
Hashing refers to using an algorithm to map data of any size to a fixed length. It’s a one-way function that is primarily used for authentication.

In this tutorial, we’ll show you how to build a password hasher to hash and store user credentials in the database.
To do this, we’ll use a technique called salt hashing. A salt is a random piece of data that is used as an additional input to a one-way function that hashes data or a password. Salts are used to safeguard passwords in storage so you can avoid storing plaintext passwords in the database.
According to the salt hashing technique, we’ll take a user-entered password and a random string of characters (salt), hash the combined string with a suitable crypto hashing algorithm, and store the result in the database.
The Replay is a weekly newsletter for dev and engineering leaders.
Delivered once a week, it's your curated guide to the most important conversations around frontend dev, emerging AI tools, and the state of modern software.
To follow along with this tutorial, you’ll need:
Basically we will have three functions to carry out each of the following tasks.
To set up a Node.js application, you’ll need a package.json file to document the dependencies. To create that, run the following on your terminal.
npm init -y
Next, create an index.js file. This is the root of the application and where we’ll be writing all our hashing codes.
touch index.js
This will create the index.js file.
Add the following to your index.js file.
console.log(`Hello...I'm a nodejs developer`)
Then, run node index on your terminal. If you get Hello...I'm a nodejs developer printed on the consol, you’re good to go.
We’ll start by requiring the Node.js crypto module and before creating a simple function to log the functions on the console.
'use strict';
let crypto = require('crypto');
// logger
let logger = func => {
console.log(func);
};
The next step is to create a function to generate the random salt. This function will take in a number as a parameter to define the length of the salt. We’ll add a simple validator to check whether the number is greater than 15.
let generateSalt = rounds => {
if (rounds >= 15) {
throw new Error(`${rounds} is greater than 15,Must be less that 15`);
}
if (typeof rounds !== 'number') {
throw new Error('rounds param must be a number');
}
if (rounds == null) {
rounds = 12;
}
return crypto.randomBytes(Math.ceil(rounds / 2)).toString('hex').slice(0, rounds);
};
logger(generateSalt(12))
Running node index on the console prints the generated random string. The .toString('hex') method converts the string to hexadecimal format, while slice(0, rounds) returns just the number of the required value.
Next, we’ll define our hashing algorithm to perform the hashing and salting logic. We’ll use the **crypto.createHmac(algorithm, key[, options])**, which creates and returns an Hmac object that uses the given algorithm and key. We’ll also use the sha512 algorithm. The second parameter will be the key, which is where we’ll pass in our salt.
let hasher = (password, salt) => {
let hash = crypto.createHmac('sha512', salt);
hash.update(password);
let value = hash.digest('hex');
return {
salt: salt,
hashedpassword: value
};
};
With this defined, we’ll write our hash function, which will call the hasher function. We’ll perform all our validations here, such as making sure the salt is a string, a plain password is provided, and both password and salt are provided in the parameter.
let hash = (password, salt) => {
if (password == null || salt == null) {
throw new Error('Must Provide Password and salt values');
}
if (typeof password !== 'string' || typeof salt !== 'string') {
throw new Error('password must be a string and salt must either be a salt string or a number of rounds');
}
return hasher(password, salt);
};
logger(hash('Wisdom', generateSalt(12)))
Start by verifying that both the salt and the plain password are provided, then check that both password and salt is a type of string.
Use our logger function to test your function. Running node index will print the hash password and the salt on the console.
{
salt: 'f844b09ff50c',
hashedpassword: '2d2528d4534394d1e2702f53826d11c16ed4422f6bd466745cb4f1aa0e042b52b98fc5e65b86d73a6ce4807679b773fb955c4824b0471015354e1a872d42cb62'
}
Copy this and save it in a variable. We’ll use it later to test the compare password function.
Before we can do that, we must define the compare password function. This will actually use the same algorithm to hash the password entered and then test whether the new hash matches the stored hash.
let compare = (password, hash) => {
hash = {
salt: 'f844b09ff50c',
hashedpassword: '2d2528d4534394d1e2702f53826d11c16ed4422f6bd466745cb4f1aa0e042b52b98fc5e65b86d73a6ce4807679b773fb955c4824b0471015354e1a872d42cb62'
}
if (password == null || hash == null) {
throw new Error('password and hash is required to compare');
}
if (typeof password !== 'string' || typeof hash !== 'object') {
throw new Error('password must be a String and hash must be an Object');
}
let passwordData = hasher(password, hash.salt);
if (passwordData.hashedpassword === hash.hashedpassword) {
return true;
}
return false
};
logger(compare('wisdom'))
This function takes in the inputted password and a hash as a parameter. For testing purposes, we’ll use the salt and hashed password that we got to test the compare password function.
We’ll write some validation to check whether the password or hash is provided and also whether the type of password is a string and type of hash is an object, which contains the salt value and the hashed password.
We’ll then use the same hasher function to hash the new inputted password and then check whether the new hashed password is equal to the password stored in the database. If it matches, it will return a value of true; otherwise, it will be false.
To use the hasher function, you must export it by adding the following to the end of the file.
module.exports = {
generateSalt,
hash,
compare
}
Now we can start using the hasher function to register and log in users. We’ll keep things simple by:
Lets create a test.js file. This is where we’ll test our hasher module.
Start by installing the following packages.
express for setting up our server and routesmongoose for the MongoDB connection and querymorgan for logging routesbody-parser to accept JSON type requestsTo install these, open your terminal and run:
npm i express mongoose morgan body-parser --save
This will install all the packages and document the activity in the package.json file.
It will also create a node_modules folder, to which we need to add a .gitignore file so it won’t be committed on Git.
We’ll need to modify the codes in our test.js.
const express = require('express');
const morgan = require('morgan');
const bodyParser = require('body-parser');
const mongoose = require('mongoose');
const port = process.env.PORT || 5000;
const app = express();
// Defining middlewares
app.use(morgan('dev'));
app.use(bodyParser.json());
mongoose.Promise = global.Promise;
// Connecting to the database
mongoose.connect('mongodb://localhost:27017/hasher', {
useNewUrlParser: true
}).then(() => {
console.log("Successfully connected to the database");
}).catch(err => {
console.log('Could not connect to the database. Exiting now...', err);
process.exit();
});
app.listen(port, () => {
console.log('App is Running on port', port)
});
Here we required all the packages we installed and configure them. We used the mongoDB ORM (Mongoose) to connect to the MongoDB local server and then used the instance of express to listen to a PORT.
The next step is to define our User model using Mongoose. Create a user.model.js file and add the following.
const mongoose = require('mongoose');
const userSchema = mongoose.Schema({
name: {
type: String,
required: true
},
email: {
type: String,
required: true
},
password: {
type:Object,
required: true
}
}, {
timestamps: true
});
module.exports = mongoose.model('User', userSchema);
We can now define our register and login routes to test the hasher.
We’ll create a user.routes.js. To keep things simple, we’ll write both our write and business logic in one file.
Start by defining the register route.
module.exports = (app) => {
const User = require('./user.model')
const {
generateSalt,
hash,
compare
} = require('./index');
let salt = generateSalt(10);
app.post('/register', async (req, res) => {
try {
let user = new User({
name: req.body.name,
email: req.body.email,
password: await hash(req.body.password, salt) // dont remove the await
})
let response = await user.save();
res.status(200).json({
status: "Success",
data: response
})
} catch (err) {
//handle error
}
});
}
Next, register in the test.js file. This has to come under the Mongoose configuration.
require('./user.routes')(app);
Now we can test the register route. Open your POSTMAN and make a post request to /register following the schema you defined.

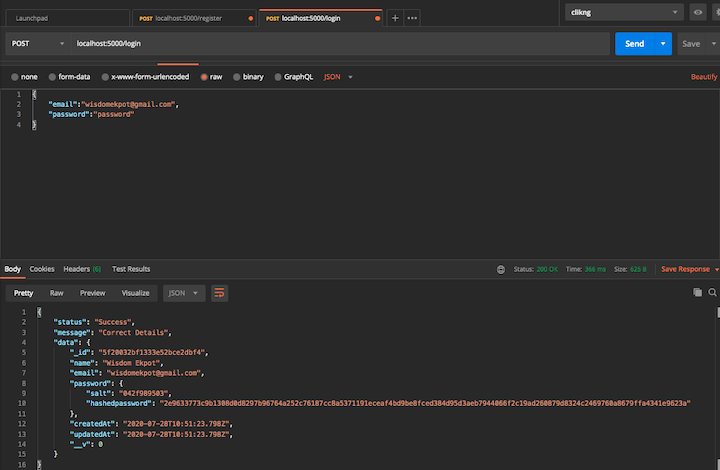
Here we stored our hashedpassword and salt in the database.
Next, implement the login route.
app.post('/login', async (req, res) => {
try {
let {
email,
password
} = req.body;
let user = await User.findOne({
email: email
})
if (!user) {
return res.status(400).json({
type: "Not Found",
msg: "Wrong Login Details"
})
}
let match = await compare(password, user.password);
if (match) {
res.status(200).json({
status: "Success",
message: "Correct Details",
data: user
})
}
} catch (err) {
// handle error
}
})
Make sure to add this inside the exports object. Remove the hash object in compare function in the index.js file.
// hash = {
// salt: 'f844b09ff50c',
// hashedpassword: '2d2528d4534394d1e2702f53826d11c16ed4422f6bd466745cb4f1aa0e042b52b98fc5e65b86d73a6ce4807679b773fb955c4824b0471015354e1a872d42cb62'
// }
Testing your code on POSTMAN will produce the following result.

Our password hasher is working perfectly!
In this guide, we demonstrated how salting works in Node.js crypto. It still has some flaws, so I wouldn’t recommend using this in production. Better tools, such as Bcrypt, are better for production applications.
Source code is available on GitHub.
 Monitor failed and slow network requests in production
Monitor failed and slow network requests in productionDeploying a Node-based web app or website is the easy part. Making sure your Node instance continues to serve resources to your app is where things get tougher. If you’re interested in ensuring requests to the backend or third-party services are successful, try LogRocket.
LogRocket lets you replay user sessions, eliminating guesswork around why bugs happen by showing exactly what users experienced. It captures console logs, errors, network requests, and pixel-perfect DOM recordings — compatible with all frameworks.
LogRocket's Galileo AI watches sessions for you, instantly identifying and explaining user struggles with automated monitoring of your entire product experience.
LogRocket instruments your app to record baseline performance timings such as page load time, time to first byte, slow network requests, and also logs Redux, NgRx, and Vuex actions/state. Start monitoring for free.
Learn how to solve the LLM context problem with RAG, pruning, summarization, and tool loadouts for more reliable AI systems.

Discover five practical ways to scale knowledge sharing across engineering teams and reduce onboarding time, bottlenecks, and lost context.

Discover what’s new in The Replay, LogRocket’s newsletter for dev and engineering leaders, in the March 4th issue.

Paige, Jack, Paul, and Noel dig into the biggest shifts reshaping web development right now, from OpenClaw’s foundation move to AI-powered browsers and the growing mental load of agent-driven workflows.
Hey there, want to help make our blog better?
Join LogRocket’s Content Advisory Board. You’ll help inform the type of content we create and get access to exclusive meetups, social accreditation, and swag.
Sign up now
4 Replies to "Building a password hasher in Node.js"
Copied from: https://www.echojs.com/comment/37385/1
Okay… while this is kind of correct, I would empatically NOT follow this advice.
First, sha512 is *not* sufficient for a hash, there are specific algorithms that will use sha256/512 as an underlying hash with thousands of iterations in order to create an appropriate hash.
Second, the “rounds” for a salt is a total abuse of the term. The “rounds” in a password hash has to do with the number of cycles to perform on a passphrase hash.
Third, you don’t need to convert to a hex string when passing the salt to the hashing algorithm, it can stay an ArrayBuffer/Buffer.
Fourth, the length of the salt should match the bit length of the underlying hashing algorithm to ensure than at least a full working buffer goes into the algorithm to offset for short-ish passphrases.
Here’s a better example to work from:
https://gist.github.com/tracker1/87bbebbf235e697588fc9d9b8ca4f0a2
Though, you may want to use something other than pbkdf2, the example above was using it because of legal requirements and that the algorithm is supported by node in the box.
It is quite obvious that when it has to do with hashing in Node.js, it is recommended to use packages like bcrypt or Argon2. The article was basically to explain how bcrypt works and how to build something similar. It is stated in the conclusion that this has some flaws and wouldn’t be recommended for production.
He was just explaining how salting works in Node.js crypto, inasmuch he stated that this isn’t safe to do in production.
Also, how is the ’rounds’ a waste of term? Could you explain further?
Converting to a hex string is just by choice.
Thank you for bringing up some of the flaws with this! Adding onto the list of issues, the hash comparison here is not time safe and is vulnerable to a timing-based side-channel information leak.
Also, NIST recommends at least 128-bits for a salt.
Something like Argon2 would be ideal for passwords. If you have to stay within the scope of the SHA-family, then use a keccak construction like SHA3-512 (supported by NodeJS 10+), and use a minimum of 1,000 rounds/iterations, but ideally, go with something higher. And as mentioned above, use PBKDF2.