A speech-to-text feature turns your voice into text, and a text-to-speech feature reads the text out loud. By adding this feature, users can interact with your app via voice (in addition to user gestures), enhancing the user experience. This can help you build, in essence, a Google assistant-like app.
The way it works is that you say something or ask the app something, and the app processes your request and then speaks the result.
In this tutorial, we’ll build an example using the speech recognition and text-to-speech plugin.
We’ll go through a step-by-step process for the example that gives you a base for building a voice assistant app. We’ll also cover cases not handled by the plugin by default, such as continuous listening on Android devices.
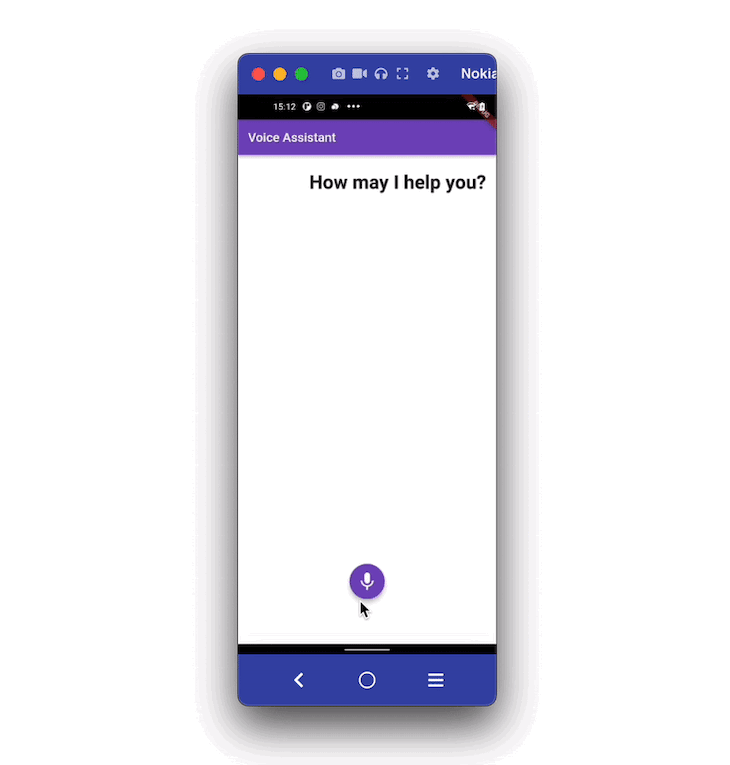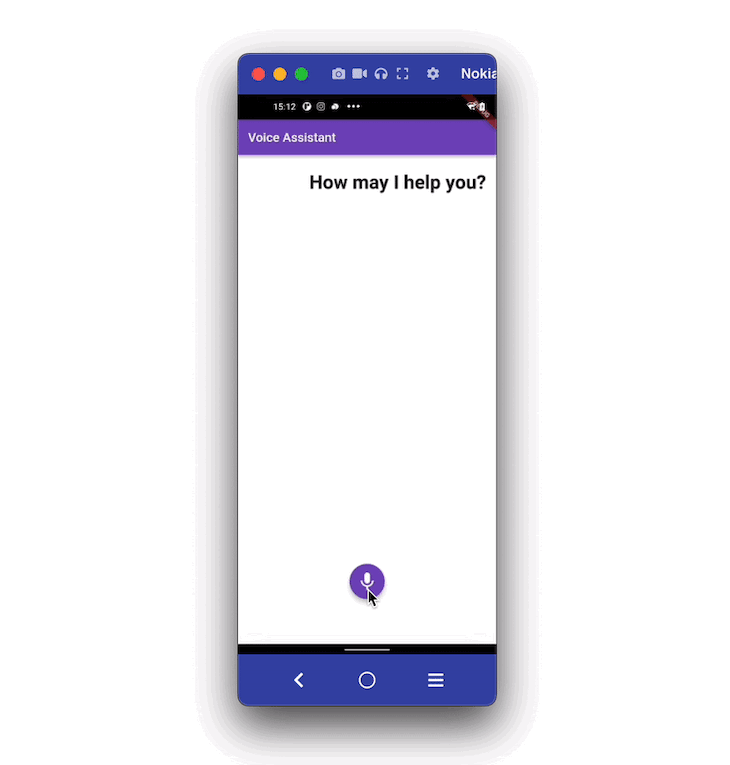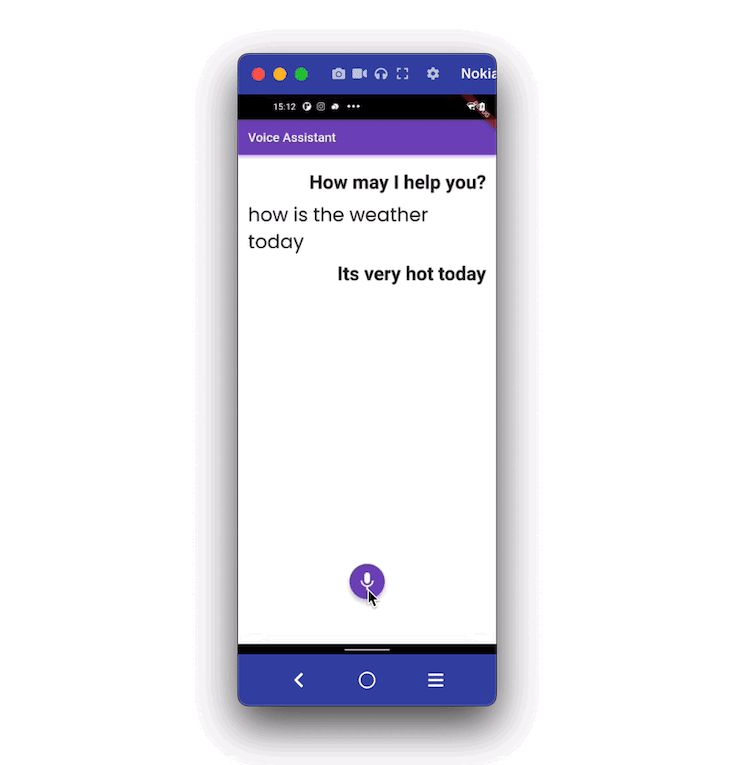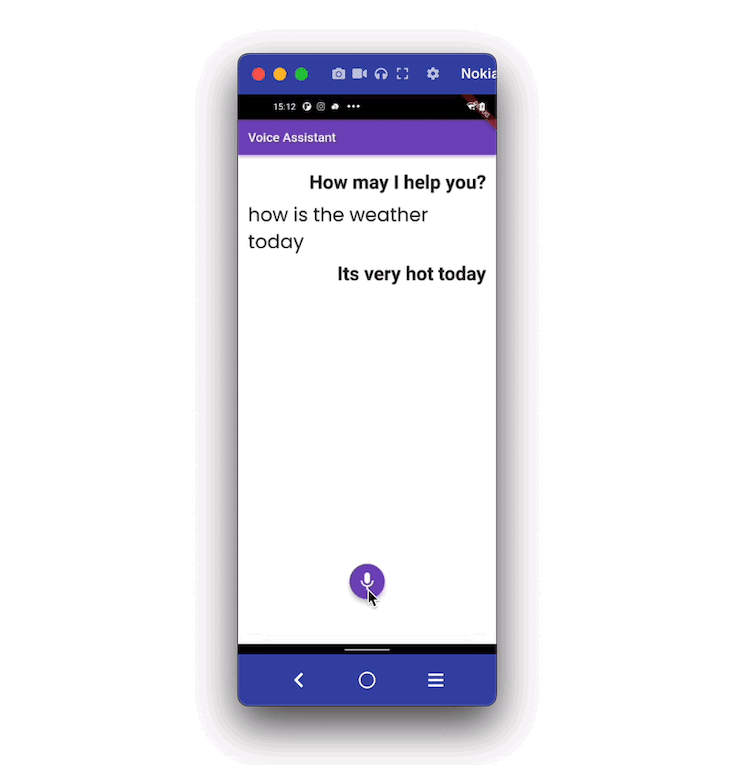
Here’s how it looks when completed:
Here’s what we are going to cover in this tutorial:
In the example app, when a user taps on the mic button, the app starts to listen. As the user begins speaking, the voice is converted into text and displayed on the screen. Users can stop the listening service by clicking on the stop button.
You can implement such a requirement by utilizing the speech recognition plugin. Internally, it uses Speech API for iOS and SpeechRecognizer for Android. It allows you to add speech recognition for any locale with devices supporting iOS10+ and Android 4.1+.
This plugin offers several helpful methods that you can use to start, stop, and cancel the listening.
Here are the step-by-step instructions on adding the speech-to-text support in Flutter.
The very first step starts with adding dependency inside the pubspec.yaml file.
The contents inside the pubspec.yaml file shoud look like this:
dependencies:
flutter:
sdk: flutter
cupertino_icons: ^1.0.2
speech_recognition: ^0.3.0+1 #NEW
For the plugin to record audio, you need to give permission for both the Android and iOS platform. For this, you can update the platform-specific files.
Locate the AndroidManifest.xml file at the your_project/android/app/src/main/AndroidManifest.xml and update the file as follows:
<manifest xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
package="com.example.speech_to_text_demo">
<!-- 1. Permission -->
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.RECORD_AUDIO" />
<!-- 2. To overcome bind to recognition service failed issue -->
<queries>
<package android:name="com.google.android.googlequicksearchbox"/>
</queries>
<application
android:label="speech_to_text_demo"
android:name="${applicationName}"
android:icon="@mipmap/ic_launcher">
<activity
android:name=".MainActivity"
android:exported="true"
android:launchMode="singleTop"
android:theme="@style/LaunchTheme"
android:configChanges="orientation|keyboardHidden|keyboard|screenSize|smallestScreenSize|locale|layoutDirection|fontScale|screenLayout|density|uiMode"
android:hardwareAccelerated="true"
android:windowSoftInputMode="adjustResize">
</application>
</manifest>
Here’s what is going on in the code above:
android.permission.RECORD_AUDIO to record audioLocate the info.plist file at the your_project/ios/Runner/info.plist and add the following permissions:
<key>NSMicrophoneUsageDescription</key> <string>This application needs to access your microphone</string> <key>NSSpeechRecognitionUsageDescription</key> <string>This application needs the speech recognition permission</string>
(Note: Above permissions will show a message to the user before starting the speech recognition)
In this step, you will add variables that are required to maintain the app state. For example, You must need a variable to know whether the speech recognition is started. These will be useful for showing and hiding widgets based on various situations.
Here are some vital variables that you need:
// 1. late SpeechRecognition _speech; // 2. bool _isSpeechStarted = false; // 3. bool _isListening = false; // 4. String transcription = ''; String currentText = ''; // 5. bool _isEndOfSpeech = false;
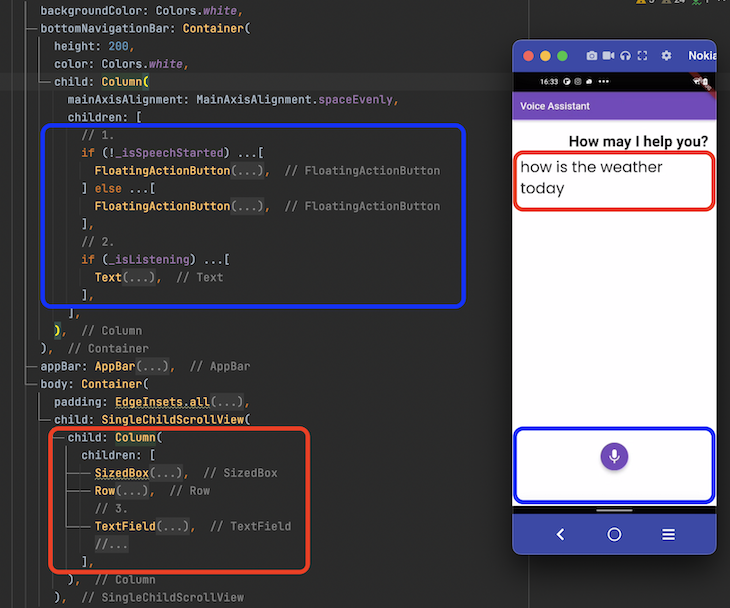
SpeechRecognition and later access it to start and stop listening_isSpeechStarted), this variable is helpful to know if user is actually speakingThe page UI consists of the two main sections. The first section displays the conversation between the voice assistant and the user; and the second section displays the area to start and stop speech recognition.
Here’s what the bare minimum code looks like for this:
SafeArea(
child: Scaffold(
backgroundColor: Colors.white,
bottomNavigationBar: Container(
height: 200,
color: Colors.white,
child: Column(
mainAxisAlignment: MainAxisAlignment.spaceEvenly,
children: [
// 1. <-- SEE HERE
if (!_isSpeechStarted) ...[
FloatingActionButton(
backgroundColor: const Color(0xff764abc),
child: Icon(
Icons.mic,
size: 35,
),
onPressed: () {
_startSpeechRecognition();
},
),
] else ...[
FloatingActionButton(
backgroundColor: const Color(0xff764abc),
child: Icon(
Icons.stop,
size: 35,
),
onPressed: () {
_stopSpeechRecognition();
},
),
],
// 2. <-- SEE HERE
if (_isListening) ...[
Text(
kListening,
style: GoogleFonts.nunito(
textStyle:
TextStyle(color: Colors.black, fontSize: 22.5)),
),
],
],
),
),
appBar: AppBar(
title: Text('Voice Assistant'),
backgroundColor: const Color(0xff764abc),
),
body: Container(
padding: EdgeInsets.all(16),
child: SingleChildScrollView(
child: Column(
children: [
SizedBox(
height: 10,
),
Row(
mainAxisAlignment: MainAxisAlignment.end,
children: [
Text(
_ttsGreet,
style: GoogleFonts.poppins(
textStyle: TextStyle(
fontSize: 30.5, fontWeight: FontWeight.bold),
),
),
],
),
// 3. <-- SEE HERE
TextField(
controller: _myController,
readOnly: true,
onChanged: (String text) {
setState(() {
_isContentsPresent = text.isNotEmpty;
});
},
//focusNode: _nodeText1,
cursorColor: Colors.grey,
style:
GoogleFonts.poppins(textStyle: TextStyle(fontSize: 30.5)),
keyboardType: TextInputType.multiline,
maxLines: null,
decoration: InputDecoration(
border: InputBorder.none,
hintStyle: GoogleFonts.nunito(),
),
),
],
),
),
),
),
);
Here’s quick rundown of the code above:
_isSpeechStarted variableTextField widget is used instead of the Text widget to enable users edit the voice command (if required)Here’s how to code translated into the design:
After setting up the variables and page UI, it’s time to call the plugin methods that are responsible for driving the speech recognition feature.
Below are some of the important methods that you will use to start and stop the recognition service.
// 1.
void _activateSpeechRecognizer() {
_requestPermission();
_speech = new SpeechRecognition();
_speech.setAvailabilityHandler(onSpeechAvailability);
_speech.setRecognitionStartedHandler(onRecognitionStarted);
_speech.setRecognitionResultHandler(onRecognitionResult);
_speech.setRecognitionCompleteHandler(onRecognitionComplete);
_speech
.activate()
.then((res) => setState(() => _speechRecognitionAvailable = res));
}
// 2.
void onRecognitionResult(String text) {
if (_isEndOfSpeech) {
_isEndOfSpeech = false;
return;
}
setState(() {
transcription = text;
_isListening = true;
print('recognized text is- $transcription');
_myController.text = transcription;
_myController.selection = TextSelection.fromPosition(
TextPosition(offset: _myController.text.length));
});
}
// 3.
void onRecognitionComplete() {
print('Recognition Completed');
if (transcription.isNotEmpty) {
_isContentsPresent = true;
_processRequest(transcription);
_toggleSpeechRecognitionStatus(isSpeechStarted: false);
}
}
TextField widgetAwesome! you now know how to add speech-to-text support. Let’s assume you have processed the request and its time to speak out the result. Let’s see take a look at how to do that.
In the example app, after displaying the user’s voice command on-screen, the voice command is processed and the result is read out by the voice assistant (in addition to displaying it on screen).
You can implement such a requirement by utilizing the text to speech (TTS) plugin. It works on iOS, Android, web, and macOS. With this plugin, you can also change Volume, Rate, and Pitch of the voice.
Here are the step-by-step instructions for adding the text-to-speech support:
Add the text to speech dependency inside the pubspec.yaml file.
The contents inside the pubspec.yaml file should look like this:
dependencies:
flutter:
sdk: flutter
cupertino_icons: ^1.0.2
speech_recognition: ^0.3.0+1
text_to_speech: #NEW
For the plugin to speak out the text, you only need to enable the permission for the Android platform.
Here what the AndroidManifest.xml (located at your_project/android/app/src/main/AndroidManifest.xml) file should look like:
<manifest xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
package="com.example.speech_to_text_demo">
<queries>
<package android:name="com.google.android.googlequicksearchbox"/>
<intent>
<action android:name="android.intent.action.TTS_SERVICE" />
</intent>
</queries>
<application
</application>
</manifest>
In this step, you will add variables that are required to start and pass the message to the TTS (text-to-speech) service.
Here are some variables that you need:
// 1. TextToSpeech tts = TextToSpeech(); // 2. String _ttsGreet = 'How may I help you?'; // 3. String _ttsStaticResult = 'Its very hot today';
TextToSpeech, which you can use to trigger the TTS serviceThe page UI simply shows a greeting message and a message answering the user’s query in a text widget (below the user query).
For the sake of simplicity, the page UI is kept simple. You can extend this and use ListView to build flexible UI that best matches your requirement.
The code looks like this:
if (_isShowResult)
Row(
mainAxisAlignment: MainAxisAlignment.end,
children: [
Text(
_ttsStaticResult,
//textAlign: TextAlign.end,
style: GoogleFonts.poppins(
textStyle: TextStyle(
fontSize: 30.5, fontWeight: FontWeight.bold),
),
),
],
),
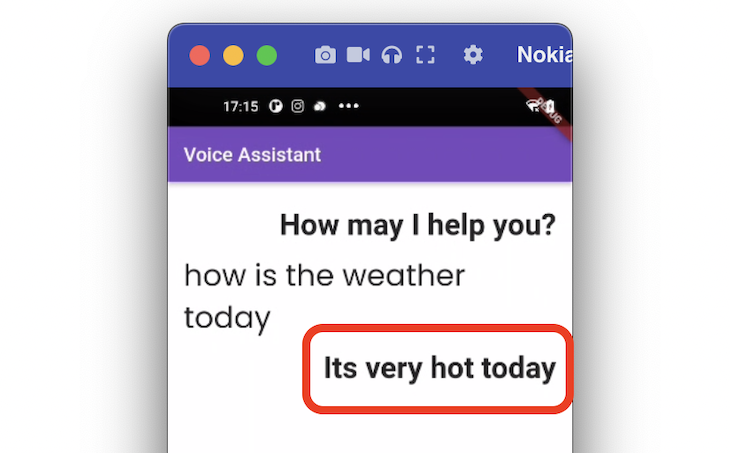
If you have set up the variables and page UI, you can trigger the speech after processing the user query by calling the speak() method on the instance of the TextToSpeech.
Here’s how you do it:
_processRequest(String transcription) {
// Process request here
/// Your business logic here
//Speak out the result
setState(() {
_isShowResult = true;
});
_tts(_ttsStaticResult);
}
_tts(String message) {
tts.speak(message); //<-- SEE HERE
}
Congratulations! now you know how to add text-to-speech support.
When you run the app with the speech recognition plugin, you will likely find that the speech recognition in Android behaves slightly different to iOS.
In Android, when you start the service and don’t speak for a moment, the system automatically stops listening (which is not the case in iOS).
Technically, it should keep the service open until the user starts speaking — the plugin doesn’t have a solution for this at the moment, so I’ll explain how to fix it yourself.
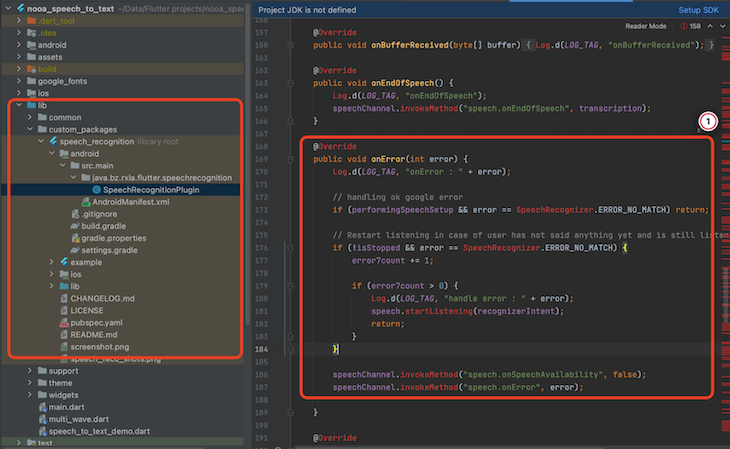
Steps to enable the continuous listening on Android are as follows:
SpeechRecognitionPlugin file at lib/custompackage/packagefolder/android/src/main/java/bz/rxla/flutter/speechrecognition.@Override
public void onError(int error) {
Log.d(LOG_TAG, "onError : " + error);
// handling ok google error
if (performingSpeechSetup && error == SpeechRecognizer.ERROR_NO_MATCH) return;
// Restart listening in case of user has not said anything yet and is still listening i.e not stopped by user
if (!isStopped && error == SpeechRecognizer.ERROR_NO_MATCH) {
error7count += 1;
if (error7count > 0) {
Log.d(LOG_TAG, "handle error : " + error);
speech.startListening(recognizerIntent);
return;
}
}
speechChannel.invokeMethod("speech.onSpeechAvailability", false);
speechChannel.invokeMethod("speech.onError", error);
}
The idea here is to restart the speech recognition when it encounters the SpeechRecognizer.ERROR_NO_MATCH error (that pops up when the service is stopped automatically).
After making changes as per the above code, the speech recognition service will keep running as long as the user manually stops it (which is what we want).
Here’s what it looks like:
The full source code can be found here.
Adding speech-to-text and text-to-speech features offers the chance to provide additional capability to for users interact with your app.
In this tutorial, we first looked at the how to add speech-to-text and then explored adding the text-to-speech service.
We went through step-by-step instructions in setting up the variables, UI, and methods. We also learned how to enable the continuous listening for Android devices.
Install LogRocket via npm or script tag. LogRocket.init() must be called client-side, not
server-side
$ npm i --save logrocket
// Code:
import LogRocket from 'logrocket';
LogRocket.init('app/id');
// Add to your HTML:
<script src="https://cdn.lr-ingest.com/LogRocket.min.js"></script>
<script>window.LogRocket && window.LogRocket.init('app/id');</script>
Hey there, want to help make our blog better?
Join LogRocket’s Content Advisory Board. You’ll help inform the type of content we create and get access to exclusive meetups, social accreditation, and swag.
Sign up now
Not sure if low-code is right for your next project? This guide breaks down when to use it, when to avoid it, and how to make the right call.
Compare Firebase Studio, Lovable, and Replit for AI-powered app building. Find the best tool for your project needs.

Discover how to use Gemini CLI, Google’s new open-source AI agent that brings Gemini directly to your terminal.

This article explores several proven patterns for writing safer, cleaner, and more readable code in React and TypeScript.
2 Replies to "Adding speech-to-text and text-to-speech support in a Flutter app"
I think the code provided should contain the custompackage for continual listening!
Does it work for any languages (not english)?