The world of frontend development is fast-paced and can be pretty daunting to even the most experienced developers.

Each new framework, design system, and architecture pattern comes with rather bold claims about changing the future of how we’ll write code.
In this post, we’ll look at Rust — a language empowering everyone to build reliable and efficient software.
I know what you’re thinking: “I’ve heard this rhetoric before.”
You’re not wrong. Nevertheless, I can assure you that Rust lives up to the hype.
The goal of this article is to introduce you to Rust and explain why it’s useful.
As a frontend developer, you’ve probably mostly interacted with JavaScript as your primary language. Its dynamic, loosely-typed nature can make it a little difficult to quickly pick up other languages that doesn’t share these traits.
However, Rust was designed to make the learning curve of strict-typed languages less steep, meaning you won’t experience the typical frustration of learning languages like c++.
There are very minor similarities between Rust and JavaScript, such as the use of let and const for variable declarations.
This isn’t a huge deal, but I found that I felt more at ease using Rust since I was already familiar with these keywords.
Another benefit to Rust is that the syntax isn’t verbose — it’s very straightforward and clean.
According the the official documentation, “The Rust programming language helps you write faster, more reliable software. High-level ergonomics and low-level control are often at odds in programming language design; Rust challenges that conflict.
By balancing powerful technical capacity and a great developer experience, Rust gives you the option to control low-level details (such as memory usage) without all the hassle traditionally associated with such control.”
If you’re entirely new to programming, Rust probably isn’t for you.
The official documentation inclusive assumes you’ve written code in another programming language, but it doesn’t make any assumptions about which one.
If you’re usually concerned with memory-efficient code, Rust will be an especially good fit for you.
With Rust, anyone can do systems-level work traditionally reserved for the elite club of coders who have mastered the low-details of memory management, data representation, and concurrency.
Sound boring?
Here are some exciting facts: Rust isn’t limited to low-level systems programming, and it’s expressive and ergonomic enough to make CLI apps, web servers, and many other kinds of fun piece of software you’re excited to build.
Setting up Rust is easy regardless of your operating system.
I don’t want to clutter this piece, so just head over to the installation guideline page and it will automatically detect your OS and walk you through the recommended setup for your machine.
Note : If you’re on a Linux or Mac, you should see something like in the image below:
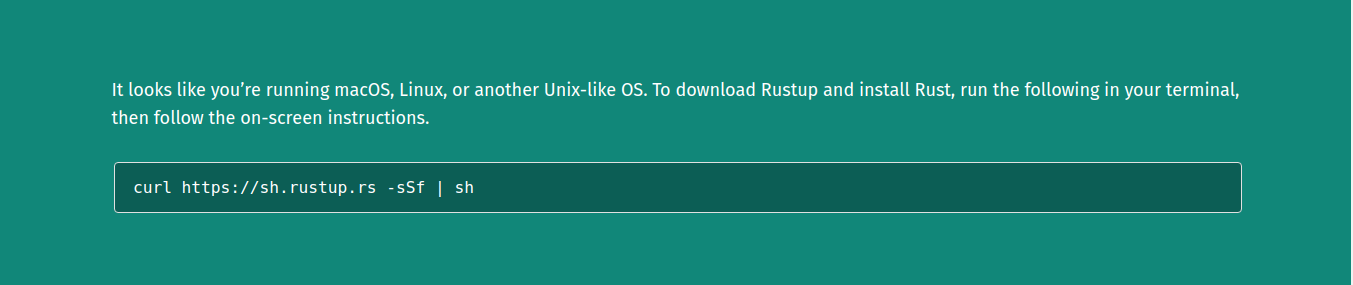
For the purposes of this post, we’ll be using a UNIX-based system (All Linux distributions and Macs). Run the command below in your terminal and follow the onscreen instructions.
Note: If you are using a Windows subsystem for Linux, the command works for you too.
curl https://ah.rustup.rs -sSf | sh`
If you’re on a Windows machine, yours would look something like this:
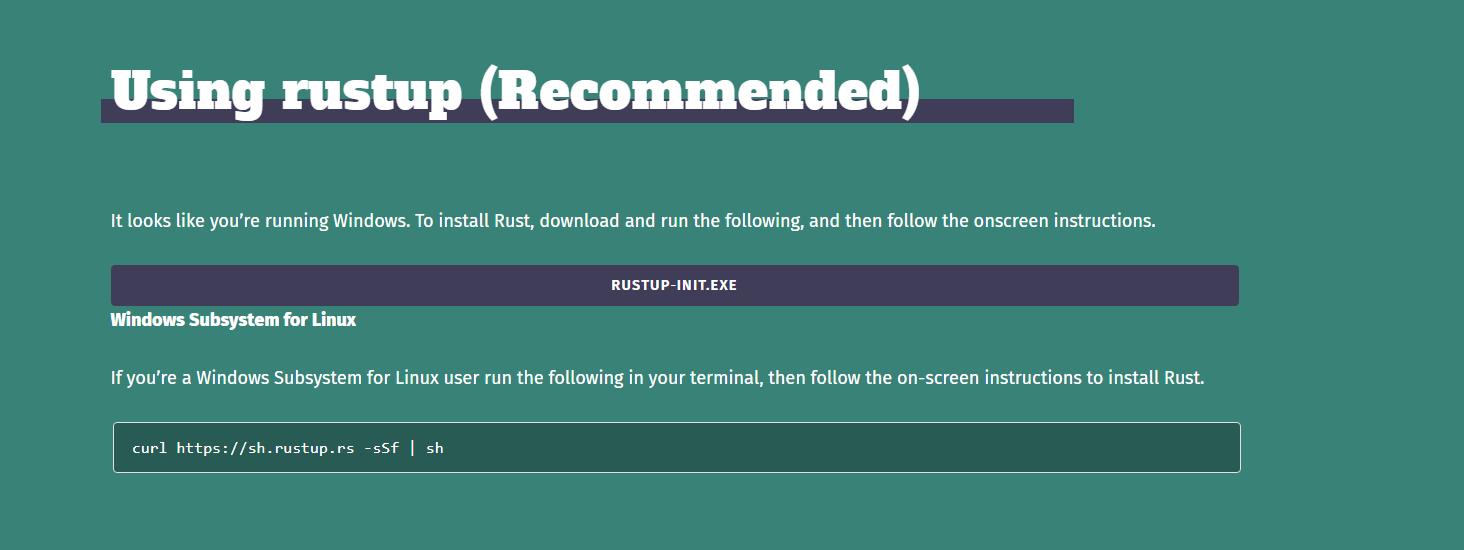
As usual, click on the link to download the executable and follow the onscreen instructions.
In this article, we’ll use VS Code.
To boost efficiency, I’d recommend using the Rust extension, which helps with code-completion, error detection, etc.
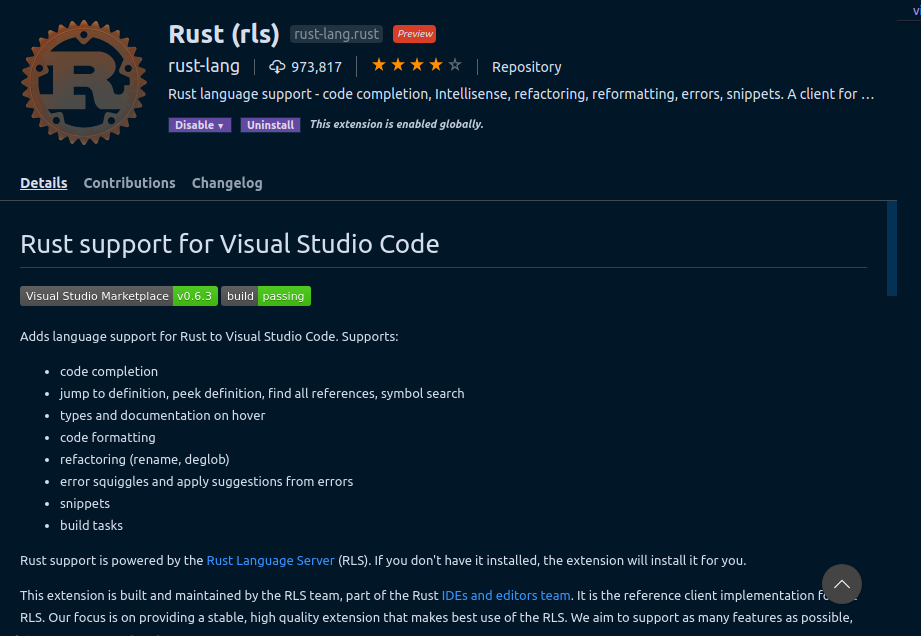
It’s worth noting that regardless of your code editor of choice, there are bound to be extensions or plugins for Rust. Check your editor’s extensions marketplace and you should see one.
Install it as instructed and you’re good to go.
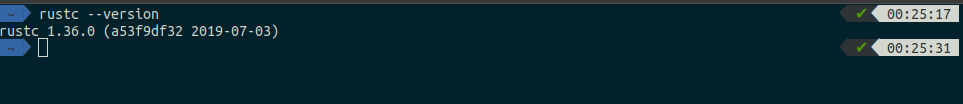
Once you’ve gotten all that out of the way, run the following command to see if you’ve got Rust installed on your machine.
rustc --version
If all went well, you should see something like this:
If you’ve followed the installation properly but failed to run this command in your terminal, the most likely cause is that you didn’t configure the PATH environment variable properly.
Head over to the installation guide to see how you can sort that out.
Note: remember to restart your terminal after the installation procedure before you run this command.
You don’t need to scour the internet for books or resources to learn Rust.
With your installation comes a copy of the book “The Rust Programming Language” by Steve Klabnik and Carol Nichols, with contributions from the Rust community.
It walks you through setup, basics, and advanced topics with a hands-on approach. It’s a top-notch resource.
You can read the book online or use the command below for an offline copy. Be sure to install rustup on your machine if you didn’t do so during your initial Rust setup.
rustup docs --book
Alternatively, you can choose to do the rustlings course. It guides you through downloading and setting up the Rust tool chain, and teaches you the basics of reading and writing Rust syntax on the command line.
You can also check out Rust by Example if reading hundreds of pages about a language isn’t really your style.
While the book talks about code with a lot of words, RBE shows off a bunch of code, and keeps the talking to a minimum. It also includes fun exercises.
Having come this far, you’re probably wondering how you can get your hands dirty with Rust on the frontend.
Typically, to use Rust (or any other language aside from JavaScript) on the frontend, you need to use WebAssembly.
If you’re not already familiar with WebAssembly (wasm for short), it is a binary instruction format that promises near native performance, allowing developers to build applications with high level languages like rust , c++, or any language of your choice (other than JavaScript of course) on the web for client and server applications.
Learn more here.
A key advantage here is that Rust is compiled down to machine code, so there is no virtual machine.
There also isn’t an interpreter sitting between your code and the machine, making it highly performant.
As this benchmark suggests, a direct comparison of REST API performance with Rocket for Rust and Restify for Node.js shows that Rust handles 72,000 requests per second compared to Node.js’ 8,000, and uses just over 1 mb of memory when idle compared to Node.js’ 19 mb.
This comes as no surprise since Rust is a systems programming language.
Rust responds to requests nearly 100 times faster on average than Node, and you won’t run into the compile time errors that JavaScript apps are usually prone to.
Once you’re done with the setup for the standard Rust development tool chain, setting up for frontend dev is also easy.
First, you need to get wasm-pack installed. It’s a comprehensive package for building, testing, and publishing Rust-generated WebAssembly.
Run the command below in your terminal if you’re on a Mac or Linux distribution:
curl https://rustwasm.github.io/wasm-pack/installer/init.sh -s Sf | sh
For Windows machines, download the installer, run it, and follow the on-screen instructions.
You can also install cargo-generate by using an existing git repository as a template. It helps you quickly get started with a new Rust project.
Install with this command:
cargo install cargo-generate
This should work fine if you have the Rust tool-chain properly configured on your machine. Cargo is the package manager for Rust.
You also need to have npm installed. Follow these instructions to install npm.
If you already have npm installed, be sure you’re up to date. Do so with the following command:
npm install npm@latest -g
Here is a good book to get you started with Rust on the frontend
Rust has a lot of advantages and uses:
Then comes my personal favorite: its error messages are as descriptive as it gets. It features a friendly compiler with useful error messages and top-notch tooling. You really can’t ask for more.
Here’s an example:
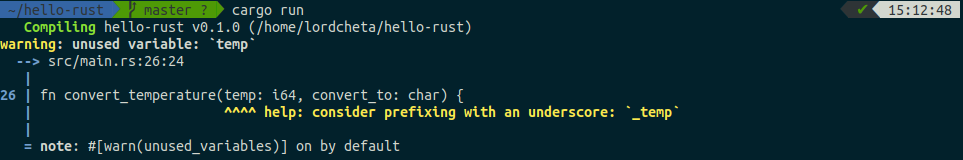
Rust is completely reliable. It’s rich type system and ownership model guarantee memory-safety and thread-safety and enable you to eliminate many classes of bugs at compile-time.
Here’s something else I love about Rust: when you write a program in rust, that program can run on any machine without Rust installed on it.
JavaScript web applications struggle to attain and retain reliable performance. JavaScript’s dynamic type system and garbage collection pauses don’t help. Seemingly small code changes can result in drastic performance regressions if you accidentally wander off the JIT’s happy path.
Rust gives programmers low-level control and reliable performance. It is free from the non-deterministic garbage collection pauses that plague JavaScript. Programmers have control over indirection, monomorphization, and memory layout.
Rust and WebAssembly integrate with existing JavaScript tooling. It supports ECMAScript modules, and you can continue using the tooling you already love, like npm and Webpack.
When it comes to performance advantages, code size is incredibly important since the .wasm must be downloaded over the network. Rust lacks a run time, enabling small .wasm sizes because there is no extra bloat included like a garbage collector. You only pay (in code size) for the functions you actually use.
Existing code bases don’t need to be thrown away. You can start by porting your most performance-sensitive JavaScript functions to Rust to gain immediate benefits.
From web apps to embedded systems and CLI apps, Rust provides a solid tool set to create highly-sustainable and scaleable code bases.
There’s a popular saying: “Always bet on JavaScript.”
You can rest assured the same holds true for Rust.
The odds are staggeringly in its favor. Several companies already use Rust in production, including npm, Yelp, Dropbox, and others.
You can learn more about how these companies use Rust here.
Whether you’re a team of developers, students, companies, open source developers, or anyone that values speed and stability, Rust is for you.
Debugging Rust applications can be difficult, especially when users experience issues that are hard to reproduce. If you’re interested in monitoring and tracking the performance of your Rust apps, automatically surfacing errors, and tracking slow network requests and load time, try LogRocket.
LogRocket lets you replay user sessions, eliminating guesswork around why bugs happen by showing exactly what users experienced. It captures console logs, errors, network requests, and pixel-perfect DOM recordings — compatible with all frameworks.
LogRocket's Galileo AI watches sessions for you, instantly identifying and explaining user struggles with automated monitoring of your entire product experience.
Modernize how you debug your Rust apps — start monitoring for free.
Would you be interested in joining LogRocket's developer community?
Join LogRocket’s Content Advisory Board. You’ll help inform the type of content we create and get access to exclusive meetups, social accreditation, and swag.
Sign up now
Which AI frontend dev tool reigns supreme in July 2025? Check out our power rankings and use our interactive comparison tool to find out.

Learn how OpenAPI can automate API client generation to save time, reduce bugs, and streamline how your frontend app talks to backend APIs.

Discover how the Interface Segregation Principle (ISP) keeps your code lean, modular, and maintainable using real-world analogies and practical examples.

<selectedcontent> element improves dropdowns
2 Replies to "Rust for frontend developers"
Really appreciate the article… Been enjoying learning Rust. I did remove it from echojs as it was too far off topic though.
Also, for anyone reading, may want to take a look at Yew stack.
https://github.com/yewstack/yew