Laravel has dominated the PHP web framework landscape for many years now. If you build custom PHP websites, chances are you have used the framework once or twice and know that a Laravel update comes out every six months.
Laravel v9 released on 8 February 2022, and it offers plenty of new features.
While past releases of Laravel occurred every six months, the new release cycle going forward will be every 12 months, which ensures the release syncs with Symfony — which Laravel uses behind the scenes — and allows the development team more time to fix any bugs that occur when interacting with the Symfony framework.
Here is a breakdown of the most recent and upcoming Laravel releases:
| Version | PHP Version | Release | Bug Fixes Until | Security Fixes Until |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 6 (LTS) | 7.2 – 8.0 | September 3rd, 2019 | January 25th, 2022 | September 6th, 2022 |
| 7 | 7.2 – 8.0 | March 3rd, 2020 | October 6th, 2020 | March 3rd, 2021 |
| 8 | 7.3 – 8.1 | September 8th, 2020 | July 26th, 2022 | January 24th, 2023 |
| 9 (LTS) | 8.0 – 8.1 | February 8th, 2022 | February 8th, 2024 | February 8th, 2025 |
| 10 | 8.0 – 8.1 | February 7th, 2023 | August 7th, 2024 | February 7th, 2025 |
You can see that version 9 is the new long-term support version, replacing version 6, which will no longer be supported by the end of this year. As of this month, v7 is no longer supported at all, so if you are using Laravel 6 or 7, it’s time to upgrade to v9.
In this article, we’ll cover the current major changes in Laravel 9, but expect to see more features and changes soon.
Laravel uses Symfony 6, which requires at least PHP 8. PHP 8 comes with the new just-in-time (JIT) compiler, the OPcache extension, named arguments, and more.
Swift Mailer, which has been used in Laravel for years, is being removed and will no longer be maintained. In Laravel v9 and future releases, you’ll have to use Symfony Mailer. If you are upgrading an existing Laravel instance, check out the upgrade guide.
You can now use the controller method of the Laravel 9 Route class to define the controller that will be used for every route in a route group.
use App\Http\Controllers\PostController;
Route::controller(PostController::class)->group(function () {
Route::get('/post/{id}', 'show');
Route::post('/post', 'store');
});
In Laravel 9, you can now use the Illuminate\Database\Eloquent\Casts\Attribute to declare a model prefix with a single non-prefixed term. Using one method call, you can now both get and set attributes.
use Illuminate\Database\Eloquent\Casts\Attribute;
public function username(): Attribute
{
return new Attribute(
get: fn ($value) => strtoupper($value),
set: fn ($value) => $value,
);
}
Fulltext indexes and where clausesIf you are using MySQL or PostgreSQL in your Laravel application, you can now use the fulltext method on the column definitions in your migration files to generate full-text indexes.
$table->text('content')->fullText();
Then, you can use the whereFullText and orWhereFullText methods to add full-text where clauses to your queries.
$laravelPosts= DB::table('post')
->whereFullText('content', 'laravel')
->get();
Laravel v9 ships with the new Laravel Scout database engine. It provides full-text search capabilities to Eloquent models. It uses model observers to keep search indexes in sync with Eloquent records and is a good choice for applications that use a small- or medium-sized database or have a light workload. This engine will use “where-like” clauses when filtering results from your database.
To use it, just add the Laravel\Scout\Searchable trait to a model:
<?php
namespace App\Models;
use Illuminate\Database\Eloquent\Model;
use Laravel\Scout\Searchable;
class Article extends Model
{
use Searchable;
}
Laravel v9 includes a complimentary Next.js frontend implementation in its Breeze starter kit. By using this starter kit scaffolding, you can build Laravel applications that serve as both a backend and a JavaScript frontend using Laravel Sanctum authentication.
If you need to transform a raw Blade template into valid HTML, you can now do that with inline Blade rendering.
use Illuminate\Support\Facades\Blade;
return Blade::render('Hello, {{ $name }}', ['name' => 'Stephan Miller']);
The new query builder interface in Eloquent makes it possible to type hint Eloquent queries. In the past, it was difficult to tell whether you were dealing with Query\Builder, Eloquent\Builder, or Eloquent\Relation, leaving devs guessing on what to fix whenever a TypeError showed up.
return Model::query()
->whereNotExists(function($query) {
// $query is a Query\Builder
})
->whereHas('relation', function($query) {
// $query is an Eloquent\Builder
})
->with('relation', function($query) {
// $query is an Eloquent\Relation
});
You can now type hints with a PHP enum in your Laravel route definitions. Laravel will then only invoke the route if the route contains a valid enum in the URI and will return a 404 if one of the enums is not found.
enum Fruit: string
{
case Apple = 'apple';
case Cherry = 'cherry';
}
This route will only be invoked if the {fruit} route matches one of the enums.
Route::get('/fruits/{fruit}', function (Fruit $fruit) {
return $fruit->value;
});
Laravel 9 can now automatically scope the query to retrieve a nested model by its parent in a route definition by using conventions to guess the relationship name of the parent. Here is an example of using scope bindings:
use App\Models\Article;
use App\Models\User;
Route::get('/users/{user}/articles/{article}', function (User $user, Article $article) {
return $article;
})->scopeBindings();
You can also use scope bindings on a group of route definitions.
use App\Models\Article;
use App\Models\User;
Route::get('/users/{user}/articles/{article}', function (User $user, Article $article) {
return $article;
})->scopeBindings();
If you have ever tried to write your own pagination code, you know it’s not fun. Laravel 9 makes it simple to add pagination to the pages in your app with Bootstrap 5 pagination views.
All you have to do is include the Illuminate\Pagination\Paginator and call its useBootstrapFive method in the boot method of your app’s App\Providers\AppServiceProvider class.
use Illuminate\Pagination\Paginator;
/**
* Bootstrap any application services.
*
* @return void
*/
public function boot()
{
Paginator::useBootstrapFive();
}
Now that Laravel is using PHP 8, its \Illuminate\Support\Str facade will use PHP 8 string functions, which come with some new methods, including str_contains, str_starts_with, and str_ends_with. New helpers include append and snake.
$string = str('Bob')->append(' Smith'); // 'Bob Smith'
$snake = str()->snake('LaravelIsGreat'); // 'laravel_is_great'
Another helper that was added is the to_route function. This function creates a redirect HTTP response for a named route. You can use it to redirect to named routes from routes and controllers.
return to_route('posts.show', ['post' => 25]);
You can now cast attribute values to PHP enums in Laravel 9. Here is an example of using casts in a model:
use App\Enums\UserStatus;
/**
* The attributes that should be cast.
*
* @var array
*/
protected $casts = [
'status' => UserStatus::class,
];
After you have defined the cast in your model, this attribute will be automatically cast to and from the enum.
if ($user->status == UserStatus::optin) {
$user->status = UserStatus::verified;
$user->save();
}
I don’t know how many times I’ve Googled, “How to set a checkbox checked in Laravel.” Laravel v9 has made this easier. Now you can use the @checked directive to set a checkbox as checked. If it evaluates to true, it will echo checked.
<input type="checkbox"
name="optin"
value="optin"
@checked(old('optin', $user->optin)) />
There is also a similar @selected directive for setting the selected option in a select.
<select name="notification">
@foreach ($notifications as $notification)
<option value="{{ $notification }}" @selected(old('notification') == $notification)>
{{ $notification }}
</option>
@endforeach
</select>
The Illuminate\Validation\Rule validation class now has a new forEach method that accepts a closure that will run on each iteration of the array attribute being validated. The closure will return an array of rules to assign to the array element.
use App\Rules\HasPermission;
use Illuminate\Support\Facades\Validator;
use Illuminate\Validation\Rule;
$validator = Validator::make($request->all(), [
'companies.*.id' => Rule::forEach(function ($value, $attribute) {
return [
Rule::exists(Company::class, 'id'),
new HasPermission('manage-company', $value),
];
}),
]);
Laravel now comes with the Soketi echo server, a Laravel Echo compatible WebSocket server written for Node.js. It is an open-source alternative to Ably and Pusher for developers who prefer to manage their own WebSocket servers.
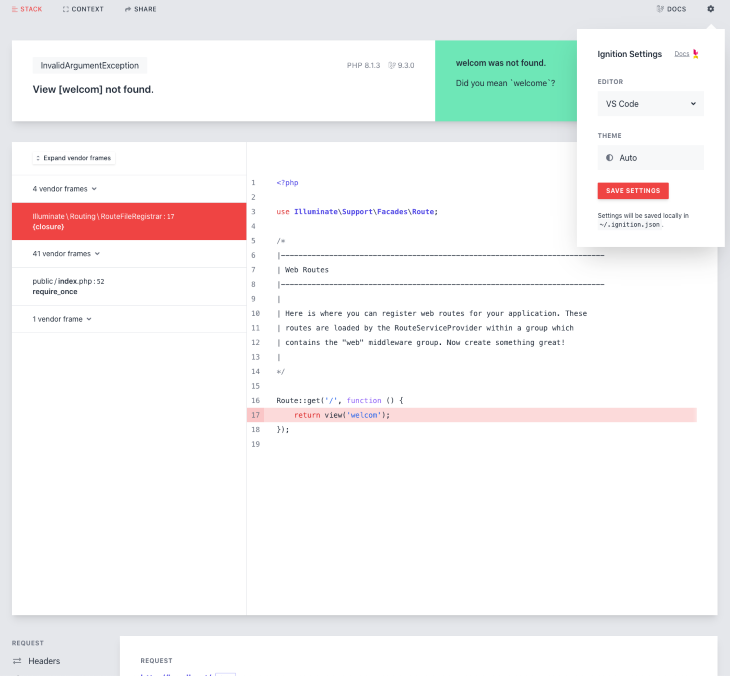
Laravel 9 also has a new and improved exception page that was redesigned from the ground up. You can choose between light and dark themes, and it even has an “open in editor” functionality.
Anonymous stub migration is now the default behavior when you perform a Laravel migration. This feature was available in Laravel 8.3, but is the default in Laravel v9. This feature prevents name collisions with migration classes. Before this change, it was difficult to re-create a database from scratch if you reused a class name. Now, you won’t have to worry about this.
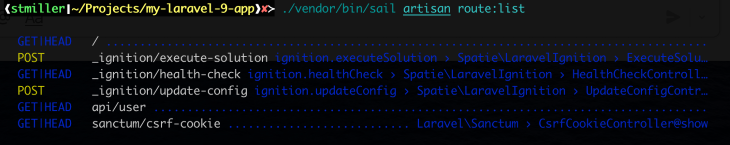
Laravel already had the route:list Artisan command, but it now offers a better, color-coded breakdown of the routes in your app.
In Laravel v9, Flysystem was migrated from v1.x to v3.x. Flysystem handles all the file manipulation functions that the Storage facade provides. Some changes you will see are:
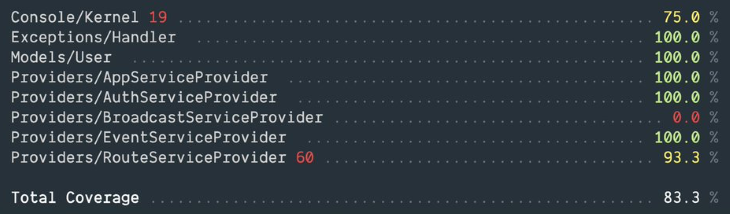
put, write, and writeStream methods now overwrite existing files by defaultput, write, and writeStream methods no longer throw an exception on a write errornull will be returnedtrueThe Artisan test command now has a --coverage option, which will output the test coverage percentages in the CLI output.
Not the biggest change in the list, but you no longer need the server.php file in your project. It will now be included with the rest of the framework.
If you are ready to try the new version of Laravel, there are a few ways you can do it. If you already have composer installed, you can create a new Laravel project with it.
composer create-project laravel/laravel my-laravel-9-app cd my-laravel-9-app php artisan serve
You can also install Laravel globally with composer and use it to create a new project.
composer global require laravel/installer laravel new my-laravel-9-app cd my-laravel-9-app php artisan serve
If you have Docker Desktop on Mac, you can run these commands to launch a Docker image running Laravel 9:
curl -s "https://laravel.build/my-laravel-9-app" | bash cd my-laravel-9-app ./vendor/bin/sail up
You can change my-laravel-9-app to whatever you want. The last command uses Laravel Sail, which is a lightweight command-line interface for interacting with Laravel’s Docker configuration. The first time you run the command may take a few minutes. After that, the app will start quicker.
In Windows, you can run the same commands above in a new terminal session in your WSL2 Linux operating system. The same commands also work in Linux — you just have to have Docker Compose installed.
Is Laravel 9 worth the extra wait? I think so. There are many improvements and more to come now that the development team will push new features during the current release. It is also the new LTS version, so it will be around for a while. Good luck with your new Laravel 9 apps!
Install LogRocket via npm or script tag. LogRocket.init() must be called client-side, not
server-side
$ npm i --save logrocket
// Code:
import LogRocket from 'logrocket';
LogRocket.init('app/id');
// Add to your HTML:
<script src="https://cdn.lr-ingest.com/LogRocket.min.js"></script>
<script>window.LogRocket && window.LogRocket.init('app/id');</script>
Would you be interested in joining LogRocket's developer community?
Join LogRocket’s Content Advisory Board. You’ll help inform the type of content we create and get access to exclusive meetups, social accreditation, and swag.
Sign up now
Discover how to use Gemini CLI, Google’s new open-source AI agent that brings Gemini directly to your terminal.

This article explores several proven patterns for writing safer, cleaner, and more readable code in React and TypeScript.

A breakdown of the wrapper and container CSS classes, how they’re used in real-world code, and when it makes sense to use one over the other.

This guide walks you through creating a web UI for an AI agent that browses, clicks, and extracts info from websites powered by Stagehand and Gemini.