
Smart contracts is a topic that has grown in significance in recent years, as they more frequently become the go-to solution for ensuring security and visibility for all parties engaging in a binding agreement.

In this blog, we’re going to take a look at smart contracts — what they’re all about and how they’re being used across different industries.
The Replay is a weekly newsletter for dev and engineering leaders.
Delivered once a week, it's your curated guide to the most important conversations around frontend dev, emerging AI tools, and the state of modern software.
Smart contracts are programs that execute based on specified logic and agreements. These programs run on decentralized networks whose ledgers cannot be tampered with or changed after registering a transaction.
A Solana smart contract, for example, stores details of the transaction in the ledger of every computer on the network — the information involved in the transaction can’t be altered by any party, not even the Solana Foundation itself.
Smart contracts are a reliable way to carry out transactions requiring trust, transparency, and anonymity among stakeholders.
Jump ahead using this table of contents:
Following the launch of Ethereum — the first smart contract platform that runs on blockchain technology — the rollout of subsequent smart contract platforms on blockchain, directed acyclic graph structures, and other distributed ledger technologies (DLTs) have become popular.
Many applications have rolled out on these smart contract platforms, with the most popular being decentralized finance (DeFi), where participants can trade assets anonymously, unlike traditional finance systems, which have a lot of state- and federally-mandated restrictions.
Below are listed examples of popular smart contract platforms:
Popular DAG platforms include:
The advent of smart contracts and the token economy has opened up various sectors of the global economy in methods of transactions and ownership due to the numerous possible applications they can fulfill.
Let’s jump in and review some unusual applications of smart contracts in different industries.
Key aspects of smart contracts to note:
Certificate and document forgery has been a significant issue individuals and institutions have faced for years. Physical and digital documents are prone to loss, and there are often no means to authenticate certificates quickly without contacting the issuer, which is a lengthy process.
In cases where timely and secure authentication is required, smart contracts can help eliminate the complexities of the process, ensuring the authenticity of a certificate or document using the explorer of the underlying distributed ledger technology (DLT).
The certificate’s public key is scanned on the explorer in this case, and since the DLT cannot be altered, the certificate’s authenticity can be trusted.
Distributed ledger technology also aids the preservation and availability of files since copies of the ledger are maintained across numerous servers.
Using smart contracts for document preservation and accessibility ensures:
Monetary transactions require high levels of trust and transparency — especially important for companies in industries which deal with large volumes of financial transactions, like insurance.
When we consider existing traditional money management processes like escrows, for example, they can be susceptible to rare human interference.
Payrolls in their current form for organizations operating in a global supply chain frequently lack self-sustainability because the global banking system is complicated and paying employees and managing streams of transactions from different countries can be difficult.
This is because many countries operate with differing systems that typically require some kind of mediative process in transactions — this can be problematic in an increasingly remote-first world where location is less of a factor in employment and business than it’s ever been.
Additionally, other areas of use, like national tax systems, can benefit as previously inefficient administrative costs and maintenance can be reduced.
Smart contracts provide solutions to these payment problems as they are transparent, secure, and inexpensive to maintain. In addition, they have a long lifespan and can be easily automated to suit whatever payment need process is in question, curbing the mismanagement of funds.
Use cases for smart contracts in administrative payments and billing include:
The decentralized and transparent nature of distributed ledger technologies can be of great use in areas like polling, notably voting processes and other statistical collations.
Smart contracts for voting, population censuses, and statistical collation aid in building confidence in outcomes, since no one individual or organization can preside over the collation of data and reading of results — everyone can see the facts and figures for themselves.
Smart contracts can be programmed to feed the state of the process as they go live — as a result, it’s easier for users to accept and trust the process.
The benefits of using smart contracts for statistical collation include:
The Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations estimates over one-third of food worldwide is wasted, and this loss is estimated to be worth approximately $940 billion. They estimate around 957 million people across 93 countries do not have enough to eat.
In the health sector, there are numerous cases of wasted medicine and materials which could have found purpose in other medical facilities; but due to the lack of a system that keeps track of what is obtainable, are not received.
Smart contracts could reduce, if not eradicate, the wastage of food and medical supplies, among others. An IoT smart contract can be written to assign public keys to packages whose data would exist on distributed ledger technology, along with the package’s location and — if necessary — the medical facility that owns it.
This way, stakeholders are able to access their needs and we can find matches between markets and commodities more effectively to build more efficiency.
A good use case for these types of smart contracts would be a situation where different blood types are available in separate locations, but facilities are lacking the visibility necessary to procure them. Thanks to smart contracts, it’s possible to remedy this and allow further flexibility within supply chains to respond effectively.
Using smart contracts for health and agricultural supply chain management means that:
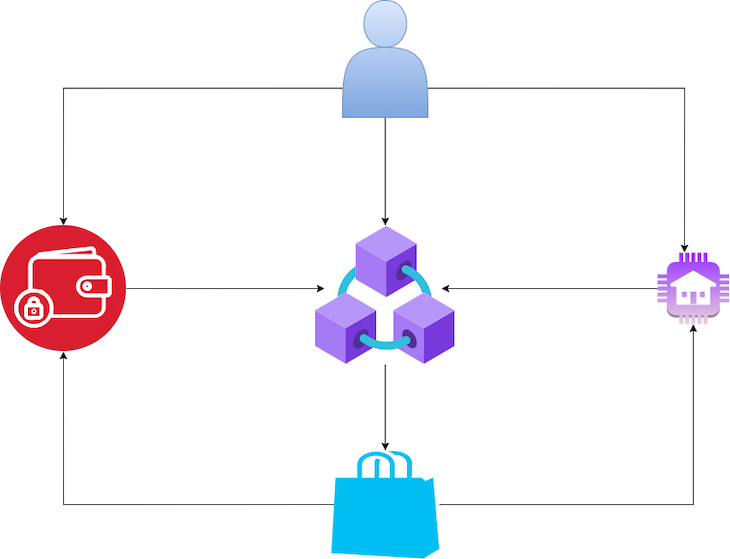
The token economy opens a broader range of opportunities when it comes to what is obtainable with real-world assets, creating markets that are readily, easily accessible and offer a broader scope of products than what currently exists.
The token economy changes how commodities are bought and sold and how funding can be raised for big projects.
Currently, if a project is to be built and funding raised, this requires lots of paperwork and time — both increasingly valuable resources in a digitized world. However, using a smart contract for the same process is a matter of clicking a button and signing on to a wallet.
In addition, various parts of an asset can be tokenized in such a way that different people can hold and own portions. They can sell them at any time on designated markets, just like how we’ve seen non-fungible tokens (NFTs) trading skyrocket.
Properties like real estate can be sold online at any time without the lengthy process and paperwork involved because of a smart contract. This is one of the numerous ways smart contracts create new market opportunities and provide flexibility.
The benefits of using smart contract technology in real estate and crowdfunding include:
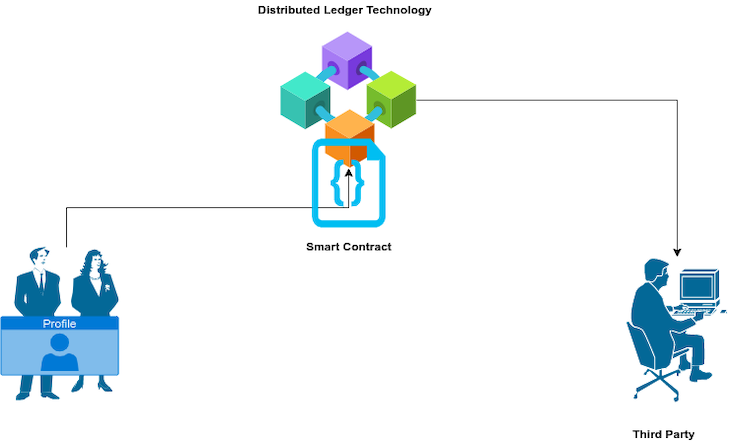
Existing technologies used to prevent crimes like identity theft aren’t as effective as they should be, as many of them do not give the owner total control of his data and the information they choose to give out.
Digital Identifier (DIDs) smart contracts built on distributed ledger technologies (decentralized) give individuals total control of their data and allow them to share the content of their data as they please, increasing security and reducing the possibility of data mismanagement or a breach.
Smart contracts help ensure the following for identity management:
Distributed ledger technologies allow for flexibility and better resource management while helping us with accountability and increasing trust in our daily financial activities.
With the increase of smart contract implementation across virtually all industries to varying degrees, smart contracts are a trend we can expect to become accustomed to.
Client-side issues that impact users’ ability to activate and transact in your apps can drastically affect your bottom line. If you’re interested in monitoring UX issues, automatically surfacing JavaScript errors, and tracking slow network requests and component load time, try LogRocket.
LogRocket lets you replay user sessions, eliminating guesswork around why bugs happen by showing exactly what users experienced. It captures console logs, errors, network requests, and pixel-perfect DOM recordings — compatible with all frameworks.
LogRocket's Galileo AI watches sessions for you, instantly identifying and explaining user struggles with automated monitoring of your entire product experience.
Modernize how you debug web and mobile apps — start monitoring for free.

Signal Forms in Angular 21 replace FormGroup pain and ControlValueAccessor complexity with a cleaner, reactive model built on signals.

Discover what’s new in The Replay, LogRocket’s newsletter for dev and engineering leaders, in the February 25th issue.

Explore how the Universal Commerce Protocol (UCP) allows AI agents to connect with merchants, handle checkout sessions, and securely process payments in real-world e-commerce flows.

React Server Components and the Next.js App Router enable streaming and smaller client bundles, but only when used correctly. This article explores six common mistakes that block streaming, bloat hydration, and create stale UI in production.
Would you be interested in joining LogRocket's developer community?
Join LogRocket’s Content Advisory Board. You’ll help inform the type of content we create and get access to exclusive meetups, social accreditation, and swag.
Sign up now