
Editor’s note: This article was updated on 4 May 2022 to include updated information for Create React App, as well as details about additional SSR frameworks.

In this article, we‘ll investigate different types of rendering for web applications. We’ll take a close look at server-side rendering in React, and we’ll examine the benefits of server-side rendering vs. traditional client-side rendering.
Jump ahead:
The Replay is a weekly newsletter for dev and engineering leaders.
Delivered once a week, it's your curated guide to the most important conversations around frontend dev, emerging AI tools, and the state of modern software.
Many of you probably use React CLI, better known as Create React App (CRA), to get your apps up and running. There are many advantages to this approach; however, building with CRA also has a few disadvantages.
For example, when you view source of a webpage from a web app initialized with CRA, you will notice that it’s an almost empty page with just the <head> section but hardly anything within <body>.
Here’s an example:
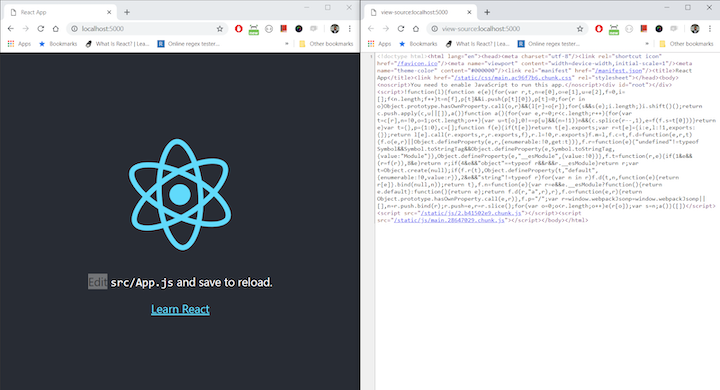
This is because CRA renders your app on the client side, meaning the built .js file is first downloaded to the user’s browser before the rest of the page starts loading. This increases the initial load time, and some web crawlers are unable to index the site.
Is there a better way to render your app? Yes!
This is where server-side rendering for React comes in.
In this article, I want to introduce you to server-side rending (SSR) with React, reasons to use it, and some popular frameworks for rendering React on the server side. I would also like to address when SSR React does not make sense. This article is aimed at developers who are already working with React on the client side.
Before diving further into server-side rendering with React, let’s review some different types of web applications so that we can better appreciate the benefits of SSR applications.
Server-side rendering is when content on your webpage is rendered on the server and not on your browser using JavaScript. For example, with a typical PHP or WordPress site, the page is loaded from content that is coming via HTTP, which was rendered on the server and comes as fully rendered HTML.
This is in contrast to a React app built with CRA, which just sends a .js file to the client, and the clients’ browser JavaScript engine creates the markup after the .js file is loaded. Examples of traditional SSR languages/frameworks are PHP, Java, ASP.NET, and Node.js.
Traditional SSR apps were predominant in the early web until the influx of client-side libraries. Now, server-side rendered React apps use Node for the server, which is a key difference from traditional server-rendered apps (we’ll see how later on in this post).
SSR apps offer faster initial load times and better SEO performance compared to client-side rendered apps, there are some downsides. First, every request leads to a new page being re-rendered from the server to the browser. This means all the scripts, styles, and templates will be reloaded on the browser each time a request is sent to the server, resulting in a poor user experience.
Single-page applications (SPAs), or client-side rendered (CSR) applications, render content in the browser using JavaScript rather than refreshing pages with each request sent to the server. The server sends raw HTML documents while the content is rendered to the HTML document via the browser’s JavaScript.
Static-generated apps are pre-generated using a static site generator (such as Gatsby) and are stored on the hosting server as static HTML pages. You don’t require Node or other server-side support to deploy these static files to a static hosting server. As a result, when the app is first loaded in the browser, you’ll always get the whole content right away, and the app will then behave like a regular SPA.
Static-generated apps do not support for real-time rendering. Therefore, this type of rendering is not a good option when building real-time web applications, like forums or chat apps.
As I said before, server-side rendering initially means every page is rendered and loaded from the server. However, with the introduction of server-side (universal) React, things are slightly different.
The initial page is rendered from the server, meaning the subsequent pages load directly from the client. So you have the best of both worlds — the power of the initial server-side content plus the speedy subsequent loads, which requests just the content that is needed for future requests.
In addition to the above benefit, here are some other advantages you get when you move to SSR:
Arunoda Susiripala, formerly an engineer from Vercel, talks about performance being the main reason for moving to server-side rendering. SSR means there is no need for loaders or spinners for the initial load. This means that, generally speaking, SSR will outperform CSR.
SSR apps break JavaScript and CSS into chunks, optimize assets, and render pages on the server before serving to the client browser, resulting in a faster initial load time.
Faster load times lead to a better experience for the end user. This is one of the reasons many large companies are taking the SSR approach for their sites.
By now, you’ve probably heard that Google now crawls web apps built with JavaScript, so you’re better off having server-side rendered content ready for Google and other search engines to crawl your site. Per 10up:
Note that as of now, Google and Bing can index synchronous JavaScript applications — synchronous being the key word. If your app starts with a loading spinner, then fetches content via Ajax, the crawler will only wait a few seconds for loading to complete. This means if you have content fetched asynchronously on pages where SEO is important, SSR might be necessary.
With SSR search engine crawlers can explore the page to improve your app’s SEO performance. This is because all pages are rendered on the server with the relevant metadata, paragraphs, and headings before being served to the client, enabling you to get the benefits of a traditional website’s SEO.
After the initial load, Universal SSR apps behave like typical SPAs in that the transition between pages and routes is seamless. Only data is sent back and forth, with the HTML content holders not being re-rendered.
The other advantage of SSR is that you get an elaborate snippet and featured image when sharing your webpage’s content via social media. This will not be possible when you have just client-side rendered apps.
For example, here is what a server-side rendered React app looks like when shared on LinkedIn:

Getting started without frameworks is possible, but I wouldn’t recommend this approach since there are many considerations and moving parts in a React SSR app. For example, you have to handle bundling, minification, and hot reload (and more) all on your own.
However, if you want to go this route, I’d recommend reading this tutorial by Roger Jin.
I recommend picking up a framework if you want to render React on the server side. Here are some frameworks to consider:
Next.js is a great framework with a robust community. Next.js offers a lot of inbuilt features and you don’t have to worry about bundling, minification, or hot reloading. You are able to create pages as React components within files.
You may be used to this if you worked with PHP. In addition to the community and support, there are many large companies using Next.js in production including npm, Netflix, and Auth0.
Razzle, a project by Jared Palmer, has been gaining a lot of traction lately. From its GitHub page:
“Razzle is a tool that abstracts all complex configuration needed for SSR into a single dependency — giving you the awesome developer experience of create-react-app, but then leaving the rest of your app’s architectural decisions about frameworks, routing, and data fetching up to you.”
It’s easy to get started with Razzle, and it uses React Router 4 by default (unlike Next.js, which does not have an inbuilt router).
Remix is a React framework with server-side rendering, easy data fetching and mutations, and resilient developer experience which makes it easy to build web applications with great user experience.
Remix provides quick page loads and fluid transitions by utilizing distributed systems and native browser features rather than clumsy static builds. Because it uses the Web Fetch API rather than Node, it can run everywhere.
React is not a silver bullet. Perhaps your team is more familiar with Vue or another JavaScript framework. Maybe a static site will best suit your use case. If you don’t want to use React or if you would like to use a Static Site Generator, there are several alternatives.
Nuxt.js is a server-side rendering framework for Vue.js and is popular in the Vue.js community. If you are looking for alternatives Next.js or Razzle in the Vue.js world, do give this a try.
Angular also provides support for server-side rendering and prerendering solution with Angular Universal. If you are looking for alternatives Next.js, remix or Razzle in the Angular world, do give this a try.
SvelteKit is an open-source framework based on Svelte for creating high-performance web apps with a quick development time. It also includes server-side rendering that can be configured per-app or per-page, allowing you to turn off SSR when it’s not needed.
You would have seen almost all popular JavaScript developers talk about Gatsby. It is a React-based Static Site Generator that has won the hearts of many with its exceptional UX (user experience) and DX (developer experience).
To be precise, it doesn’t do SSR at runtime. Rather, Gatsby does server-side rendering with Node.js at build time, where it creates static HTML, CSS, and JS when deploying the site.
This leads to blazing-fast load times and has further optimizations such as route-based code splitting and prefetching.
I explored SSR React apps a few months back and created an app with Next.js and hosted it on Now — a serverless platform. N.B.Both Next and Now are from a company called Vercel, which is doing a great job at educating developers about React and serverless technologies, along with offering other fantastic products.
My app fetches data from a WooCommerce (a WordPress eCommerce plugin) REST API endpoint and displays it in a Next.js app. You can check out my app on GitHub and take a look at the demo here.
The short answer would be no. Not all apps need server-side rendering, especially apps with a dashboard and authentication that will not need SEO or sharing via social media. Plus, the expertise for building a server-rendered React app is higher than an app initialized using create-react-app.
Most importantly, SSR React apps cost a lot more in terms of resources since you need to keep a Node server up and running. There are times you may be better off going the serverless route when you want to choose server-side rendering for your React applications.
Client-side rendered React apps are great but having apps rendered on the server have noticeable benefits.
As we covered in this post, the benefits include:
I would highly encourage you to explore server-side rendering for your React apps and use it for your next product to see these benefits in action.
Install LogRocket via npm or script tag. LogRocket.init() must be called client-side, not
server-side
$ npm i --save logrocket
// Code:
import LogRocket from 'logrocket';
LogRocket.init('app/id');
// Add to your HTML:
<script src="https://cdn.lr-ingest.com/LogRocket.min.js"></script>
<script>window.LogRocket && window.LogRocket.init('app/id');</script>

Discover five practical ways to scale knowledge sharing across engineering teams and reduce onboarding time, bottlenecks, and lost context.

Discover what’s new in The Replay, LogRocket’s newsletter for dev and engineering leaders, in the March 4th issue.

Paige, Jack, Paul, and Noel dig into the biggest shifts reshaping web development right now, from OpenClaw’s foundation move to AI-powered browsers and the growing mental load of agent-driven workflows.

Check out alternatives to the Headless UI library to find unstyled components to optimize your website’s performance without compromising your design.
Hey there, want to help make our blog better?
Join LogRocket’s Content Advisory Board. You’ll help inform the type of content we create and get access to exclusive meetups, social accreditation, and swag.
Sign up now
11 Replies to "Improve app performance with React server-side rendering"
Thank you! That was very helpful to understand SSR, especially with the framework recommendations.
Nicely explained. Thanks!!!
I don’t see why client-side rendered apps should not be able to include social meta tags or (limited) onpage seo.
A bundled react app is embedded to an html page, so you could just include these in the wrapping html. You’re right about the dynamically rendered content inside of the react app though.
Both SEO and Sharing “issues” are very easily fixed with meta tags….
“However, now, server-side rendered React apps use Node for the server, which is a key difference from traditional server-rendered apps (we’ll see how later on in this post).”
In which way is that a key difference?
Thanks for your comment, Mike!
The main difference as a I see it: when you load React only on the client-side, it means your JavaScript files have to be loaded into your browser before it starts making calls – for example, to remote APIs. When it runs on the server-side, we can make those calls in the server and give the results from those calls in the initial render itself.
Hello @muhammad Mushim,
Is react by default server side or client side ?, I am new to react so please need your assistance
SEO is waaaay more than meta tags. It’s mostly relies on page content.
As Mike mentioned, the sharing “issue” is very easily fixed with proper meta tag usage in a client-side rendered application. The line “This will not be possible when you have just client-side rendered apps.” in this article is just dead wrong in reference to social media sharing.
what exactly is ‘proper usage’? just throwing meta tags in index.html in the public folder? good luck with that if you have multiple pages. react-helmet adds meta tags to other routes but none of the social media sharing sites can read from it since its client side.
just 1 doubt,
let say i have loaded the page with all the customer list using server side rendering and now i want to click on the customer and get the result of that customer by sending the customer ID in the payload (in the post api call). In this scenario how can we achieve this subsequent api calls as a server side rendering and without downloading the complete html page aging i just want to hydrate a piece of html page (the user info for the user which i have clicked) just below that clicked user ??
is there a way to achieve this using server side rendering ?
i know we can do this using client side rendering using vanilla reactjs
thanks in advance 😀