
Editor’s note: This article was last updated 23 March 2023 to reflect the most recent information for Enzyme and react-testing-library. Check out this guide to working with Enzyme for React for more information.

When we talk about testing React components, we might end up with a handful of options that you should consider according to how well they are used in the community and how easily you can get information on them through the documentation.
These options include tools like Enzyme, react-testing-library, or React Test Renderer, which have rich documentation and use cases available in the React community.
For this post, we’ll review two of those tools: Enzyme and react-testing-library. We’ll also discuss how to migrate from Enzyme to react-testing-library and how to migrate back.
We’ll cover the following:
The Replay is a weekly newsletter for dev and engineering leaders.
Delivered once a week, it's your curated guide to the most important conversations around frontend dev, emerging AI tools, and the state of modern software.
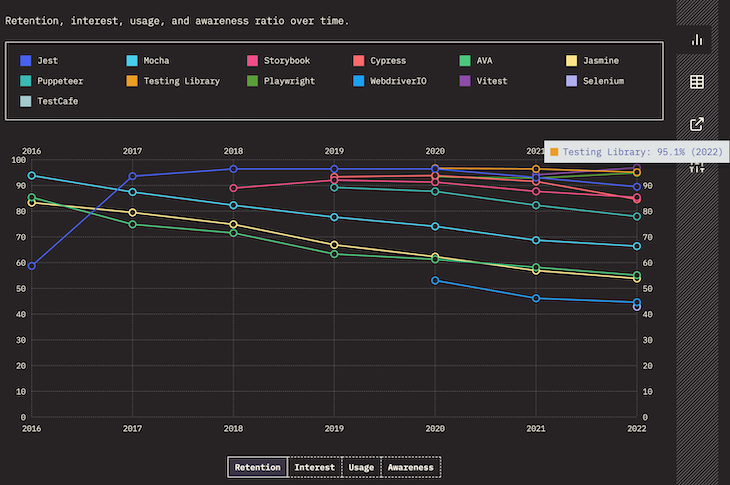
Enzyme was released in 2015. react-testing-library was released in 2018 and gained traction quickly. The latter has shown no signs of slowing down as noted in the 2022 State of JavaScript Survey that shows 95.1% user retention:
By testing our React components, we can be certain that they work the way we want them to and that they don’t break when we make changes to the codebase.
Here are some of the key reasons why we need to test React components:
React components are responsible for rendering the user interface of a web application. By testing them, developers can ensure that the UI is displayed correctly and that it responds to user interactions as expected.
Testing React components can help developers catch bugs and errors early in the development process. This can save a lot of time and effort, as it is much easier to fix a bug when it is discovered early in the development process.
Testing React components can improve the maintainability of a web application. By having a comprehensive suite of tests, developers can be more confident when making changes to the codebase, as they can quickly check if their changes have introduced any regressions.
Without testing, we run the risk of shipping an application that has bugs and errors that could affect the user experience negatively. This is why it’s crucial to test React components during the development process. It helps us identify and fix issues before the application goes live, and also gives us confidence that our code works as expected.
The React Testing Library (RTL) is a testing utility for React applications that focuses on testing component behavior rather than implementation details. It includes built-in assertions for checking expected behaviors and a simple and intuitive API for selecting and interacting with elements in your components. Tests become less brittle and more resilient to changes in the codebase by simulating user interactions.
Enzyme is a popular testing tool for React applications. It provides a set of utility functions for testing React components, similar to React Testing Library. Enzyme, on the other hand, differs from React Testing Library because it focuses on testing the implementation details of your components.
Enzyme includes APIs for mounting, rendering, and manipulating React components in tests. It enables you to inspect and manipulate component internal states and properties, as well as simulate user interactions. This can be beneficial when testing complex components with a lot of internal state or that interact with external services.
Besides the two main differences mentioned, there are several details that might help you choose one tool for your next React project.
To demonstrate that, I’ve come up with a simple component idea implemented through two different approaches: one being a functional component with React Hooks, and the other being a class component. That way, we’ll be able to compare the test structure for each type of component.
If you want to take a look at the entire code (with tests), here’s a GitHub repo you can use alongside this post.
Also, keep in mind that this post does not focus on the setup of any of those tools. If you want to see how that was done, you can look at this other LogRocket post showing what dependencies are needed for each tool.
So, we’re creating a RangeCounter component that should present two control buttons to users (for adding and subtracting) and the current count in between those buttons.
That count should be ruled by the props passed to the component (min and max).
When the user reaches any of the values in the range limit, they should see an alert message below the counter explaining why they are not able to keep increasing or decreasing the counter.
The class component looks something like this:
class RangeCounterClass extends Component {
constructor(props) {
super(props);
const { min } = props;
this.state = {
counter: min,
hasEdited: false
};
this.incrementCounter = this.incrementCounter.bind(this);
this.decrementCounter = this.decrementCounter.bind(this);
}
componentDidUpdate() { ... }
incrementCounter() { ... }
decrementCounter() { ... }
render() {
const { max, min } = this.props;
return (
<div className="RangeCounter">
<span className="RangeCounter__title">Class RangeCounter</span>
<div className="RangeCounter__controls">
<button
disabled={this.state.counter <= min}
onClick={this.decrementCounter}
>
-
</button>
<span>{this.state.counter}</span>
<button
disabled={this.state.counter >= max}
onClick={this.incrementCounter}
>
+
</button>
</div>
{(this.state.counter >= max || this.state.counter <= min) &&
this.state.hasEdited && (
<span className="RangeCounter__alert">Range limit reached!</span>
)}
</div>
);
}
}
Keep in mind that you can always check the GitHub repo for the entire component code.
The functional component will look like this:
const RangeCounterFunctional = props => {
const { max, min } = props;
const [counter, setCounter] = useState(min);
const [hasEdited, setHasEdited] = useState(false);
useEffect(() => {
if (counter !== min && !hasEdited) {
setHasEdited(true);
}
}, [counter, hasEdited, min]);
return (
<div className="RangeCounter">
<span className="RangeCounter__title">Functional RangeCounter</span>
<div className="RangeCounter__controls">
<button
disabled={counter <= min}
onClick={() => setCounter(counter - 1)}
>
-
</button>
<span data-testid="counter-value">{counter}</span>
<button
disabled={counter >= max}
onClick={() => setCounter(counter + 1)}
>
+
</button>
</div>
{(counter >= max || counter <= min) && hasEdited && (
<span className="RangeCounter__alert">Range limit reached!</span>
)}
</div>
);
};
Both have the same behavior and will look mostly the same for users (except for the title, which can be ignored for this post’s purposes).
We’ll be testing the following scenarios for both components with both tools:
Let’s look at the test for the first scenario in the list when using Enzyme:
describe("RangeCounterClass", () => {
let wrapper;
beforeEach(() => {
wrapper = shallow(<RangeCounterClass />);
});
describe("when incrementing counter is allowed", () => {
it("updates counter value correctly", () => {
wrapper.instance().incrementCounter();
expect(wrapper.state().counter).toEqual(1);
expect(wrapper.state().hasEdited).toEqual(true);
});
});
});
You’ll notice that in order to test that the component works correctly, you have to check that the correct props were received and also that the state looks correct. When that test passes, we assume that the current count showing up to the user is the one that is in the counter state variable.
Also, we check if the hasEdited variable changed to true now that we programmatically updated the counter (the value in that state can also tell us whether the alert will show up or not).
Now let’s look at that same test scenario but with react-testing-library:
describe("RangeCounterFunctional", () => {
describe("when incrementing counter is allowed", () => {
it("updates the counter value", async () => {
const { getByTestId, getByText } = render(<RangeCounterB min={2} />);
const incrementButton = getByText("+");
fireEvent.click(incrementButton);
expect(getByTestId("counter-value").innerHTML).toEqual("3");
});
});
});
It’s clear that the idea of this test is to check what is showing up in the UI. That is accomplished by getting the actual DOM element and checking its contents, which represent what the user actually sees.
The next three scenarios in the list display the same kind of pattern. The interesting one to look at now is the last scenario, in which shows that you can also use Enzyme following the same concept of react-testing-library.
Let’s take a look.
describe("RangeCounterClass", () => {
let wrapper;
beforeEach(() => {
wrapper = shallow(<RangeCounterA />);
});
it("shows range reached alert when reached limit by clicking control buttons",
() => {
wrapper = shallow(<RangeCounterA min={0} max={1} />);
wrapper.instance().incrementCounter();
wrapper.update();
const alert = wrapper.find('.RangeCounter__alert');
expect(alert.text()).toEqual('Range limit reached!');
}
);
});
describe("RangeCounterFunctional", () => {
it("shows range reached alert when reached limit by clicking control buttons",
() => {
const { getByText } = render(<RangeCounterB min={0} max={1} />);
const incrementButton = getByText("+");
fireEvent.click(incrementButton);
expect(getByText("Range limit reached!")).toBeVisible();
}
);
});
We see that both are strictly confirming that the alert is showing up in the page, but in a slightly different way.
With Enzyme, it’s common to see tests that try to find elements in the page by their class (that is not a rule though), which is not meaningful because users do not see those in the UI. After having the element, you can check the contents of it (which is what the user actually sees).
With react-testing-library, the idea is that you search directly by the actual text that the user sees without the overhead work of finding the element that contains that text.
Imagine a scenario where you have tons of child components and a more tangled HTML structure. You’d probably have more trouble following the same concept when using Enzyme.
After reading this post, you may be wondering if you can migrate your tests from one of these tools to the other. Let’s take a look.
To migrate tests from react-testing-library to Enzyme, you’ll need to install an additional library called enzyme-adapter-react-[react-version]. This adapter library is necessary and there are different setup steps depending on your version. Here is a list with all the versions. However, at the time of writing, Enzyme’s adapters only go up to React v.16. An unofficial adapter exists for React v.17, but none yet for React v.18.
If that is not an issue for you, then install the adapter library and choose your test runner. Enzyme isn’t opinionated and offers many different options (e.g., Jest, Mocha, and others). Here’s a list of all the different guides.
Migrating tests from Enzyme to react-testing-library is a little more straightforward. In fact, Kent C. Dodds, the creator of React Testing Library, wrote a complete guide to help developers migrate their tests easily. The guide includes all the necessary installation steps, as well as multiple examples for adapting your tests.
No tool is objectively better than the other: you must consider the variables you have to account for when making a decision about which tool to use.
This specific comparison is based on how developers used to think about tests when using these tools, and how easy it is to follow the idea of testing user behavior instead of component implementation with each tool.
It’s clear that react-testing-library makes that a lot easier with all of the helper methods for querying and the matchers from jest-dom, so it’s natural that you’d want to use that instead.
However, there are limitations to react-testing-library, such as not being able to access component state (which might be intentional because you shouldn’t be doing that, in theory).
However, if you feel like you really need that, then Enzyme may be a better option. Just make sure that you write tests that resemble user experience whenever possible.
Install LogRocket via npm or script tag. LogRocket.init() must be called client-side, not
server-side
$ npm i --save logrocket
// Code:
import LogRocket from 'logrocket';
LogRocket.init('app/id');
// Add to your HTML:
<script src="https://cdn.lr-ingest.com/LogRocket.min.js"></script>
<script>window.LogRocket && window.LogRocket.init('app/id');</script>

Signal Forms in Angular 21 replace FormGroup pain and ControlValueAccessor complexity with a cleaner, reactive model built on signals.

Discover what’s new in The Replay, LogRocket’s newsletter for dev and engineering leaders, in the February 25th issue.

Explore how the Universal Commerce Protocol (UCP) allows AI agents to connect with merchants, handle checkout sessions, and securely process payments in real-world e-commerce flows.

React Server Components and the Next.js App Router enable streaming and smaller client bundles, but only when used correctly. This article explores six common mistakes that block streaming, bloat hydration, and create stale UI in production.
Would you be interested in joining LogRocket's developer community?
Join LogRocket’s Content Advisory Board. You’ll help inform the type of content we create and get access to exclusive meetups, social accreditation, and swag.
Sign up now
3 Replies to "Testing React components: react-testing-library vs. Enzyme"
That is just an amazing and great comparison. Very elaborate, yet concise.
Thank you very much.
It’s like bkack-box testing (react-testing-library) versus white-box testing (enzyme) or BDD (react-testing-library) versus unit-testing (Enzyme).
This blog certainly made me continue in the direction of react-testing-library.
Hey Jarl, thanks for the feedback!
That’s exactly how I think about those two tools and the reason why I think people should look more into tools that test user behavior over code. In general it gives you more confidence on how users are in fact perceiving your app.
Thanks for writing this up, though as a fan of Enzyme, I feel like it’s being a bit misrepresented here.
1) In enzyme you absolutely can simulate a user click:
`wrapper.find(SELECTOR).simulate(‘click’)`
And from there the developer can choose how they want to assert that it was handled correctly (state value, or actual display)
2) While it is true that RTL allows for more user-facing ways of interacting with the code, it seems to do so at the expense of allowing many other developer-only ways of interacting with the code (without polluting production).
If I want to test that a certain sub-component ( or ) is rendered given certain business logic conditions, with RTL I have two options:
A) Peek into the downstream HTML and confirm it’s there
B) Apply some sort of additional label, like a data-testid
A is faulty since it balloons the scope of tests, and B feels like a code smell of including test-only code in production files.
Ultimately, it’s possible that I just need to give up the idea that certain things are ever testable in the clear-cut way that I’ve grown accustomed to, and embrace this more ‘hit and run’ style of testing. I just can’t shake the feeling that I’m compromising too much on the core ideology of my test code, which is to help prevent accidental regressions and instill a sense of safety when refactoring.