
Editor’s note: This article was last updated on 12 August 2022 to verify code accuracy and include additional images and diagrams.

REST APIs are great because they are logically simple. They don’t keep complex states in memory, and they deal with resources instead of loose, unconnected functions, making their entire business logic cohesive.
However, due to the nature and mechanics underlying REST APIs, securing them is not always straightforward. What happens after the user submits their credentials? You can’t keep a state on your server side to signal when a user has logged in on their subsequent requests, so how can you know that they’ve done so correctly?
In this article, we’ll cover one very powerful yet simple way to secure a REST API using JSON Web Tokens (JWT), reviewing some best practices and implementing an example. Let’s get started!
The Replay is a weekly newsletter for dev and engineering leaders.
Delivered once a week, it's your curated guide to the most important conversations around frontend dev, emerging AI tools, and the state of modern software.
JSON Web Tokens are an open, standard way for you to represent your user’s identity securely during a two-party interaction.
When two systems exchange data, you can use a JSON Web Token to identify your user without having to send private credentials on every request. If you apply this to a REST API, you’ll see how our client-server interactions can benefit from these mechanics:
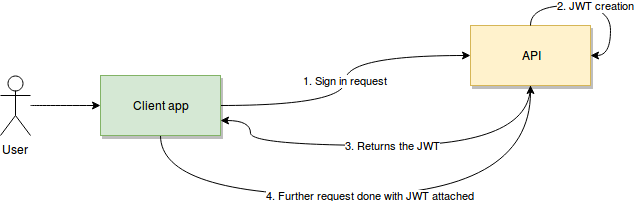
First, the user or client app sends a sign-in request. In this step, essentially, a username, password, or any other type of sign-in credentials the user provides will travel to the API. Once verified, the API will create a JSON Web Token and sign it using a secret key. Then, the API will return that token back to the client application.
Finally, the client app will receive the token, verify it on its own side to ensure it’s authentic, and then use it on every subsequent request. Therefore, it can authenticate the user without them having to send their credentials anymore.
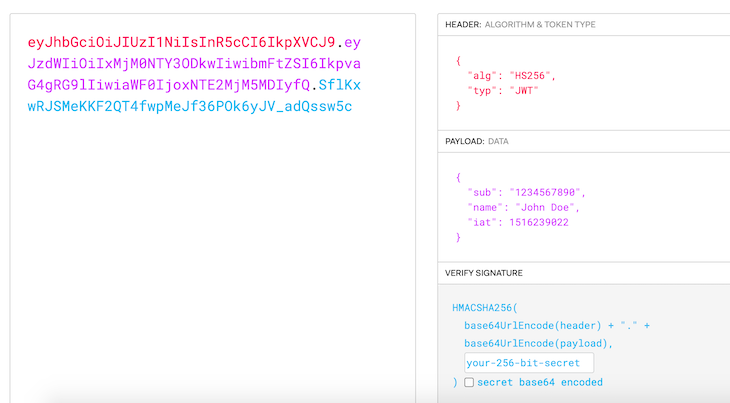
The token itself, which is returned by the API, is simply an encoded string. It comprises three different sections, separated from each other by a dot character:
header.payload.signature

Each section contains a vital piece of the puzzle. Once decoded, the first two sections will be JSON representations of data that contain relevant information, and the last one will be used to verify the authenticity of the token.
The header will contain data related to the type of token we’re dealing with and the algorithm used for its generation. There are several compatible algorithms that you can specify here, but the most common ones are HS256 and RS256. The right choice will depend on what security standards and measures you’re looking for.
In these two examples, one uses a secret key known by both the server and the client, and the other one uses a private key used by the server in combination with a public key known by the client.
In the image above, we see that the payload contains the algorithm, which is set to use HS256, and the type is JWT.
The payload will contain data pertaining to the request and the user making it. There are a set of standard key/value pairs that are defined as part of JWT, which you can use on your implementation:
Sub (Subject): Identifies the user making the request and being authenticatedIss (Issuer): The server that issued the token. In our case, it would make sense to include the URI usedAud (Audience): Provides some form of identification of the recipient of this tokenExp (Expiration date): Tokens usually don’t last forever. Exp ensures that whoever is using the token provides a recently generated tokenWhile there are other attributes you can add to the payload object defined as part of the standard, the ones listed above are the most common. You can use them or just define your own as long as both the client and server are in agreement about the implementation.
Finally, the signature is just an encoded string used by both the server and the client to verify the authenticity of the payload. Now that we’ve covered the basics, let’s review everything that we’ve covered with an example.
Let’s pretend we’re developing a client for our company’s payroll API. The API is meant to issue payments to company employees, retrieve historical information about them, and finally, edit the employees’ information.
To prevent human error, the developers of the API decided that some of these actions will require admin privileges. So, we’ll have users with normal access who can only review information and users with super access, or admins, who can also issue payments and edit data.
Although this example is somewhat basic, it should provide a clear idea of our logic with JWT. As stated above, any interaction with our secure API would start with a login request, which would look something like the following:
POST /api/users-sessions
The payload is as follows:
{
“Username”: “fernando”
“Password”: “fernando123”
}
Assuming the credentials are valid, the system would return a new JSON Web Token. Let’s go over the details of this token. Particularly, let’s think about the information inside our payload. Some interesting options could be:
Iss: Contains the username of the logged in user, which is especially useful since we might want to show that in our UIExp: We’ll only allow our new token to be used for the next eight hours, which is about how long users should need it on a daily basisAdmin: Boolean describing the role of the user. This comes in handy for the UI, since we’ll need to understand whether to show or hide some UI elementsTo keep things simple, we’ll use an HS256 algorithm for encoding the data, meaning we’ll use the same secret on both our client and our API.
Let’s consider what the different sections of our token should look like:
// Header
{
“alg”: “HS256”,
“typ”: “JWT”
}
// Payload
{
“Iss”: “fernando”
“Exp”: 1550946689,
“Admin”: false
}
To create the actual token, we need to encode the items above and then sign the resulting values to add the final piece to the token:
Base64(header) = ewoiYWxnIjogIkhTMjU2IiwKInR5cCI6ICJKV1QiCn0K Base64(payload) = ewoiSXNzIjogImZlcm5hbmRvIiwKIkV4cCI6IDE1NTA5NDY2ODksCiJBZG1pbiI6IGZhbHNlCn0K HS256(Base64(header) + “.” + Base64(payload), “A secret API example”) = TseARzVBAtDbU8f3TEiRgsUoKYaW2SbhCWB0QlKpdp8
The code below shows the final token returned by the API:
ewoiYWxnIjogIkhTMjU2IiwKInR5cCI6ICJKV1QiCn0K.ewoiSXNzIjogImZlcm5hbmRvIiwKIkV4cCI6IDE1NTA5NDY2ODksCiJBZG1pbiI6IGZhbHNlCn0K.TseARzVBAtDbU8f3TEiRgsUoKYaW2SbhCWB0QlKpdp8
Upon receiving this token, the client application can decipher and validate it by grabbing the header and payload portions, then signing it on its own. This, of course, is possible because both the client and server know the secret phrase. Doing so can ensure that no one changed the content of the message and that it’s safe to use.
At the same time, any further requests sent by the client app will contain this same token. In turn, the token will be validated by the server, which signs it every time and compares the results with the signature portion of the token.
In a typical JWT request, you’ll pass the token as part of the authorization header on the client-side after the client logged in, like Authorization:Bearer.
Doing so would prevent, for example, someone from meddling with the message’s payload and changing the admin attribute to true, allowing a fake, or even a valid non-admin user, to execute a privileged action, like issuing a payment to some specific employee.
Such an action would modify the payload content to be something like this:
ewoiSXNzIjogImZlcm5hbmRvIiwKIkV4cCI6IDE1NTA5NDY2ODksCiJBZG1pbiI6IHRydWUKfQo=
In turn, this would cause the final token sent by the client app to be the following:
eyJhbGciOiJIUzI1NiIsInR5cCI6IkpXVCJ9.ewoiSXNzIjogImZlcm5hbmRvIiwKIkV4cCI6IDE1NTA5NDY2ODksCiJBZG1pbiI6IHRydWUKfQo=.TseARzVBAtDbU8f3TEiRgsUoKYaW2SbhCWB0QlKpdp8
The signature for this token would look like the code below:
doRnK7CoVjFOiFmvrQ2wvxcGeQuCYjzUchayNAYx1jw
This would not match the one sent as part of the message, thereby proving that the request had been tampered with.
Hopefully, you’ve grasped the basics of what JWT security entails and learned that securing your REST APIs is actually not all that difficult.
Naturally, there are variations to what I covered in this article, and I recommend exploring that on your own by visiting jwt.io. On their site, you have the ability to generate and validate JSON Web Tokens, as well as links to the main JWT libraries for the most common programming languages. Essentially, everything you need to begin adding JWT security into your APIs is already easily accessible through their website.
Although the mechanics I’ve covered here are quite straightforward and accessible to everyone, you should understand that only adding JWT security into your API won’t be enough to bulletproof your app; smart hackers will find ways around it.
Security is about covering all your fronts, not just implementing one generic security scheme. Securing all your network traffic with an HTTPS connection is an extra layer of protection that always goes well with JWT. In other words, make sure everything that the user sends and receives goes through port 443, or whatever custom number you might be using, and not the unsecured port 80.
I hope you enjoyed this article, and please be sure to leave a comment if you have any questions. Happy coding!
Install LogRocket via npm or script tag. LogRocket.init() must be called client-side, not
server-side
$ npm i --save logrocket
// Code:
import LogRocket from 'logrocket';
LogRocket.init('app/id');
// Add to your HTML:
<script src="https://cdn.lr-ingest.com/LogRocket.min.js"></script>
<script>window.LogRocket && window.LogRocket.init('app/id');</script>

Within roughly the same six-month window, Anthropic shipped Agent Teams for Claude Code, OpenAI published Swarm and the production-ready Agents […]

Compare the top AI development tools and models of March 2026. View updated rankings, feature breakdowns, and find the best fit for you.

Discover what’s new in The Replay, LogRocket’s newsletter for dev and engineering leaders, in the March 11th issue.

Buying AI tools isn’t enough. Engineering teams need AI literacy programs to unlock real productivity gains and avoid uneven adoption.
Would you be interested in joining LogRocket's developer community?
Join LogRocket’s Content Advisory Board. You’ll help inform the type of content we create and get access to exclusive meetups, social accreditation, and swag.
Sign up now
7 Replies to "How to secure a REST API using JWT authentication"
You swapped the meaning of the issuer and the subject. The issuer is the authentication server which issued the token (usually a URI). The subject is the user being authenticated.
this is best article, I have read every with context of explaining. you have explaines evrythig nicely and to the point. Thank you very much.
That is a nice explanation! What about the need of changing the shared key, in case of symmetric encryption and signing? What option is there?
I think the asymmetric encryptions would not be feasible for many client apps and even those keys have to be changed after some time!
What problem does this solve that isn’t solved by, for example, Basic Authentication with a simple shared secret? How do you revoke access for a live JWT?
Overall good explanation with the exception of having the JWT-secret known to the client.
The only validation of the JWT that the client should do is to check the expiration-date of the JWT before using it.
If it’s expired, then the client can go the route of re-authenticating the user.
The back-end (API) is the only place that should know the JWT-secret so that it can verify if any JWT it receives was actually created by the back-end and was not tampered with.
How would you implement signout here
Great article. Note that JSON Web Tokens come in two flavors (or structures) – JSON Web Signature (JWS) and JSON Web Encryption (JWE). From the RFC: “JWT – A string representing a set of claims as a JSON object that is encoded in a JWS or JWE, enabling the claims to be digitally signed or MACed and/or encrypted.”
The JWE compact serialization results in 5 parts, JWS is 3 parts.