mutation: createUser
})
const exists = await prisma.$exists.user({id : res.data.createUser.id});
expect(exists).toBe(true);
});
it('should not create two users with the same crededntials', async () => {
const createUser = gql`
mutation {
createUser(data: {
name: "Gbolahan Olagunju",
email: "[email protected]",
password: "dafeMania"
}){
token
user {
name
password
email
id
}
}
}
`;
await expect(client.mutate({
mutation: createUser
})).rejects.toThrowError("A unique constraint would be violated on User. Details: Field name = email");
});
});
The above code works as expected.
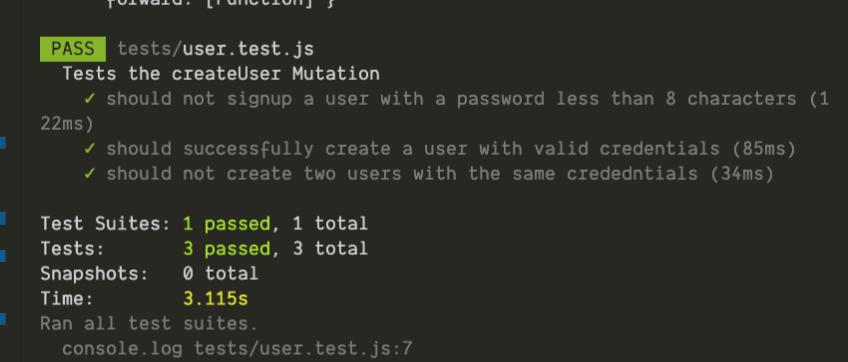
[Output gotten from running npm test]
We need our tests to behave consistently, so we have to clear our database before all the test runs. To achieve this, we’ll add a beforeAll block at the start of our test.
...
onError: (e) => { console.log(e) },
});
beforeAll(async () => {
await prisma.deleteManyUsers()
})
...
Let’s move on to writing tests for our createTodo , updateTodo, and deleteTodo mutation.
Having already interacted with playground at localhost, we know we need a user to be authenticated to perform this action.
As a result, we need to update the way we create clients to cater to authenticated users. The current code created an unauthenticated user.
Let’s modify this instance of our Apolloclient to reflect this change.
// ~/Documents/ultimate-todo/tests/utils
import ApolloClient from 'apollo-boost';
export const getClient = (token) => {
return new ApolloClient({
uri: 'http://localhost:4000/',
request: (operation) => {
if(token) {
operation.setContext({
headers: {
"Authorization": `Bearer ${token}`
}
})
}
},
onError: (e) => { console.log(e) },
});
}
Next, we’re going to write tests to cover all TODO type test cases.
//~/Documents/ultimate-todo/tests/todo.test/js
import 'cross-fetch/polyfill';
import { gql } from 'apollo-boost';
import { prisma } from '../src/generated/prisma-client';
import { getClient } from './utils/getClient';
const client = getClient();
let authenticatedClient;
let todoId;
beforeAll(async () => {
await prisma.deleteManyUsers()
await prisma.deleteManyTodoes();
const createUser = gql`
mutation {
createUser(data: {
name: "Gbolahan Olagunju",
email: "[email protected]",
password: "dafeMania"
}){
token
user {
id
}
}
}
`;
const authenticatedUser = await client.mutate({
mutation: createUser
});
authenticatedClient = getClient(authenticatedUser.data.createUser.token);
});
describe('Tests that can be performed on the Todo Mutation', () => {
it('should not allow an authenticated user create a TODO ', async () => {
const createTodo = gql`
mutation {
createTodo(data: {
title: "Buy Potatoes",
body: "Buy yam from the supermarket for everyone to eat at 10pm"
}){
title
body
id
}
}
`;
await expect(client.mutate({
mutation: createTodo
})).rejects.toThrowError("Authentication required");
});
it('should create a todo for a authenticated user', async () => {
const createTodo = gql`
mutation {
createTodo(data: {
title: "Buy Potatoes",
body: "Buy yam from the supermarket for everyone to eat at 10pm"
}){
title
body
id
}
}
`;
const todo = await authenticatedClient.mutate({
mutation: createTodo
});
todoId = todo.data.createTodo.id
const exists = await prisma.$exists.todo({id: todoId});
expect(exists).toBe(true);
});
it('should update a TODO', async () => {
const variables = {
id: todoId
}
const updateTodo = gql`
mutation($id: ID!){
updateTodo(id: $id , data: {
title: "Buy Ice Cream",
body: "Buy Ice Cream from the store"
}){
title
body
}
}
`;
const updatedTodo = await authenticatedClient.mutate({
mutation: updateTodo, variables
});
expect(updatedTodo.data.updateTodo.title).toBe('Buy Ice Cream');
expect(updatedTodo.data.updateTodo.body).toBe('Buy Ice Cream from the store');
});
it('should delete a TODO', async () => {
const variables = {
id: todoId
}
const deleteTodo = gql`
mutation($id: ID!){
deleteTodo(id: $id){
title
body
}
}
`;
const deletedTodo = await authenticatedClient.mutate({
mutation: deleteTodo, variables
});
const exists = await prisma.$exists.todo({id : todoId});
expect(exists).toBe(false);
});
});
Lastly, we’ll be writing tests to cover for our queries both for the TODO type and for the USER type.
To achieve this, we will be seeding the database to dummy data that we can make assertions on.
touch queries.test.js
////~/Documents/ultimate-todo/tests/queries.test/js
import 'cross-fetch/polyfill';
import { gql } from 'apollo-boost';
import { prisma } from '../src/generated/prisma-client';
import { getClient } from './utils/getClient';
const client = getClient();
beforeAll( async () => {
await prisma.deleteManyUsers()
const createUser = gql`
mutation {
createUser(data: {
name: "Gbolahan Olagunju",
email: "[email protected]",
password: "dafeMania"
}){
token
user {
id
}
}
}
`;
await client.mutate({
mutation: createUser
});
});
describe('the Queries that can be performed on TODO and USER type', () => {
it('should be able to see author\'s profile without sensitive info being displayed', async () => {
const userQuery = gql`
query {
users {
id
name
}
}
`;
const { data } = await client.query({
query: userQuery
});
expect(data.users.length).toBe(1);
expect(data.users[0].name).toBe('Gbolahan Olagunju');
});
});
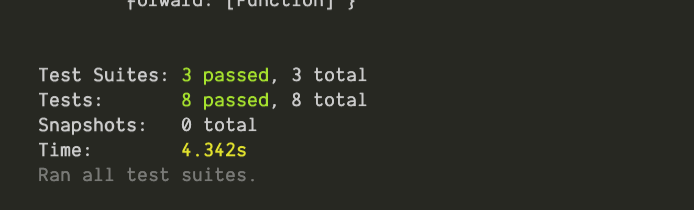
Here, we’ve demonstrated the details of how to write end-to-end tests with Jest on GraphQL servers using Apollo server.
While GraphQL has some features for debugging requests and responses, making sure GraphQL reliably serves resources to your production app is where things get tougher. If you’re interested in ensuring network requests to the backend or third party services are successful, try LogRocket.

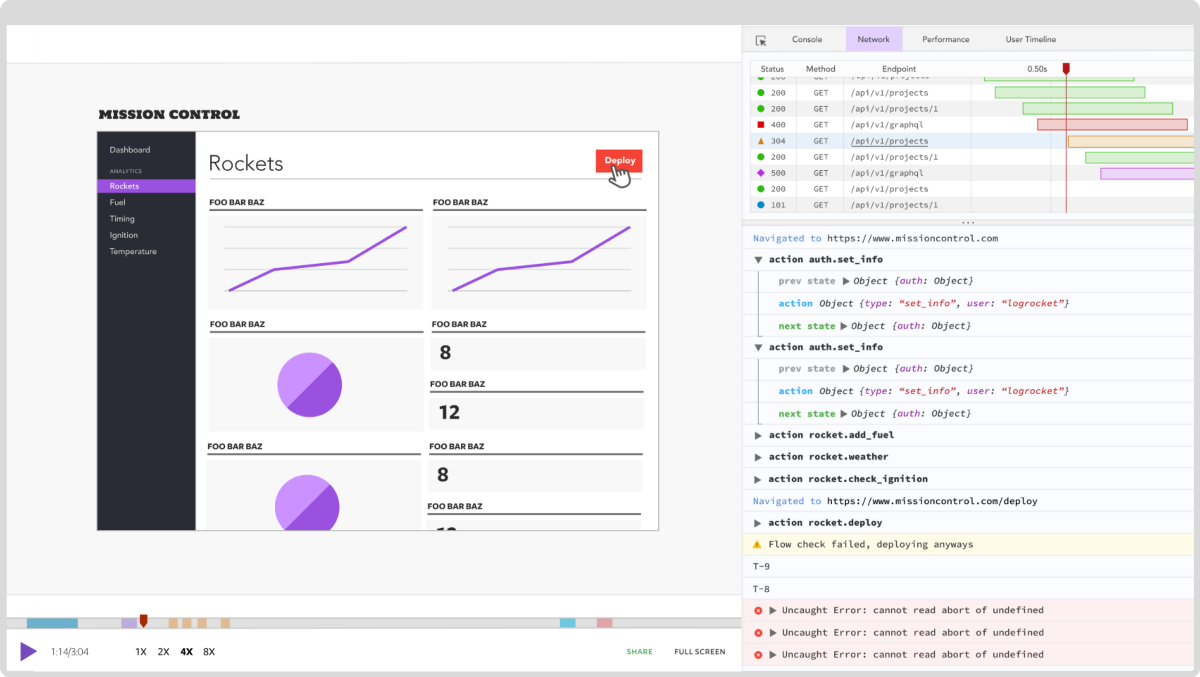
LogRocket lets you replay user sessions, eliminating guesswork around why bugs happen by showing exactly what users experienced. It captures console logs, errors, network requests, and pixel-perfect DOM recordings — compatible with all frameworks.
LogRocket's Galileo AI watches sessions for you, instantly aggregating and reporting on problematic GraphQL requests to quickly understand the root cause. In addition, you can track Apollo client state and inspect GraphQL queries' key-value pairs.

Within roughly the same six-month window, Anthropic shipped Agent Teams for Claude Code, OpenAI published Swarm and the production-ready Agents […]

Compare the top AI development tools and models of March 2026. View updated rankings, feature breakdowns, and find the best fit for you.

Discover what’s new in The Replay, LogRocket’s newsletter for dev and engineering leaders, in the March 11th issue.

Buying AI tools isn’t enough. Engineering teams need AI literacy programs to unlock real productivity gains and avoid uneven adoption.
Would you be interested in joining LogRocket's developer community?
Join LogRocket’s Content Advisory Board. You’ll help inform the type of content we create and get access to exclusive meetups, social accreditation, and swag.
Sign up now
4 Replies to "Writing end-to-end tests for GraphQL servers using Jest"
Good Article, thanks. I think this is not end to end testing, this is more Integration Testing, more specifically API testing.
i get this Error when i run user.test.js : GraphQL error: Task slick.basic.BasicBackend$DatabaseDef$$anon$3@6f15a91c rejected from slick.util.AsyncExecutor$$anon$1$$anon$2@5f09a5c0[Running, pool size = 1, active threads = 1, queued tasks = 1000, completed tasks = 2984]
What could be the problem
I am using TS and getting this error
`Property ‘server’ does not exist on type ‘typeof globalThis & { __DEV__: boolean | undefined; }’.ts(2339)`
Any suggestion to solve it? Thanks in advance!
There is a typographical Error here.
`gbolbal`