
Editor’s note: This article was updated by Oyinkansola Awosan on 29 January 2024 to update the information for all tools and add five new AI developer tools to the list.
Behind any high-quality piece of software is a team of developers, designers, project managers — the list goes on — each of whom plays a valuable role in the software development lifecycle. But what of the humble developer who, on their own, has an idea for an app or a way to enhance an existing app?
Without a full team, learning new features or fixing old issues can take up a disproportionate amount of time — potentially hours of searching, reading documentation, and watching instructional videos. Fortunately, advancements in AI have dramatically sped up this process.
The AI juggernaut that everyone immediately thinks about is ChatGPT, which has been available since November 2022. It may feel like it’s been much longer because of how dramatically AI has shaken up the day-to-day life of the humble developer.
However, ChatGPT is fairly general-purpose. Where AI really stands to shine is in purpose-built tools that exist to resolve a specific issue within the development world.
There are a lot of tools that meet this description, but let’s go ahead and take a look at ten of them and understand what purpose they serve. You can check out the AI dev tools summary table at the end of this article to better understand how each tool can fit into your workflow.
If you’re planning to leverage these or any other AI tools for developers, make sure you read all the way through to my small word of caution to read about a few considerations to keep in mind. Otherwise, let’s get started!
The Replay is a weekly newsletter for dev and engineering leaders.
Delivered once a week, it's your curated guide to the most important conversations around frontend dev, emerging AI tools, and the state of modern software.
Kicking off our list is Phind, a tool that promises to be a search engine, but tailored toward developers. Whereas a more generalized tool like ChatGPT is for pretty much any question, Phind is specifically tailored toward developers.
Interestingly, this position of “search engine” means that Phind’s responses typically consist of two parts:
Oftentimes, you’ll bounce between asking the AI questions and navigating the search results to dial into what you’re after.
One of the more annoying things about using AI to solve programming questions is that, when the AI model isn’t quite sure of the answer, it can start to bluff its way through things. As a result, it may give you answers that seem plausible, but simply don’t work.
This is frustrating because you can invest considerable time in something that should work, only to find out after some time that the AI has essentially led you astray. There’s probably nothing worse for your productivity than to chase after something that was never going to work in the first place.
Let’s take Phind for a spin by asking it how we can connect to Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE) devices on Windows using Rust. This is an interesting question because, although Bluetooth is ubiquitous, finding samples on how to search and connect to BLE devices is quite difficult.
Using “Find and connect to BLE devices on Windows in Rust” as input in Phind results in the following:
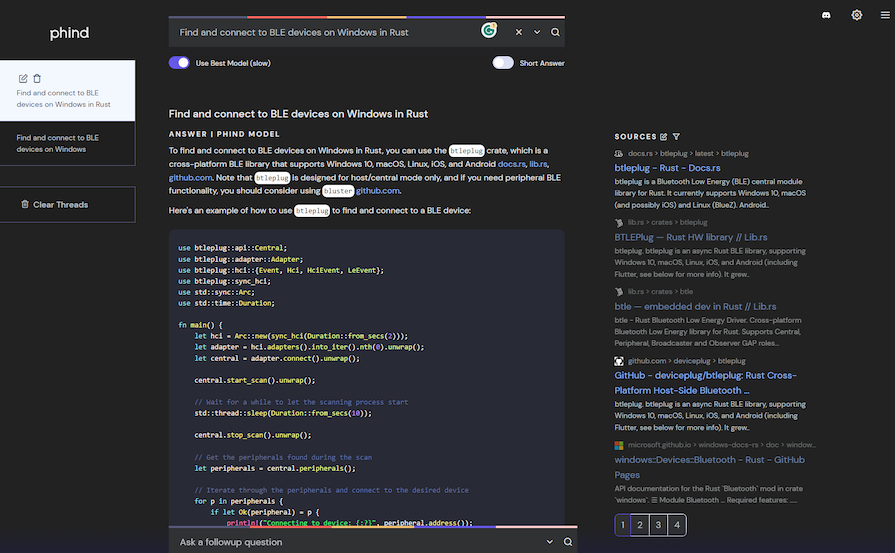
On the left, we get a code sample that uses the btleplug package, which is the right package to use for this.
On the right, we also get search results, so we can quickly jump to the cargo page for the btleplug crate. This means that we can quickly jump between an example of how to use the code and the documentation itself.
Asking ChatGPT the same question, by comparison, told us to use the rumble crate, which is older than btleplug and doesn’t support Windows. So Phind definitely yielded better results in this case.
As of January 2024, Phind is free, but has Plus and Pro tiers that provide “faster answers, longer context, image uploads, and access to GPT-4.”
In summary, here’s what sets Phind apart:
At various times, I’ve had reason to clone various GitHub repositories to my computer. Typically, I’ve done this either to try to fix a certain bug or to learn how the given repository solves a certain problem.
Whenever I do this, there’s always a period at the start where I have to understand how the repository is structured and where to find the code I’m looking for. This “onboarding” can take anywhere from minutes to hours.
bloop.ai looks to expedite this process. You can clone whole GitHub projects and then ask bloop.ai questions about the repository. In this case, I cloned the btleplug repository, and asked it about how the BLE scan worked for Windows devices:
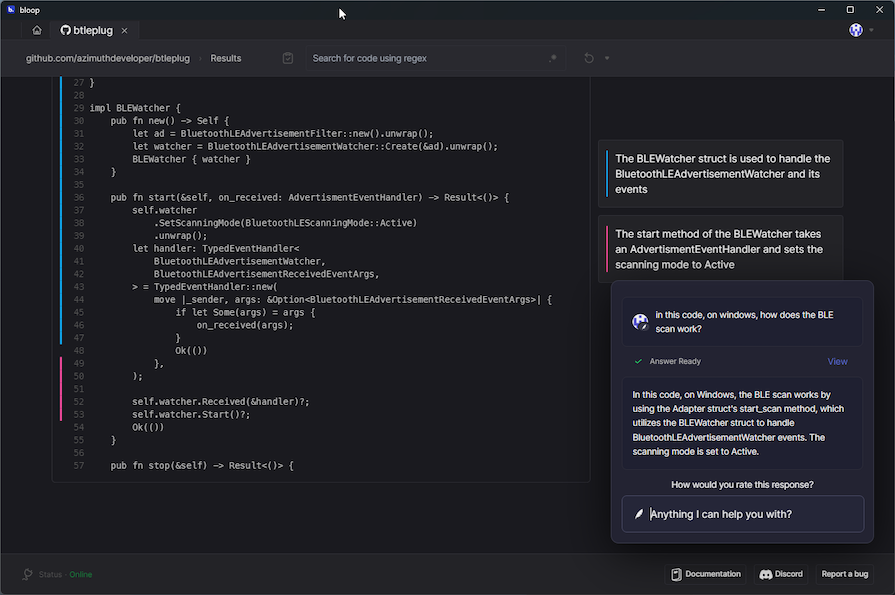
This is actually a pretty hard question. The library in question supports four different platforms, so bloop.ai had to locate the Windows-specific code.
Additionally, the btleplug code is abstracted behind an interface to normalize the API surface regardless of what platform you are on. Because of this, bloop.ai also had to find the actual platform implementation.
bloop.ai is also free for individuals, although there is a paid version that offers additional features such as indexing multiple branches. To use bloop.ai, you have to:
Once you’ve done that, you can clone and inspect repositories to your heart’s content.
Another way that bloop.ai can really help productivity is within the context of when developers leave organizations.
I’ve inherited codebases that have been the product of other developers’ expertise, and it’s not been easy to understand how the app holds together. Being able to load the repository into an AI-assisted tool and then hammer it with questions would definitely remove a lot of trial and error.
Finally, the desktop app looks great 👌 The high degree of polish makes the app a joy to use.
Here’s a summary of what makes bloop.ai great for developers:
You’ve likely heard about other AI-assisted tools for programming, like GitHub Copilot. Codeium works a lot like that, providing contextual suggestions within your codebase as you write your code. It’s pretty impressive.
For example, if you write a function in Rust like calculate_fibonacci_sequence(), the Codeium plugin will suggest a function that does just that:
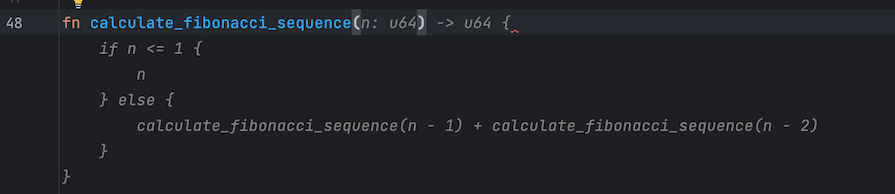
In the above example, I just wrote the function name, and Codeium suggested a function that could meet this need. Whereas ChatGPT or even Phind might take a few minutes to suggest an answer, Codeium only took a few seconds to roll out a function that could work most of the time.
Codeium’s suggestions aren’t always perfect, but it’s often faster than writing an entire function from scratch yourself.
It’s great for your productivity because you don’t have to search for how to achieve a given function. Sometimes, just giving your function the name of what you want it to do is enough for Codeium to fill in the rest.
Where Codeium really shines is in editor support. While VS Code is the de facto standard for many a Rust developer these days, I was pleased to find native support for CLion and many other JetBrains IDEs. The list of supported editors is nothing short of impressive.
Add to this a pretty compelling message from the Codeium team about why Codeium for Individuals is and will continue to be free, and this tool seems to be a great offering in this space.
In summary, Codeium provides:
You can make the best app in the world, but if it’s painful to look at, or if it’s even just ugly, people will struggle to engage with it. Finding complementary colors and themes that look good can sometimes require a well-trained eye — or a lot of trial and error.
Fortunately, ColPat provides an easy way of creating themes and colors for your website or app:
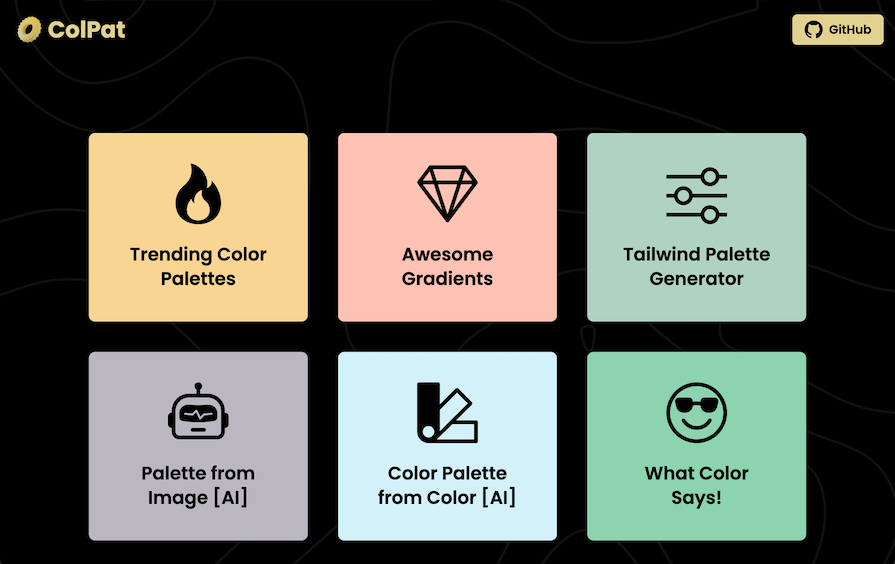
Only two of ColPat’s tools — Palette from Image and Color Palette from Color — specifically identify as using AI to prepare the results. Otherwise, it seems like this all happens locally; from browsing the source repository, it’s not clear how AI actually gets involved in generating the color palettes, or if it does at all.
But still, ColPat is a great tool, and it can definitely help you to produce a complementary color scheme for your website or app.
In summary, ColPat is:
At some point in your development career, you’re going to need to filter text out of a bigger text string. Potential reasons for this are numerous — maybe you’re trying to convert data from one type to another type, or maybe you’re trying to automate something.
In the early days of your career, you’d probably settle for splitting some strings and juggling character counts. But eventually, you’ll probably wind up using a RegEx.
RegExes are ubiquitous within software development because of how powerful they are. However, they’re not very easy to read.
For example, Google provides a few examples that show a few RegExes written for a certain purpose, but they’re not very easy to interpret. There are also complex posts on sites like StackOverflow from people who find the syntax incredibly cryptic.
For example, this RegEx matches email addresses ending in yahoo, hotmail, and gmail:
(\W|^)[\w.\-]{0,25}@(yahoo|hotmail|gmail)\.com(\W|$)
There are other websites like Regex 101 that let you provide some input and then play around with your RegEx until it does what you want it to do.
Traditionally, this method — supplying the input, then trying to craft the query until you get what you’re after — is how you would achieve many of these goals. Of course, that comes after visiting approximately every StackOverflow question on how RegExes work. This can be a time-intensive process.
Fortunately, we can just fast-forward a lot of this process by using RegExGPT. Instead of guessing your way around a RegEx, you can simply supply the string along with the value you expect to get from it.
For more complex queries, you can also supply a natural language prompt — such as, “I want the third value from the comma-separated array” — and RegExGPT will pump out a RegEx that does exactly what you want it to do.
For example, at the risk of summoning Zalgo, I can use RegEx to read a href from HTML anchor tabs:
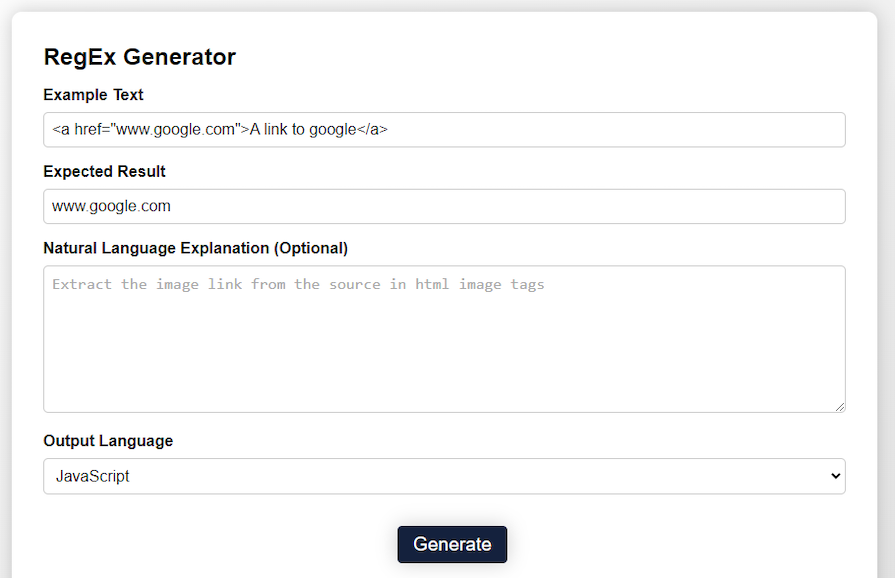
To which RegExGPT gives this helpful reply:
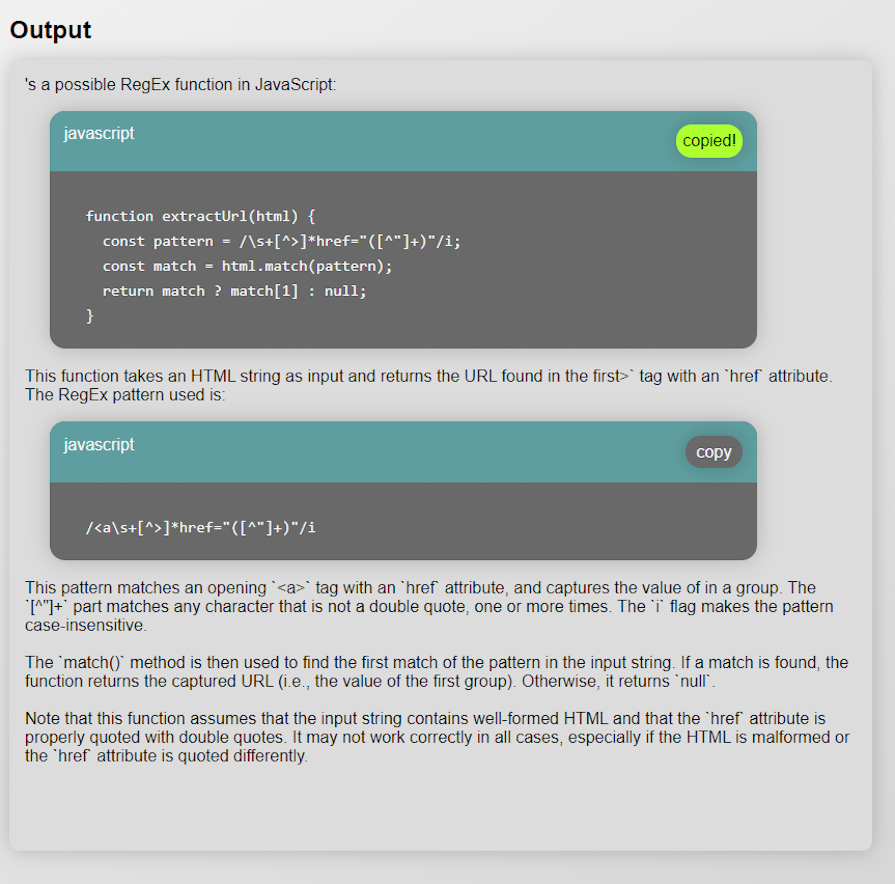
When taking it for a spin in the Chrome developer console, we can see the result is as expected:
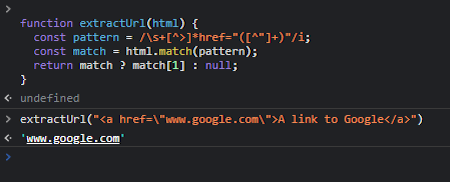
RegEx has never been so easy!
In summary, you can use RegExGPT to:
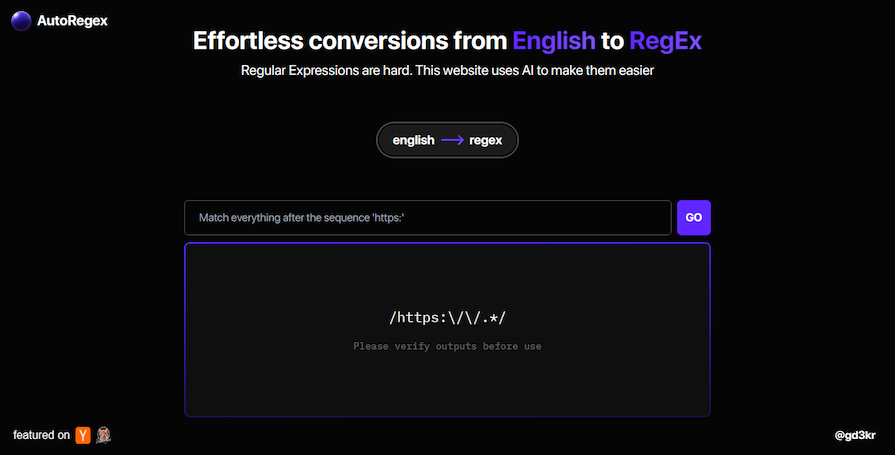
As we’ve already discussed, RegEx syntax can be pretty confusing and difficult to grasp even for advanced developers. AutoRegex bridges this gap by translating regular expressions to English and vice versa.
AutoRegex understands natural descriptions of patterns and generates corresponding RegExes for them. It also generates or explains RegExes, translating them to layman’s terms as seen in the image below:
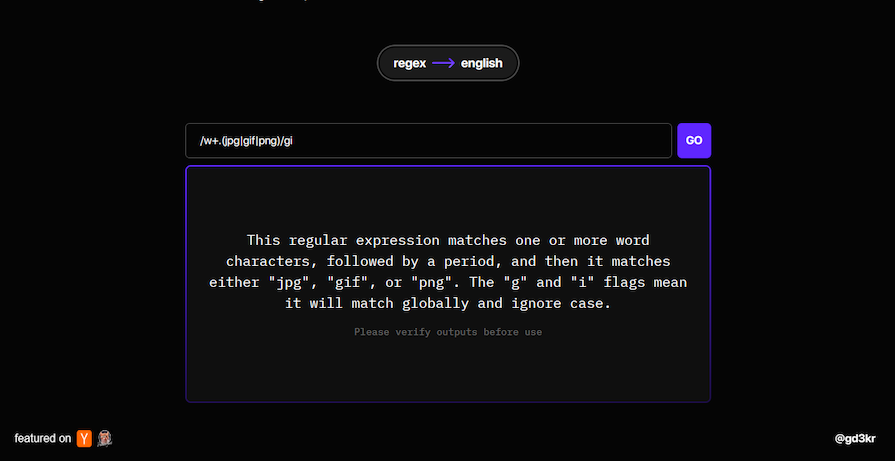
This eliminates the need for developers to have in-depth knowledge of RegEx syntax, making it easier to work with this powerful tool for text manipulation and pattern matching.
Also, AutoRegex checks the validity of the generated RegExes to ensure they match the intended patterns accurately and can optimize the generated RegExes for efficiency and performance.
AutoRegex is pretty straightforward to use, available via the web, and free — for now. It is a great tool that will definitely boost developer productivity simply because it takes care of everything RegEx.
In summary, you can use AutoRegex to:
I have had several moments — especially when I was starting out as a developer — where I was confused by everything related to Git. This is likely true for any developers who know what they want to do, but don’t know yet what the right command is to execute it.
GitFluence bridges the gap by giving you the right code for your situation. Here’s how GitFluence works:
It should look something like the below:
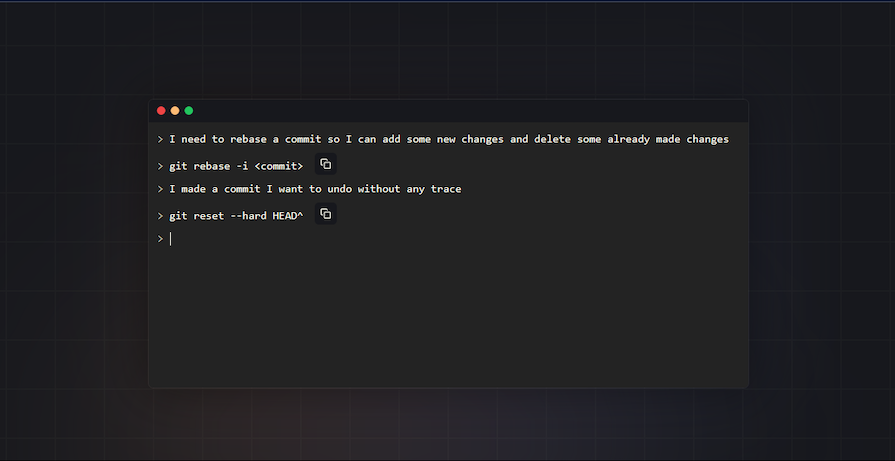
GitFluence can help you find the right Git commands quickly and easily without having to search through documentation or remember complex syntax. Gitfluence’s suggestions are based on a large dataset of Git commands, so you can be confident that you’re using the right command for the job.
In summary, Gitfluence is great because:
Cursor is an AI-powered IDE that offers features like lint fixing, chatbot, code generation, and code editing directly within the editor window. It also supports advanced features like auto-debugging, bug-finding, and repo-wide understanding.
Cursor can understand and respond to natural language questions, making it easy for developers to interact with the AI directly in their code editor. You can ask it questions about your codebase, for code completions, or even to generate code snippets.
Although Cursor is great, keep in mind that its freemium version is somewhat limited. Make sure to check out the plan descriptions so you know what you’re getting into.
In summary, Cursor is great because:
Unit tests are great for any and every codebase. However, they can be quite tedious to carry out. Codium — not to be confused with Codeium, which we covered earlier — is a tool that helps relieve the burden of unit testing for developers.
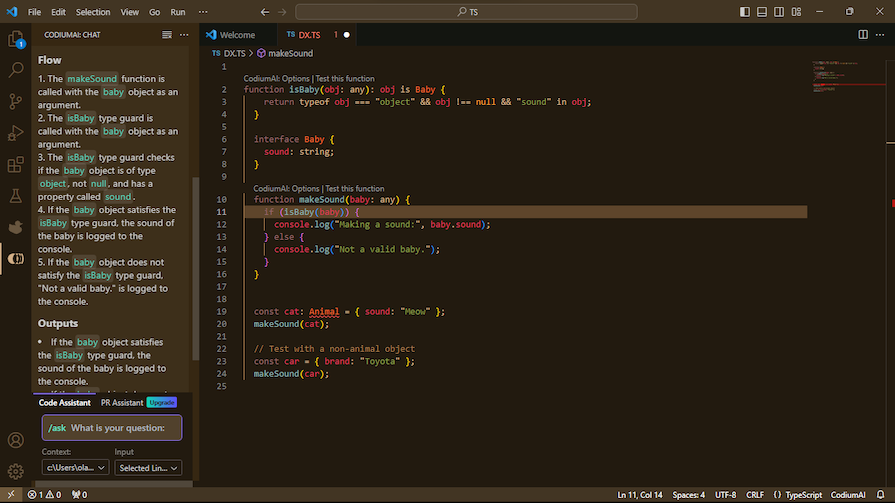
Codium analyzes everything in and about your code and then suggests tests as you code. This effectively removes the need to brainstorm and write test cases, as Codium does it for you. The suggested tests are typically useful and necessary. However, you can dismiss a test suggestion and even give the AI feedback.
Codium interacts with you, analyzes your code, and asks for your input as it suggests tests. This ensures that the suggested tests are relevant and align with your goals for the code. Beyond providing unit tests, Codium also looks at different test cases — like invalid input or invalid file format.
Also, Codium has a pull request (PR) agent that will help review your PR, automatically generate a PR description, suggest code to improve the PR, update the changelog, and even answer questions relating to the PR:
The Codium AI tool is available to individual developers for free via VSCode and JetBrains IDE plugins, although there are paid team and enterprise plans. The tool currently supports JavaScript, Python, and TypeScript.
In summary, Codium is great because:
Quack AI helps software development teams enhance collaboration, streamline processes, and optimize code quality. This tool effectively analyzes code, pinpoints potential issues, and suggests improvements. It also automates repetitive tasks like code reviews and testing, freeing up time for other tasks.
For effective collaboration, Quack AI facilitates code reviews by identifying potential problems and proposing solutions before you merge the code into your codebase.
Quack AI also has automated testing capabilities that generate test cases and execute them, allowing you to effectively identify potential defects, minimize the risk of bugs, and make sure your code adheres to established team or organizational standards.
Enforcing code style guidelines through Quack AI enables you to maintain a consistent coding style across your entire development team. This standardization enhances code readability and promotes a cohesive development style.
You can get started with Quack AI via its VS Code extension. If you’re interested in learning more, you can check out the Quack AI GitHub repo or join the community Discord.
In summary, Quack AI is great because:
So, when you’ve got a specific issue, what tool should you reach for?
| Tool | Great for… |
|---|---|
| Phind | …finding answers to questions that are specifically linked to coding, in a more detailed form than ChatGPT |
| bloop.ai | …understanding how a code base works when you haven’t seen it before so you can quickly get started on it |
| Codeium | …getting contextual suggestions and auto-complete in a surprisingly wide variety of coding tools |
| ColPat | …quickly generating color palettes for your apps (even if it’s not technically AI-powered) |
| RegExGPT | …generating RegEx queries for your language of choice |
| GitFluence | …getting the correct Git command you need for your situation |
| Cursor | …debugging code faster and more efficiently |
| AutoRegex | …generating RegExes and translating them |
| Codium | …generating meaningful code tests |
| Quack AI | … enhancing team collaboration and optimizing code quality |
With all the AI-assisted tooling, trying to solve development problems is suddenly a lot easier. But a lot of these technologies are based on GPT-3.5 or GPT4. These language models are a gigantic leap forward and are helpful for a wide range of applications.
However, as of right now, sometimes asking an AI model a question can result in the AI model not knowing. When this happens, instead of telling you that it doesn’t know, the model will often just try to bluff its way through an answer. These are technically known as hallucinations.
This is possibly problematic for two reasons. For starters, you could be given wrong information that sounds plausible but is completely wrong.
Subsequently, because it sounds plausible, you could spend quite a bit of time trying to get an AI solution to work before realizing that it’s never going to work. That’s quite a waste of time and works against your productivity, which is the entire point of why we’re here in the first place.
If your AI solution isn’t working for you, don’t be afraid to fail fast and try a different prompt.
Secondly, consider what happens when you ask someone in the workplace how to fix a certain problem. If that “solution” introduces a bigger problem, you have someone to go back to ask what’s wrong with the code. With GPT-based solutions, that’s not the case.
For example, imagine that you generated a RegEx query with a GPT-assisted language model. If that RegEx works once for you on a small test but fails in production on a much larger set of data, that’s entirely on you.
No senior developer would ever accept, “But AI suggested that particular RegEx query!” as an excuse for something like an outage. And of course, deploying patches for issues possibly introduced by AI-written code is going to work against your productivity as well.
The bottom line is this: AI can definitely help you with a variety of situations and be of incredible help. But only you, as the developer, can endorse the given solutions.
Whether you are writing the code or AI is helping you write the code, quality is always important. Using unit tests and automated testing to prove that your code works is now more important than ever.
It’s a great time to be a developer, with AI providing solutions to many issues that developers have faced over the years. Whether you are writing new code, trying to understand an existing codebase, or just want a new color palette, there’s a tool to be used.
Making wise use of these tools will equate to many hours saved, and no doubt we will continue to see this space evolve dramatically. If you’ve found another AI-powered tool that has helped you, definitely let us know in the comments!
Install LogRocket via npm or script tag. LogRocket.init() must be called client-side, not
server-side
$ npm i --save logrocket
// Code:
import LogRocket from 'logrocket';
LogRocket.init('app/id');
// Add to your HTML:
<script src="https://cdn.lr-ingest.com/LogRocket.min.js"></script>
<script>window.LogRocket && window.LogRocket.init('app/id');</script>

Signal Forms in Angular 21 replace FormGroup pain and ControlValueAccessor complexity with a cleaner, reactive model built on signals.

Discover what’s new in The Replay, LogRocket’s newsletter for dev and engineering leaders, in the February 25th issue.

Explore how the Universal Commerce Protocol (UCP) allows AI agents to connect with merchants, handle checkout sessions, and securely process payments in real-world e-commerce flows.

React Server Components and the Next.js App Router enable streaming and smaller client bundles, but only when used correctly. This article explores six common mistakes that block streaming, bloat hydration, and create stale UI in production.
Hey there, want to help make our blog better?
Join LogRocket’s Content Advisory Board. You’ll help inform the type of content we create and get access to exclusive meetups, social accreditation, and swag.
Sign up now
3 Replies to "10 AI tools for developers to help boost your productivity"
It was nice walkthrough
This is a very informative. going to check these ai.
Another way to boost productivity thanks to AI is by using productivity tools that have AI features. https://kanbantool.com/ is one of such tools. It offers the help of an AI assistant, which makes generating tasks and organizing workflow even easier and quicker.