A little over 10 years ago, Google bought a smaller company called GIPS for a bit less than $70 million. This marked the beginning of Google’s endeavor to bring real-time communication (RTC) natively to browsers. By open-sourcing GIPS’s primary product, Google set a standard that was first implemented by Ericsson and then solidified in a W3C specification.

Today, this standard is known as WebRTC and is widely supported among all major browsers and platforms. This technology gives you the ability to provide a way of exchanging video, audio, and other data between different users on your page, independently of the users’ specific browser and device types.
One of the downsides of WebRTC is that it is quite complex. Luckily, we can use PeerJS — a library that simplifies WebRTC and provides a complete, configurable, and easy-to-use peer-to-peer connection API.
Like most JS libraries these days, you can use PeerJS either in your bundled project via an import statement, or by including the script directly from a CDN such as unpkg.
You can include PeerJS on a page with a script as below:
<script src="https://unpkg.com/[email protected]/dist/peerjs.min.js"></script>
This will make the Peer class available, which then allows us to create an instance and start something like a chat:
const peer = new Peer({
host: "0.peerjs.com",
port: 443,
path: "/",
pingInterval: 5000,
});
Above, we’ve created an instance using the default settings. PeerJS requires a central server to identify what peers are available.
To complete the chat, we still need to open a connection to a chat partner and send and receive messages. Let’s see how this is done in PeerJS:
const conn = peer.connect("other-peer-id");
conn.on("open", () => {
conn.send("Hello World!");
});
conn.on("data", (data) => {
console.log("Received data", data);
});
Very often, it’s not about creating a connection, but actually receiving or handling a connection request. The incoming requests can be handled by the connection event present on a Peer instance.
peer.on("connection", (conn) => {
conn.on("data", (data) => {
console.log("Received data", data);
});
});
Going from here, PeerJS also allows us to utilize the data connection for more than just text. In combination with the getUserMedia API from the browser, we can do:
getUserMedia(
{ video: true, audio: true },
(stream) => {
const call = peer.call("other-peer-id", stream);
call.on("stream", (remoteStream) => {
// Show stream in some video/canvas element.
});
},
console.error
);
Likewise, receiving video and audio streams is possible, too:
peer.on("call", (call) => {
getUserMedia(
{ video: true, audio: true },
(stream) => {
call.answer(stream);
call.on("stream", (remoteStream) => {
// Show stream in some video/canvas element.
});
},
console.error
);
});
Let’s use the code from the previous section to construct a simple example that will allow us to make and receive one-to-one video calls. Our example should follow this workflow:
We’ll start by initializing a new project and adding all the dependencies:
npm init -y npm i peerjs react react-dom react-router react-router-dom --save npm i @types/react @types/react-dom @types/react-router-dom typescript parcel@next --save-dev
Now, we need to create an HTML file that will act as an entry point for Parcel.
Parcel is a bundler that will convert all the different sources we’ll use to write our app into files that the web browser can understand. For example, for styling we use SASS and for the script we use TypeScript — two formats that no browser understands.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge" />
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" />
<title>PeerJS Example</title>
<link rel="stylesheet" href="./style.scss" />
</head>
<body>
<div id="app"></div>
<script type="module" src="./app.tsx"></script>
</body>
</html>
We’ll start without any design elements, and instead focus on creating a text-based chat application for two peers. For the sake of convenience, the example app is written using React, but feel free to choose your favorite UI library or framework.
Essentially, what we’ll do is:
const App = () => {
return (
<BrowserRouter>
<Switch>
<Route exact path="/" component={NameInput} />
<Route exact path="/overview" component={Overview} />
<Route exact path="/call" component={Call} />
</Switch>
</BrowserRouter>
);
};
render(<App />, document.querySelector("#app"));
We’ll use three components for the three different areas of our application:
NameInput to let the user choose their nameOverview to allow users to make or receive callsCall to handle an ongoing callWe’ll also keep things simple by placing the values for Peer and connection globally. They may still be used in the components — e.g., for the NameComponent, we write:
const NameInput = () => {
const history = useHistory();
// use local copy of the global to manage the different behaviors reliably
const [availablePeer, setAvailablePeer] = React.useState(peer);
const submit = React.useCallback((ev) => {
const input = ev.currentTarget.elements.namedItem("name");
const user = input.value;
ev.preventDefault();
// let's set the peer
setAvailablePeer(new PeerJs(user));
}, []);
React.useEffect(() => {
// apply the local peer to the global variables
peer = availablePeer;
// entering the name is only necessary if we don't have a peer yet;
// if we have then let's show the overview
if (availablePeer) {
history.replace("/overview");
}
}, [availablePeer]);
return (
<form onSubmit={submit}>
<label>Your name:</label>
<input name="name" />
<button>Save</button>
</form>
);
};
The same is true for the Overview component:
const Overview = () => {
const history = useHistory();
const [availablePeer] = React.useState(peer);
// use local copy of the global to manage the different behaviors reliably
const [availableConnection, setAvailableConnection] =
React.useState(connection);
const submit = React.useCallback(
(ev) => {
const input = ev.currentTarget.elements.namedItem("name");
const otherUser = input.value;
ev.preventDefault();
// make the call
setAvailableConnection(availablePeer.connect(otherUser));
},
[availablePeer]
);
React.useEffect(() => {
connection = availableConnection;
if (!availablePeer) {
// no peer yet? we need to start at the name input
history.replace("/");
} else if (availableConnection) {
// already a connection? then let's show the ongoing call
history.replace("/call");
} else {
// let's wait for a connection to be made
peer.on("connection", setAvailableConnection);
return () => peer.off("connection", setAvailableConnection);
}
}, [availablePeer, availableConnection]);
return (
<div>
<h1>Hi, {availablePeer?.id}</h1>
<form onSubmit={submit}>
<label>Name to call:</label>
<input name="name" />
<button>Call</button>
</form>
</div>
);
};
For Call, it mainly comes down to using three functions:
useEffect Hook)In code, this looks as follows:
React.useEffect(() => {
connection = availableConnection;
if (!availableConnection) {
history.replace('/overview');
} else {
const dataHandler = (data: string) => {
setMessages((msgs) => [...msgs, data]);
};
const closeHandler = () => {
setAvailableConnection(undefined);
};
availableConnection.on('data', dataHandler);
availableConnection.on('close', closeHandler);
return () => {
availableConnection.off('data', dataHandler);
availableConnection.off('close', closeHandler);
};
}
}, [availableConnection]);
const submit = React.useCallback(
(ev) => {
const input = ev.currentTarget.elements.namedItem('message');
const message = input.value;
ev.preventDefault();
availableConnection.send(message);
input.value = '';
},
[availableConnection],
);
const disconnect = React.useCallback(() => {
availableConnection.close();
setAvailableConnection(undefined);
}, [availableConnection]);
The result of the above code should look as presented below. Keep in mind that the UX and overall styling were not our focus for this part of the demo. The chat works quite well and, from a functionality point of view, it fulfills the requirements.
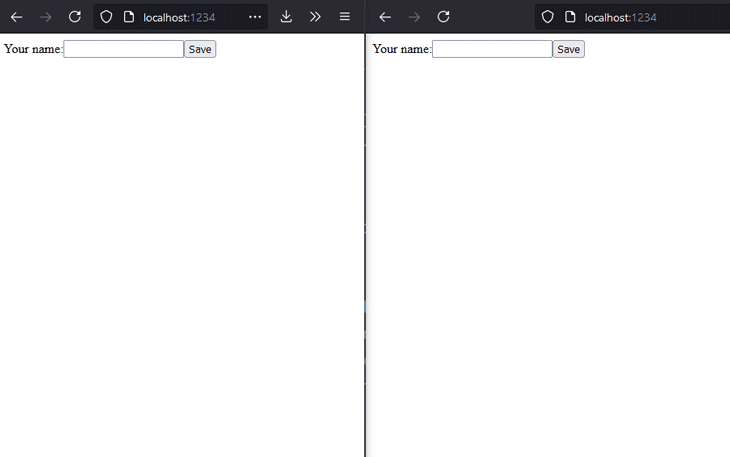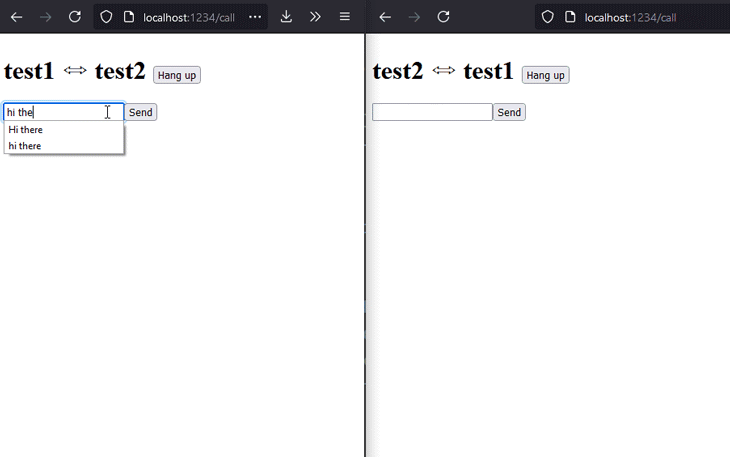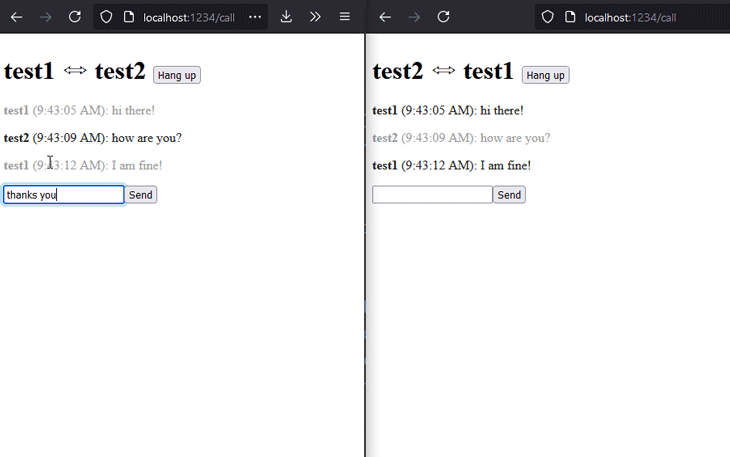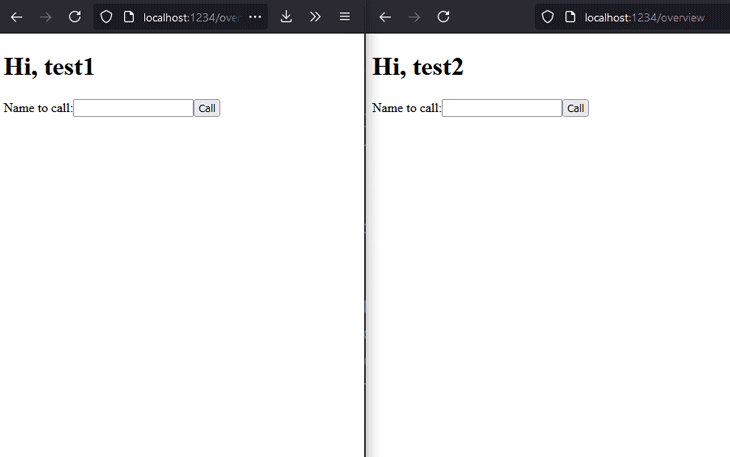
Now, it’s time to make the chat even better by also adding audio and video capabilities.
PeerJS provides audio and video streams by building upon the getUserMedia browser API.
The first thing to do is to obtain a reference to getUserMedia. We’ll exclusively use the “old” and more established API, which can be accessed directly from navigator, even though there is a new API available at navigator.mediaDevices. Since this works slightly differently, but more importantly, is not yet as widespread and supported as the old API, we’ll avoid it for now.
With that in mind a solid way of obtaining a reference to getUserMedia is:
const getUserMedia = navigator.getUserMedia || navigator["webkitGetUserMedia"] || navigator["mozGetUserMedia"];
After we obtain a working reference (or not — in this case, it should actually error out or have some kind of fallback), we can use it.
Let’s build upon the previous chat message example and add the information about who actually called whom in the connection:
// if we are the ones who called
connection["caller"] = availablePeer.id;
// if the other party called and we received
const handler = (connection) => {
connection["caller"] = connection.peer;
setAvailableConnection(connection);
};
Now, we can add the following Hook to the Call component:
React.useEffect(() => {
if (availableConnection && availablePeer) {
let dispose = () => {};
const handler = (call) => {
getUserMedia(
{ video: true, audio: true },
(stream) => {
showVideo(stream, selfVideo.current);
call.answer(stream);
},
(error) => {
console.log("Failed to get local stream", error);
}
);
dispose = showStream(call, otherVideo.current);
};
if (availableConnection["caller"] === availablePeer.id) {
getUserMedia(
{ video: true, audio: true },
(stream) => {
showVideo(stream, selfVideo.current);
dispose = showStream(
availablePeer.call(availableConnection.peer, stream),
otherVideo.current
);
},
(error) => {
console.log("Failed to get local stream", error);
}
);
} else {
availablePeer.on("call", handler);
}
return () => {
availablePeer.off("call", handler);
dispose();
};
}
}, [availableConnection, availablePeer]);
Quite a few things are happening here, so let’s go over them one by one:
getUserMediaThe video elements are just references, i.e.:
// define refs
const otherVideo = React.useRef();
const selfVideo = React.useRef();
// ...
<video ref={otherVideo} width={500} height={500} />
<video ref={selfVideo} width={200} height={200} />
Great, trying this out could result in an application like this:
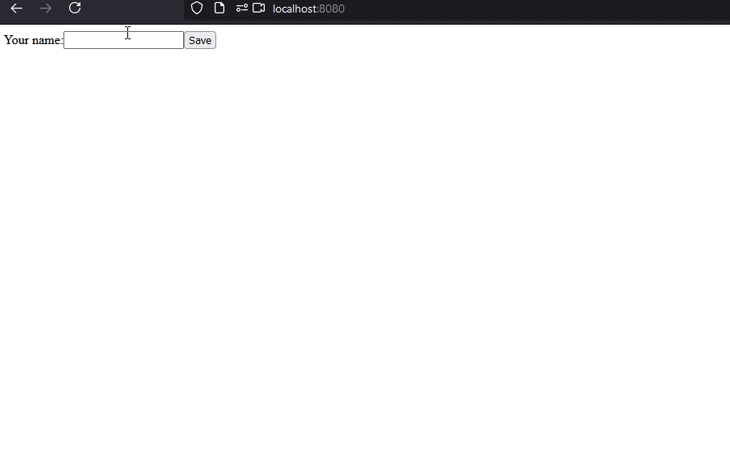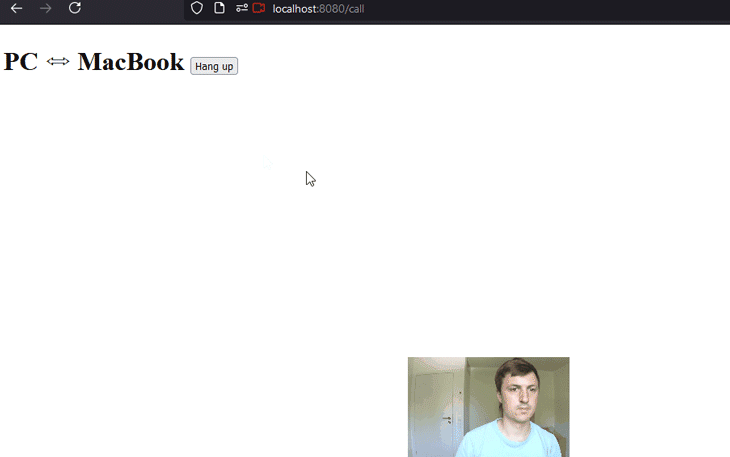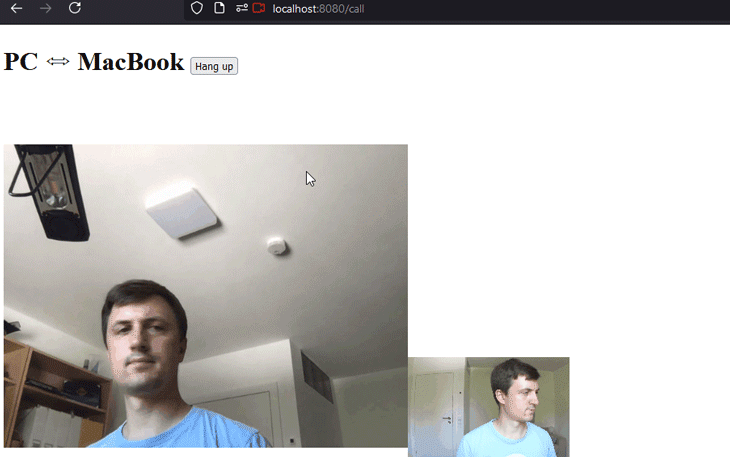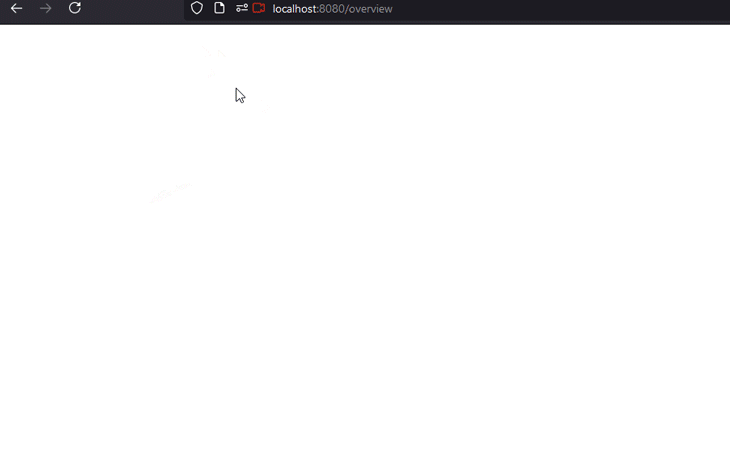
You can find the example we constructed in this article on my GitHub.
So, what can you do with PeerJS? A lot. You can think about your own alternative to clunky video chat solutions such as Teams or Slack. Of course, you may quickly conclude that these solutions, while bulky, come with some nice features and the necessary resilience that you’d want for production-grade software. But for simple things, there isn’t much you’d need outside of what we built in this article.
I’ve used this to build a home communication web app. Each tablet and computer in my home has access to a small webserver hosted on a Raspberry Pi, which offers the chat page and a PeerJS server instance. This allows discovery of everyone in my home, and for easy, frictionless communication without any middle layer.
PeerJS is a great library to use if you need to tame the WebRTC beast and easily enable video and audio call capabilities in your web app. It’s convenient to get started and provides all the necessary means to help you get production-ready quickly.
While using the provided cloud service is a great start, the provided open-source Node.js server also works as a boilerplate for hosting your own peer broker.
What will you build with WebRTC and PeerJS?
There’s no doubt that frontends are getting more complex. As you add new JavaScript libraries and other dependencies to your app, you’ll need more visibility to ensure your users don’t run into unknown issues.
LogRocket is a frontend application monitoring solution that lets you replay JavaScript errors as if they happened in your own browser so you can react to bugs more effectively.
LogRocket works perfectly with any app, regardless of framework, and has plugins to log additional context from Redux, Vuex, and @ngrx/store. Instead of guessing why problems happen, you can aggregate and report on what state your application was in when an issue occurred. LogRocket also monitors your app’s performance, reporting metrics like client CPU load, client memory usage, and more.
Build confidently — start monitoring for free.
Would you be interested in joining LogRocket's developer community?
Join LogRocket’s Content Advisory Board. You’ll help inform the type of content we create and get access to exclusive meetups, social accreditation, and swag.
Sign up now
A breakdown of the wrapper and container CSS classes, how they’re used in real-world code, and when it makes sense to use one over the other.

This guide walks you through creating a web UI for an AI agent that browses, clicks, and extracts info from websites powered by Stagehand and Gemini.

This guide explores how to use Anthropic’s Claude 4 models, including Opus 4 and Sonnet 4, to build AI-powered applications.

Which AI frontend dev tool reigns supreme in July 2025? Check out our power rankings and use our interactive comparison tool to find out.